
In an ammeter 0.2% of main current passes through the galvanometer. If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be
$\eqalign{
& {\text{A}}{\text{.}}\dfrac{1}{{499}}G \cr
& {\text{B}}{\text{.}}\dfrac{{499}}{{500}}G \cr
& {\text{C}}{\text{.}}\dfrac{1}{{500}}G \cr
& {\text{D}}{\text{.}}\dfrac{{500}}{{499}}G \cr} $
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: An ammeter is a measuring device used to measure the current flowing through a closed electrical circuit. In an ammeter, a galvanometer is connected in parallel to a shunt resistance. In a parallel connection, the potential will be the same. These two pieces of information will help us to get the solution.
Formula Used:
Ohm’s law, $V = IR$
Complete step by step answer:
In an ammeter, a resistor having a very small resistance is connected in parallel with the coil. This resistor is known as the shunt. The current to be measured is passed through the ammeter by connecting it in series with the segment which carries the current. Clearly, because the resistor is connected with a parallel connection, the potential drop across it and the coil remains the same. The following figure shows the circuit diagram for the given problem:
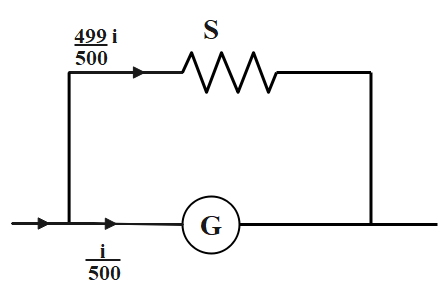
Let us assume that the current passing through the resistor having resistance R is I, then the potential difference across the resistor will be given by ohm’s law as:
$V = IR \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Again assume that I is the main currentS is the shunt resistance and G be the resistance of the galvanometer as given in the question itself. It is given that the current through the galvanometer is 0.2% of the main current.
Mathematically,
$\eqalign{
& {I_G} = 0.2\% {\text{ of }}I \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_G} = \dfrac{{0.2}}{{100}} \times I \cr
& \therefore {I_G} = 0.002I \cr} $
So, naturally, the remaining current will be flowing through the shunt resistor. So we have:
$\eqalign{
& {I_S} = I - 0.002I \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_S} = 0.998I \cr} $
From equation (1), we know that the product of the current flowing through the resistor and the resistance of the resistor is equal to the potential drop across them. Thus substituting the values from above we have:
$\eqalign{
& {I_G} \times G = V = {I_S} \times S \cr
& \Rightarrow G \times 0.002 = 0.998 \times S \cr
& \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{G \times 0.002}}{{0.998}} \cr
& \therefore S = \dfrac{G}{{499}} \cr} $
So, the resistance offered by the ammeter is $\dfrac{1}{{499}}G$. Thus, our correct option is option A.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The galvanometer is very similar to an ammeter in construction. When no current passes through it, the needle stays in the middle of the graduate scale. This point is marked as zero. The students can wrongly assume the value of equivalent resistance to be the correct answer to the question. So, to avoid the same, read the question properly and also, solve as many numeric problems as one can to have a firm grasp on the concepts and their application.
Formula Used:
Ohm’s law, $V = IR$
Complete step by step answer:
In an ammeter, a resistor having a very small resistance is connected in parallel with the coil. This resistor is known as the shunt. The current to be measured is passed through the ammeter by connecting it in series with the segment which carries the current. Clearly, because the resistor is connected with a parallel connection, the potential drop across it and the coil remains the same. The following figure shows the circuit diagram for the given problem:

Let us assume that the current passing through the resistor having resistance R is I, then the potential difference across the resistor will be given by ohm’s law as:
$V = IR \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Again assume that I is the main currentS is the shunt resistance and G be the resistance of the galvanometer as given in the question itself. It is given that the current through the galvanometer is 0.2% of the main current.
Mathematically,
$\eqalign{
& {I_G} = 0.2\% {\text{ of }}I \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_G} = \dfrac{{0.2}}{{100}} \times I \cr
& \therefore {I_G} = 0.002I \cr} $
So, naturally, the remaining current will be flowing through the shunt resistor. So we have:
$\eqalign{
& {I_S} = I - 0.002I \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_S} = 0.998I \cr} $
From equation (1), we know that the product of the current flowing through the resistor and the resistance of the resistor is equal to the potential drop across them. Thus substituting the values from above we have:
$\eqalign{
& {I_G} \times G = V = {I_S} \times S \cr
& \Rightarrow G \times 0.002 = 0.998 \times S \cr
& \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{G \times 0.002}}{{0.998}} \cr
& \therefore S = \dfrac{G}{{499}} \cr} $
So, the resistance offered by the ammeter is $\dfrac{1}{{499}}G$. Thus, our correct option is option A.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The galvanometer is very similar to an ammeter in construction. When no current passes through it, the needle stays in the middle of the graduate scale. This point is marked as zero. The students can wrongly assume the value of equivalent resistance to be the correct answer to the question. So, to avoid the same, read the question properly and also, solve as many numeric problems as one can to have a firm grasp on the concepts and their application.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




