
In an experiment, the resistance of a material is plotted as a function of temperature (in some range). As shown in the figure, it is a straight line. One may conclude that:
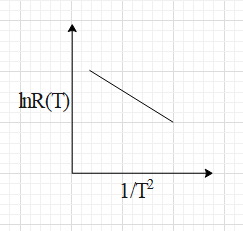
A. $R(T)=\dfrac{{{T}_{0}}}{{{T}^{2}}}$
B. $R(T)={{\operatorname{R}}_{0}}{{e}^{\dfrac{-{{T}^{2}}}{T_{0}^{2}}}}$
C. $R(T)={{\operatorname{R}}_{0}}{{e}^{\dfrac{-T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}}}}$
D. $R(T)={{\operatorname{R}}_{0}}{{e}^{\dfrac{{{T}^{2}}}{T_{0}^{2}}}}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Let us define some values of the temperature and resistance to help us in our calculations. Also we can see some extra terms or variables used in the options. check for which one we get a negative slope and positive constant.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given graph we can see that the x-axis represents a function of temperature T , i.e. $\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}$ and the y-axis represents a function of resistance R, i.e. $\ln R$.
The given graph represents a straight line and we know that the equation of a straight line can be written in the form $y=mx+c$ …... (i).
In this case, $y=\ln R$ and $x=\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$.
m is the slope of the line and c is the y intercept.
Let x coordinate $\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}=0$, the y coordinate be $\ln {{R}_{0}}$. This means that the y intercept of the line is $c=\ln {{R}_{0}}$.
Let y coordinate $\ln R=0$, the x coordinate be $\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$. This means that the x intercept of the line is $x=\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$.
This can be depicted in the graph shown below.
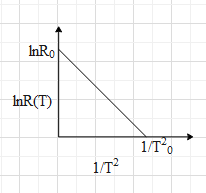
From the figure we get that slope $m=\dfrac{\ln {{R}_{0}}-0}{0-\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}}=-T_{0}^{2}\ln {{R}_{0}}$.
Substitute the values of x, y, m and c in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow \ln R=\left( -T_{0}^{2}\ln {{R}_{0}} \right)\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}+\ln {{R}_{0}}$
$\Rightarrow \ln R=\ln {{R}_{0}}\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{e}^{\ln R}}={{e}^{\ln {{R}_{0}}\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R={{e}^{\ln {{R}_{0}}}}.{{e}^{\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R={{R}_{0}}{{e}^{\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R=({{R}_{0}}e){{e}^{\left( \dfrac{-T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Note that the constant that we defined and the constants used in the options are not the same. Therefore, it is not necessary that the equation in the solution and the option must be the same.
We can also check the correct option by the log to the base e on both sides of each and write in the form of the equation of a straight line. Then check for which one we get a negative slope and positive constant.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given graph we can see that the x-axis represents a function of temperature T , i.e. $\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}$ and the y-axis represents a function of resistance R, i.e. $\ln R$.
The given graph represents a straight line and we know that the equation of a straight line can be written in the form $y=mx+c$ …... (i).
In this case, $y=\ln R$ and $x=\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$.
m is the slope of the line and c is the y intercept.
Let x coordinate $\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}=0$, the y coordinate be $\ln {{R}_{0}}$. This means that the y intercept of the line is $c=\ln {{R}_{0}}$.
Let y coordinate $\ln R=0$, the x coordinate be $\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$. This means that the x intercept of the line is $x=\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}$.
This can be depicted in the graph shown below.

From the figure we get that slope $m=\dfrac{\ln {{R}_{0}}-0}{0-\dfrac{1}{T_{0}^{2}}}=-T_{0}^{2}\ln {{R}_{0}}$.
Substitute the values of x, y, m and c in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow \ln R=\left( -T_{0}^{2}\ln {{R}_{0}} \right)\dfrac{1}{{{T}^{2}}}+\ln {{R}_{0}}$
$\Rightarrow \ln R=\ln {{R}_{0}}\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{e}^{\ln R}}={{e}^{\ln {{R}_{0}}\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R={{e}^{\ln {{R}_{0}}}}.{{e}^{\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R={{R}_{0}}{{e}^{\left( 1-\dfrac{T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
$\Rightarrow R=({{R}_{0}}e){{e}^{\left( \dfrac{-T_{0}^{2}}{{{T}^{2}}} \right)}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Note that the constant that we defined and the constants used in the options are not the same. Therefore, it is not necessary that the equation in the solution and the option must be the same.
We can also check the correct option by the log to the base e on both sides of each and write in the form of the equation of a straight line. Then check for which one we get a negative slope and positive constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




