
In an equilateral triangle , the inradius, circumradius, and one of the ex –radii are
In the ratio
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. 2:3:5}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 1:2:3}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 1:3:7}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 3:7:9}} \\
$
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we have to have knowledge of inradius circumradius and ex-radius and then using the property of the solution of the triangle we have to find their ratio. And also keep in mind it is an equilateral triangle so all sides are the same.
Complete step-by-step answer:
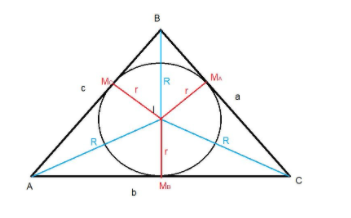
We have given a equilateral triangle and we know inradius is denoted by ‘r’ and circumradius is denoted by ‘R’ and one of the ex-radius is ${r_1}$
We have to find $r:R:{r_1}$
Now we know,
Area of equilateral triangle =$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$
Perimeter of equilateral triangle = 3a =2s, $\therefore s = \dfrac{{3a}}{2}$
Now using the properties of solution of triangle
$r = \dfrac{\Delta }{s} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}}{{\dfrac{{3a}}{2}}} = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
Now we know
$R = \dfrac{{abc}}{{4\Delta }}$ and here equilateral triangle triangle is given so a = b = c
$\therefore R = \dfrac{{{a^3}}}{{4 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}} = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
And we also know
${r_1} = \dfrac{\Delta }{{s - a}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}}{{\dfrac{{3a}}{2} - a}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} \times \dfrac{2}{a} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
Now we have
$r = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }},R = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }},{r_1} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
So we have to find ratio of all these three
$r:R:{r_1} = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }}:\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }}:\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
On simplifying this we get,
1:2:3
Hence option B is the correct option.
Note: Whenever we get this type of question the key concept of solving is we should have remembered all this formulae ${r_1} = \dfrac{\Delta }{{s - a}},R = \dfrac{{abc}}{{4\Delta }},2s = {\text{perimeter}}$ then we can solve easily this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given a equilateral triangle and we know inradius is denoted by ‘r’ and circumradius is denoted by ‘R’ and one of the ex-radius is ${r_1}$
We have to find $r:R:{r_1}$
Now we know,
Area of equilateral triangle =$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$
Perimeter of equilateral triangle = 3a =2s, $\therefore s = \dfrac{{3a}}{2}$
Now using the properties of solution of triangle
$r = \dfrac{\Delta }{s} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}}{{\dfrac{{3a}}{2}}} = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
Now we know
$R = \dfrac{{abc}}{{4\Delta }}$ and here equilateral triangle triangle is given so a = b = c
$\therefore R = \dfrac{{{a^3}}}{{4 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}} = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
And we also know
${r_1} = \dfrac{\Delta }{{s - a}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}}}{{\dfrac{{3a}}{2} - a}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2} \times \dfrac{2}{a} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
Now we have
$r = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }},R = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }},{r_1} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
So we have to find ratio of all these three
$r:R:{r_1} = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 3 }}:\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 3 }}:\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a$
On simplifying this we get,
1:2:3
Hence option B is the correct option.
Note: Whenever we get this type of question the key concept of solving is we should have remembered all this formulae ${r_1} = \dfrac{\Delta }{{s - a}},R = \dfrac{{abc}}{{4\Delta }},2s = {\text{perimeter}}$ then we can solve easily this question.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




