
In an n-type semiconductor, majority charge carriers are
A) Electrons
B) Neutrons
C) Holes
D) Protons
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Semiconductor is a material that has a conductivity between conductor and insulator. Two types of semiconductors are here, one is a pure(intrinsic) semiconductor and another is an impure(extrinsic) semiconductor. This extrinsic semiconductor is two types, one is a p-type semiconductor, another is an n-type semiconductor. Pure semiconductors are silicon (Si), germanium(Ge), etc.
Complete step by step answer:
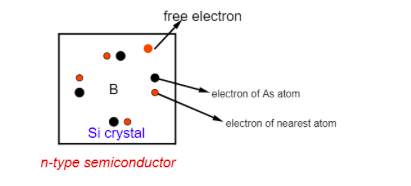
An n-type semiconductor is made by doping some impure substances of valence 5 (As) with a pure semiconductor to raise it’s conductivity many times. Here the majority charge carrier is the electron(negative charge) and the minor charge carrier is the hole(positive charge).
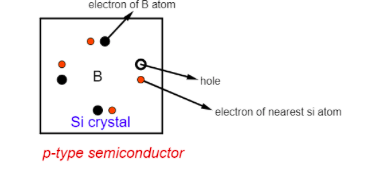
A p-type semiconductor is made by doping some impure substances of valence 3 (B) with a pure semiconductor to raise it’s conductivity many times. Here the majority carrier is the hole (positive charge) and the minor carrier is the electron (negative charge).
Now we consider the given options,
Option A – electrons- the number density of electrons in an n-type semiconductor is high.so, the major carrier of n-type semiconductor is an electron.
Option B- neutrons- it is present in the nucleus, the charge is zero. It does not affect conductivity.
Option C- holes- there are a few numbers of holes present in an n-type semiconductor that means the number density of hole is lesser. So, this can not be a major carrier.
Option D- protons- it is also present in the nucleus, positively charged. it is not a part of conductivity.
Hence, the option (A) is the correct one.
Notes:
A process of adding substances with the pure semiconductor material is known as doping.
Adding some arsenic(As), phosphorus(P) with pure silicon, and germanium we get an n-type semiconductor. Here the majority charge carrier is an ‘electron’ and the minor charge carrier is the ‘hole’.
Adding some boron(B), aluminum (Al) with silicon and germanium, we get a p-type semiconductor. Here the major carrier is the ‘hole’ and the minor carrier is the ‘electron’.
Major charge carriers are the more abundant charge carriers. In an n-type semiconductor electron is more than the holes.
Complete step by step answer:
An n-type semiconductor is made by doping some impure substances of valence 5 (As) with a pure semiconductor to raise it’s conductivity many times. Here the majority charge carrier is the electron(negative charge) and the minor charge carrier is the hole(positive charge).

A p-type semiconductor is made by doping some impure substances of valence 3 (B) with a pure semiconductor to raise it’s conductivity many times. Here the majority carrier is the hole (positive charge) and the minor carrier is the electron (negative charge).

Now we consider the given options,
Option A – electrons- the number density of electrons in an n-type semiconductor is high.so, the major carrier of n-type semiconductor is an electron.
Option B- neutrons- it is present in the nucleus, the charge is zero. It does not affect conductivity.
Option C- holes- there are a few numbers of holes present in an n-type semiconductor that means the number density of hole is lesser. So, this can not be a major carrier.
Option D- protons- it is also present in the nucleus, positively charged. it is not a part of conductivity.
Hence, the option (A) is the correct one.
Notes:
A process of adding substances with the pure semiconductor material is known as doping.
Adding some arsenic(As), phosphorus(P) with pure silicon, and germanium we get an n-type semiconductor. Here the majority charge carrier is an ‘electron’ and the minor charge carrier is the ‘hole’.
Adding some boron(B), aluminum (Al) with silicon and germanium, we get a p-type semiconductor. Here the major carrier is the ‘hole’ and the minor carrier is the ‘electron’.
Major charge carriers are the more abundant charge carriers. In an n-type semiconductor electron is more than the holes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




