
In an octahedral complex, CFSE (in ${{\Delta }_{0}}$ units) will be zero in a strong ligand field a:
(A) ${{d}^{5}}case$
(B) ${{d}^{6}}case$
(C) ${{d}^{3}}case$
(D) ${{d}^{10}}case$

Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: The crystal field theory is an electrostatic model that describes the distribution of electrons in the d orbitals that may lead to the stability of some complexes depending on the specific ligand field geometry and metal d-electron configurations. Depends on electron configuration and splitting of patterns leads to calculating the stabilization energy of coordination complexes.
Complete step by step answer:
The crystal fields theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model in which the metal-ligand coordination covalent bond is purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand.
In an octahedral coordination entity with six ligands surrounding metal atoms or ions. The metal d-orbitals are repulsion with electrons of the ligands. When metal away from the ligand, the repulsion will be more for d orbitals of metal. In the spherical crystal, ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ orbitals are towards axes along the direction of the ligand will repulsive more repulsion than ${{d}_{xy,}}{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{yz}}$ orbital.
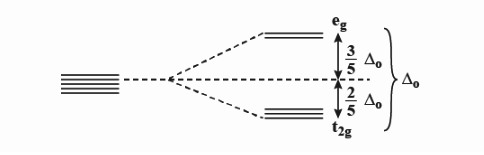
Crystal field splitting in an octahedral field,
${{e}_{g}}$ - The higher energy set of orbitals (${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$)
${{t}_{2g}}$ - The lower energy set of orbitals (${{d}_{xy,}}{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{yz}}$)
${{\Delta }_{0}}$ Or 10Dq - the energy separation between the two levels
In general, the increasing field strength depends on ligands can be arranged in a series of increasing order,
${{I}^{-}}This series is termed as spectrochemical series. As strong field ligands give low spin complexes, so the value of CFSE is,
In an octahedral complex, CFSE (in ${{\Delta }_{0}}$ units) will be zero in a strong ligand field with a low spin ${{d}^{10}} case$.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Similar CFSE values can be constructed for non-octahedral ligand field geometries when d orbital splitting and have electron configuration within those orbitals. With the help of CFSE values of octahedral to calculate thermodynamic preference for a metal-ligand combination to favor the octahedral geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
The crystal fields theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model in which the metal-ligand coordination covalent bond is purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand.
In an octahedral coordination entity with six ligands surrounding metal atoms or ions. The metal d-orbitals are repulsion with electrons of the ligands. When metal away from the ligand, the repulsion will be more for d orbitals of metal. In the spherical crystal, ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ orbitals are towards axes along the direction of the ligand will repulsive more repulsion than ${{d}_{xy,}}{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{yz}}$ orbital.
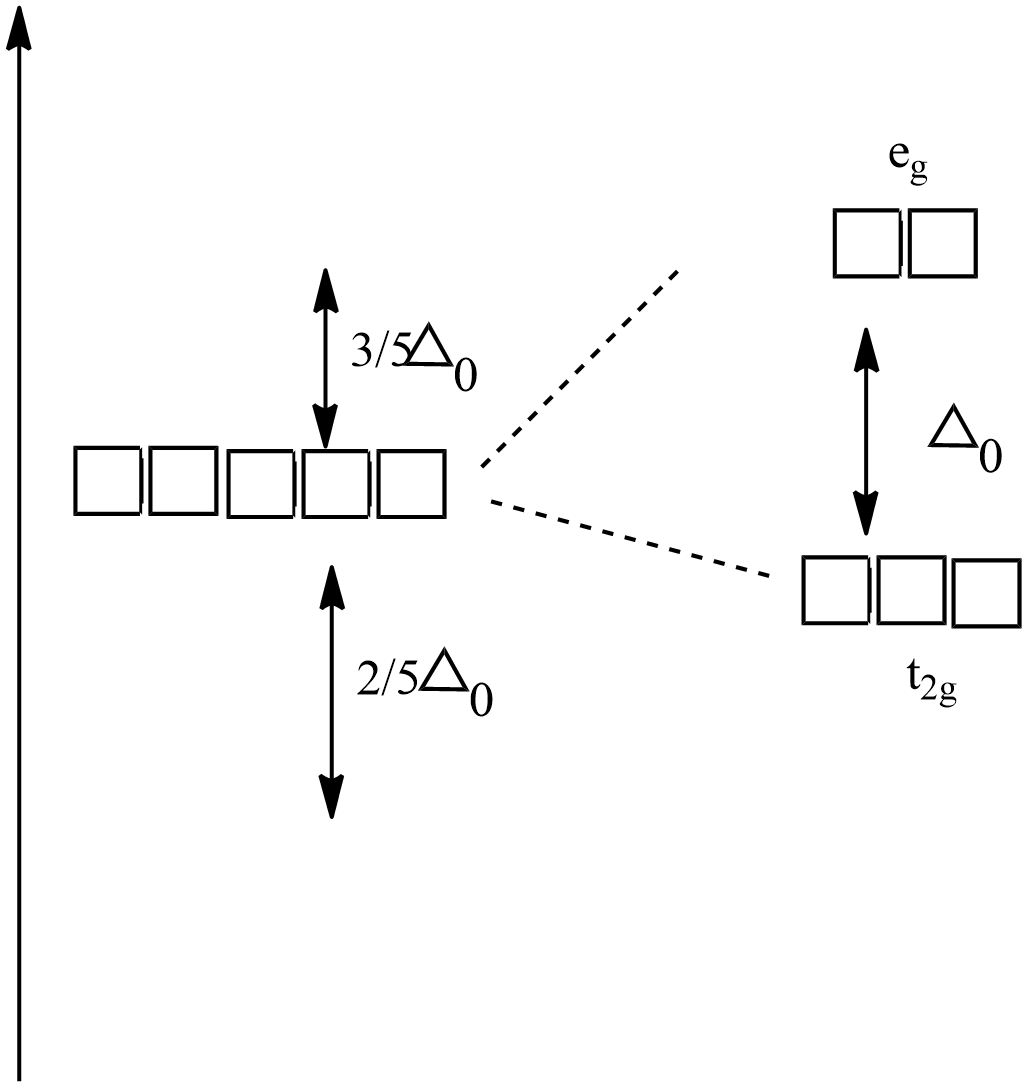
Crystal field splitting in an octahedral field,

${{e}_{g}}$ - The higher energy set of orbitals (${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$)
${{t}_{2g}}$ - The lower energy set of orbitals (${{d}_{xy,}}{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{yz}}$)
${{\Delta }_{0}}$ Or 10Dq - the energy separation between the two levels
In general, the increasing field strength depends on ligands can be arranged in a series of increasing order,
${{I}^{-}}
| Total d-electron | Octahedral low spin | Crystal field stabilization energy |
| ${{d}^{3}}$ | ${{t}_{2g}}^{3}{{e}_{g}}^{0}$ | $-\dfrac{6}{5}{{\Delta }_{0}}$ |
| ${{d}^{5}}$ | ${{t}_{2g}}^{5}{{e}_{g}}^{0}$ | $-\dfrac{10}{5}{{\Delta }_{0}}+P$ |
| ${{d}^{6}}$ | ${{t}^{6}}_{2g}{{e}_{g}}^{0}$ | $-\dfrac{12}{5}{{\Delta }_{0}}+P$ |
| ${{d}^{10}}$ | ${{t}_{2g}}^{6}{{e}_{g}}^{4}$ | 0 |
In an octahedral complex, CFSE (in ${{\Delta }_{0}}$ units) will be zero in a strong ligand field with a low spin ${{d}^{10}} case$.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Similar CFSE values can be constructed for non-octahedral ligand field geometries when d orbital splitting and have electron configuration within those orbitals. With the help of CFSE values of octahedral to calculate thermodynamic preference for a metal-ligand combination to favor the octahedral geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




