
In a transformer, the coefficient of mutual inductance between primary and secondary coil is 0.2 H. When the current changes by 5 Na in the primary, then the induced era in the secondary will be:
A. 0.5 V
B. 1 V
C. 1.5 V
D. 2.0 V
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The transformer works on the principle of mutual inductance. The mutual inductance is a phenomenon in which there is a change in the emf in the second coil due to the change in flux in the primary coil.
Complete step by step answer:
The transformer consists of two coils wound on a soft-core. They are completely insulated from each other. The coil on the left is called the primary coil where the input AC voltage is applied. The coil on the right is called the secondary coil where the output AC voltage is realized.
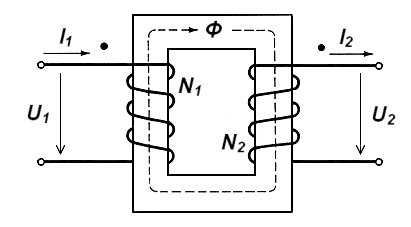
The number of turns on these coils are not the same. These coils are wound differently, based on the purpose of the transformation. The number of turns in the primary coil is ${N_1}$ and the number of turns in the secondary coil is ${N_2}$.
Let ${I_1}$ be the current flowing through the primary coil of turns ${N_1}$, it sets up a magnetic flux in the secondary coil of turns ${N_2}$. Let us denote the flux linkage by ${\phi _2}$. As per the principle of mutual induction, this flux linkage is directly proportional to the current in the primary coil.
${N_2}{\phi _2} \propto {I_1}$
Removing the proportionality constant, we get –
${N_2}{\phi _2} = {M_{12}}{I_1}$
where ${M_{12}}$ is called the coefficient of mutual inductance or just mutual inductance and measured in henry ($H$).
The induced voltage in the secondary coil:
$e = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
Given, the change in current, $\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = 5$
Also, mutual inductance, $M = 0.2H$
Therefore, the induced voltage in the secondary coil is:
$e = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
On substituting the corresponding values, we get
$e = 0.2 \times 5 = 1V $
The induced emf in the secondary coil is 1V. Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note:
There are two kinds of transformers – Step-up and Step-down transformers.
In the step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary is lesser than that of the secondary coil. This is used for increasing the voltage by the ratio of the number of turns.
In the step-down transformer, the number of turns in the primary is greater than that of the secondary coil. This is used for decreasing the voltage by the ratio of the number of turns.
Complete step by step answer:
The transformer consists of two coils wound on a soft-core. They are completely insulated from each other. The coil on the left is called the primary coil where the input AC voltage is applied. The coil on the right is called the secondary coil where the output AC voltage is realized.

The number of turns on these coils are not the same. These coils are wound differently, based on the purpose of the transformation. The number of turns in the primary coil is ${N_1}$ and the number of turns in the secondary coil is ${N_2}$.
Let ${I_1}$ be the current flowing through the primary coil of turns ${N_1}$, it sets up a magnetic flux in the secondary coil of turns ${N_2}$. Let us denote the flux linkage by ${\phi _2}$. As per the principle of mutual induction, this flux linkage is directly proportional to the current in the primary coil.
${N_2}{\phi _2} \propto {I_1}$
Removing the proportionality constant, we get –
${N_2}{\phi _2} = {M_{12}}{I_1}$
where ${M_{12}}$ is called the coefficient of mutual inductance or just mutual inductance and measured in henry ($H$).
The induced voltage in the secondary coil:
$e = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
Given, the change in current, $\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = 5$
Also, mutual inductance, $M = 0.2H$
Therefore, the induced voltage in the secondary coil is:
$e = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
On substituting the corresponding values, we get
$e = 0.2 \times 5 = 1V $
The induced emf in the secondary coil is 1V. Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note:
There are two kinds of transformers – Step-up and Step-down transformers.
In the step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary is lesser than that of the secondary coil. This is used for increasing the voltage by the ratio of the number of turns.
In the step-down transformer, the number of turns in the primary is greater than that of the secondary coil. This is used for decreasing the voltage by the ratio of the number of turns.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




