
In a triangle PQR PD is perpendicular on QR such that D lies on QR. If \[PQ = a\], \[PR = b\] , \[QD = c\] and \[DR = d\],then
A) \[\left( {a - d} \right)\left( {a + d} \right) = \left( {b - c} \right)\left( {b + c} \right)\]
B) \[\left( {a - c} \right)\left( {b - d} \right) = \left( {a + c} \right)\left( {b + d} \right)\]
C) \[\left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)\]
D) \[\left( {a - b} \right)\left( {c - d} \right) = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {c + d} \right)\]
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Firstly we will calculate the length of perpendicular in both the triangles \[\Delta PQD\] and \[\Delta PRD\] using Pythagoras formula in both the triangles and then equate its value to get the desired answer.
The Pythagoras formula is given by:-
\[{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]
The identity used is:
\[{x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
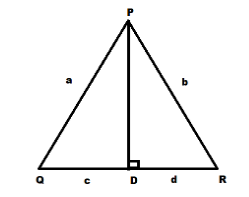
In \[\Delta PQD\],
\[PQ = a = {\text{hypotenuse}}\]
\[QD = c = {\text{base}}\]
\[PD = {\text{ perpendicular}}\]
Applying the Pythagoras formula we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{a^2} = {c^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} = {a^2} - {c^2}.............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
In \[\Delta PRD\],
\[\begin{gathered}
PR = b = {\text{hypotenuse}} \\
QR = d = {\text{base}} \\
PD = {\text{ perpendicular}} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Applying the Pythagoras formula we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{b^2} = {d^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} = {b^2} - {d^2}.............\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Equating equations 1 and 2 we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow {a^2} - {c^2} = {b^2} - {d^2} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} - {b^2} = {c^2} - {d^2} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Now applying the following identity on both LHS and RHS:
\[{x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\]
We get:-
\[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)\]
Hence option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: In a right angled triangle, the longest side is hypotenuse and the sides containing the right angle are the base and the perpendicular.
The Pythagoras formula is given by:-
\[{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]
The identity used is:
\[{x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step answer:

In \[\Delta PQD\],
\[PQ = a = {\text{hypotenuse}}\]
\[QD = c = {\text{base}}\]
\[PD = {\text{ perpendicular}}\]
Applying the Pythagoras formula we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{a^2} = {c^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} = {a^2} - {c^2}.............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
In \[\Delta PRD\],
\[\begin{gathered}
PR = b = {\text{hypotenuse}} \\
QR = d = {\text{base}} \\
PD = {\text{ perpendicular}} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Applying the Pythagoras formula we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{b^2} = {d^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} = {b^2} - {d^2}.............\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Equating equations 1 and 2 we get:-
\[\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow {a^2} - {c^2} = {b^2} - {d^2} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} - {b^2} = {c^2} - {d^2} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Now applying the following identity on both LHS and RHS:
\[{x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\]
We get:-
\[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)\]
Hence option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: In a right angled triangle, the longest side is hypotenuse and the sides containing the right angle are the base and the perpendicular.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




