
In an insulator, the forbidden energy gap between the valence and conduction band is of the order of
\[
{\text{A}}{\text{. 1 }}MeV \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 0}}{\text{.1 }}MeV \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 1 }}eV \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 5 }}eV \\
\]
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The width of the forbidden energy gap decides the amount of energy required to transfer electrons from valence band to conduction band. The insulators are those materials which are not able to conduct electrons because of the large difference between valence band and conduction band.
Complete step by step answer:
In band theory, for every material we have a lower energy band called valence band which contains the charge carriers, electrons. There is a higher energy band called conduction band whose energy is more than that of the valence band. In order to conduct electricity through the material, the electrons from the valence band need to be excited to the conduction band.
Based on the amount of energy required to excite electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, we have three types of materials: Conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
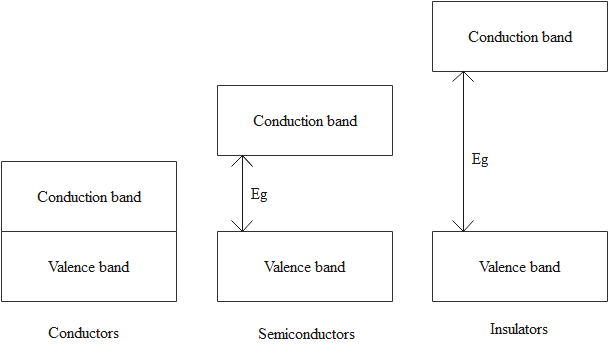
The insulators are those materials which have a very large energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band in order of eV. This energy difference is known as the forbidden energy gap (Eg) and in insulators. Its value is around 5eV. For example: Diamond is an insulator whose energy gap is about 5.5eV.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Additional information:
In case of conductors, the two bands overlap each other and there is no forbidden gap between the bands. This allows free conduction of electrons at all energies which is a characteristic of conductors.
In case of semiconductors, there is some energy difference between the two bands but it is smaller than that of insulators. It is of order of 0.1 to 3eV. This allows conduction of electrons only at certain energies.
Note:
The energy gap is said to be forbidden because no charge carrier can possess any energy value which lies in the energy gap of the given material. The material can conduct electricity only if the energy greater than equal to the band gap energy is available to material. Insulators need very high energy which is not available at normal temperatures.
Complete step by step answer:
In band theory, for every material we have a lower energy band called valence band which contains the charge carriers, electrons. There is a higher energy band called conduction band whose energy is more than that of the valence band. In order to conduct electricity through the material, the electrons from the valence band need to be excited to the conduction band.
Based on the amount of energy required to excite electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, we have three types of materials: Conductors, semiconductors and insulators.

The insulators are those materials which have a very large energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band in order of eV. This energy difference is known as the forbidden energy gap (Eg) and in insulators. Its value is around 5eV. For example: Diamond is an insulator whose energy gap is about 5.5eV.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Additional information:
In case of conductors, the two bands overlap each other and there is no forbidden gap between the bands. This allows free conduction of electrons at all energies which is a characteristic of conductors.
In case of semiconductors, there is some energy difference between the two bands but it is smaller than that of insulators. It is of order of 0.1 to 3eV. This allows conduction of electrons only at certain energies.
Note:
The energy gap is said to be forbidden because no charge carrier can possess any energy value which lies in the energy gap of the given material. The material can conduct electricity only if the energy greater than equal to the band gap energy is available to material. Insulators need very high energy which is not available at normal temperatures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




