
In an experiment of verification of Ohm's law, following observations are obtained.
Potential Difference V (in volt) 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Current (in Ampere) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
From observation table the resistance in the circuit is
A. $2.5 \Omega$
B. $2\Omega$
C. $5\Omega$
D. $3\Omega$
| Potential Difference V (in volt) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| Current (in Ampere) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Use Ohm's law. It shows the relationship between voltage, current and resistance in an electric circuit. Ohm's law states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across two points. Substitute the given values in that formula and calculate the resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Ohm's Law,
$V=IR$
Where, V is the potential difference across the conductor
I is the current flowing through the resistor
R is the resistance
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$R= \dfrac {V}{I}$
Substituting each value of potential difference and current in the above equation we get,
$R= \dfrac {0.5}{0.2}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {1.0}{0.4}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {1.5}{0.6}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {2.0}{0.8}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {2.5}{1.0}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
Thus, the resistance in the circuit is $2.5\Omega$.
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. $2\Omega$.
Note:
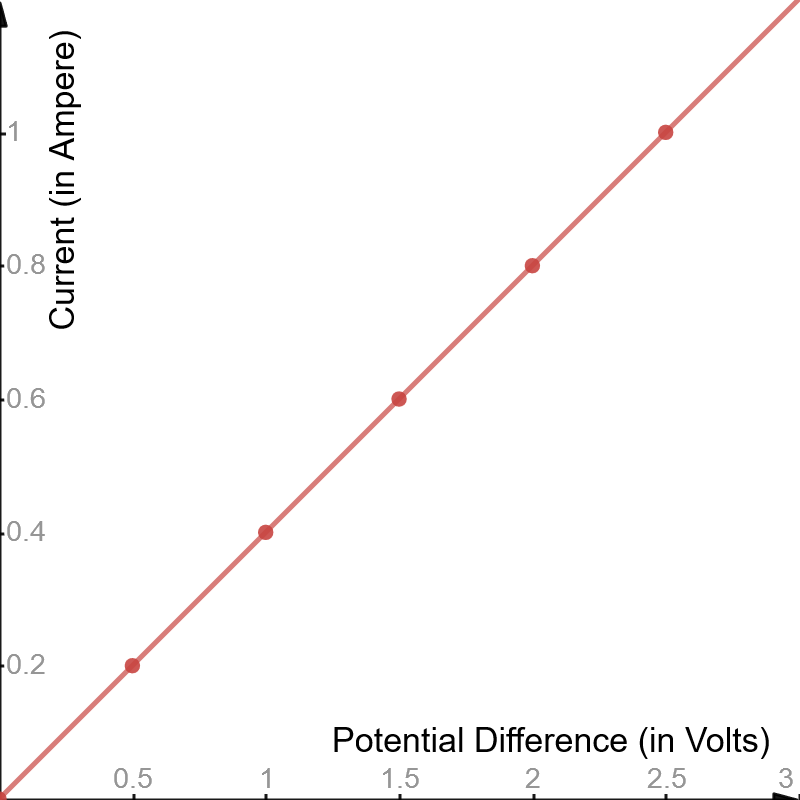
Current-Voltage relationship is generally represented in the form of graphs. Voltage is plotted along the X-axis of the graph and current is plotted along the Y-axis of the graph. Voltage versus current graph gives a straight line and has a constant slope. If the conductor has a constant slope in current versus voltage graph then it is called a Ohmic Conductor. But if the conductor does not obey Ohm's law and the resistance is not constant then the conductor is called Non-ohmic conductor.
The graph for the given table is shown below:
Complete step by step answer:
According to Ohm's Law,
$V=IR$
Where, V is the potential difference across the conductor
I is the current flowing through the resistor
R is the resistance
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$R= \dfrac {V}{I}$
Substituting each value of potential difference and current in the above equation we get,
$R= \dfrac {0.5}{0.2}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {1.0}{0.4}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {1.5}{0.6}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {2.0}{0.8}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
$R= \dfrac {2.5}{1.0}$
$\therefore R= 2.5\Omega$
Thus, the resistance in the circuit is $2.5\Omega$.
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. $2\Omega$.
Note:
Current-Voltage relationship is generally represented in the form of graphs. Voltage is plotted along the X-axis of the graph and current is plotted along the Y-axis of the graph. Voltage versus current graph gives a straight line and has a constant slope. If the conductor has a constant slope in current versus voltage graph then it is called a Ohmic Conductor. But if the conductor does not obey Ohm's law and the resistance is not constant then the conductor is called Non-ohmic conductor.
The graph for the given table is shown below:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




