
In an octahedral structure, the pair of d-orbitals involved in ${{\text{d}}^2}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridization is:
A. ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
B. ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}\,{{\text{d}}_{{\text{XZ}}}}$
C. ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{XY}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{\text{YZ}}}}$
D. ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}},{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:To answer we should know the difference in all d-orbitals. We should know where the d-orbitals lie on the axis or in between the axis. An octahedral complexes form when six ligands approach the metal so metal in an octahedral complex requires six hybrid orbitals for the interaction with ligands. The ligand approach on the axis so, we will determine the d-orbitals which lie on the axis.
Complete solution:The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{XZ}}$,${{\text{d}}_{YZ}}$, and${{\text{d}}_{XY}}$.
The positions of these five d-orbitals on the axis is represented as follows:
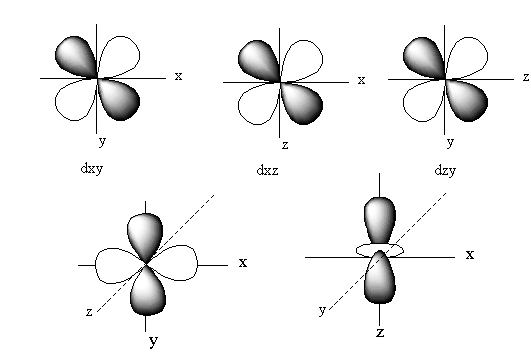
rbital of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis. The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lie on the the x and y-axis.
So, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$pairs of d-orbitals lies along the axis.
A general octahedral complex is shown as follows:

When six ligands approach the metal through the axis, an octahedral complex forms. The ligands approach from the axis so, the ligand forms a bond with the d-orbitals which lie on the axis that are${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$.
Two d-orbital, one s and two p-orbital combines and forms six hybrid orbital. The hybridization is known as ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization.
Thus, the correct options is (D).
Note: Hybrid orbitals form sigma bond only. The name of the complex itself indicates the number of hybrid orbitals such as the octahedral complex has six hybrid orbitals so, the hybridization can be ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ or ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$. In ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization, the inner shell d-orbitals are involved and in ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridization outer shell d-orbitals are involved. The three p-orbitals lie on the axis and all three have the same energy, so all three participate in the formation of an octahedral complex.
Complete solution:The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{XZ}}$,${{\text{d}}_{YZ}}$, and${{\text{d}}_{XY}}$.
The positions of these five d-orbitals on the axis is represented as follows:

rbital of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis. The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lie on the the x and y-axis.
So, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$pairs of d-orbitals lies along the axis.
A general octahedral complex is shown as follows:

When six ligands approach the metal through the axis, an octahedral complex forms. The ligands approach from the axis so, the ligand forms a bond with the d-orbitals which lie on the axis that are${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$.
Two d-orbital, one s and two p-orbital combines and forms six hybrid orbital. The hybridization is known as ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization.
Thus, the correct options is (D).
Note: Hybrid orbitals form sigma bond only. The name of the complex itself indicates the number of hybrid orbitals such as the octahedral complex has six hybrid orbitals so, the hybridization can be ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ or ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$. In ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization, the inner shell d-orbitals are involved and in ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridization outer shell d-orbitals are involved. The three p-orbitals lie on the axis and all three have the same energy, so all three participate in the formation of an octahedral complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




