
In a series $RL$ circuit, ${\rm{12}}\;{\rm{V}}$ rms is the voltage across the resistor, and ${\rm{14}}\;{\rm{V}}$ rms is the voltage across the inductor. The peak value of the source voltage is
A.$20\;{\rm{V}}$
B.$18.4\;{\rm{V}}$
C.$26.0\;{\rm{V}}$
D.$2\;{\rm{V}}$
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: To find the value of the peak value of the source voltage, we will derive the relation between root mean square voltage and voltage across resistor and inductor. Then, we will find the root mean square voltage by substituting the values of voltage across a resistor and inductor. We will then use the relation between root square voltage and maximum voltage to find the peak value of source voltage.
Formula used: We will use the expression for root mean square velocity.
${V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{V_L}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{V_R}} \right)}^2}} $
Where ${V_{rms}}$ is the root mean square voltage, ${V_L}$ is the voltage across the inductor and ${V_R}$is the voltage across the resistor.
Also, we will use the relation between rms voltage and maximum voltage.
${V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \;{V_{rms}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The voltage across the resistor is ${V_R} = 12\;{\rm{V}}$ .
The voltage across the inductor is ${V_L} = 14\;{\rm{V}}$.
Let us say \[V\] represents the source voltage in the circuit and ${V_{rms}}$ is the root mean square voltage.
We will assume $R$ as the ohmic resistance and $L$ as the inductance in series. Also, we will assume $I$ as the current flowing in the circuit.
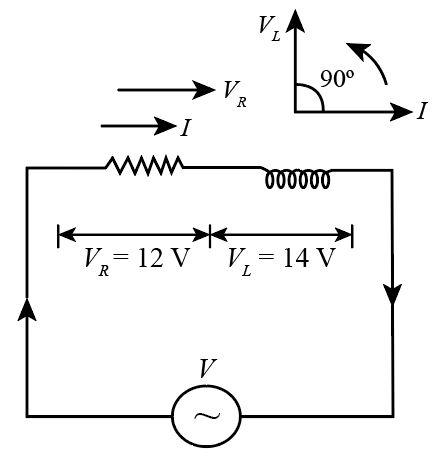
Now, we will write the expression for the emf $V$ which is applied by the source voltage as
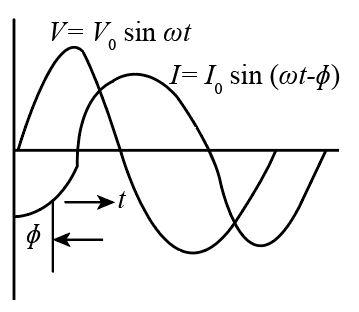
$V = {V_o}\sin \omega t$
We will now write the expression for the potential difference across the inductance $L$ due to current $I$.
${V_L} = I{X_L}$
where ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
Then, we will now write the expression for the potential difference across the resistance $R$ due to current $I$.
${V_R} = IR$
We know that $I$ and ${V_R}$ are in the same phase but ${V_L}$ lead ${V_R}$ by ${90^ \circ }$ .
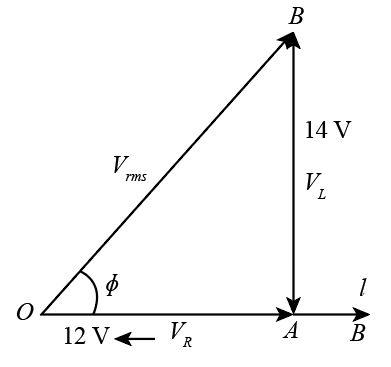
Hence, we can write
${V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{V_L}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{V_R}} \right)}^2}} $
Now we will substitute $12\;{\rm{V}}$for ${V_R}$and $14\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_L}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {12\;{\rm{V}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {14\;{\rm{V}}} \right)}^2}} \\
{V_{rms}} = \sqrt {144 + 196} \;{\rm{V}}\\
{V_{rms}} = 18.43\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
We know that the peak value of source voltage is the $\sqrt 2 $ times of ${V_{rms}}$. This can be expressed as:
${V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \;{V_{rms}}$
We will substitute $18.43\;{\rm{V}}$for ${V_{rms}}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \; \times 18.43\;{\rm{V}}\\
{V_{\max }} = 26.07\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the peak value of the source voltage is $26.07\;{\rm{V}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We can define the peak value of the voltage as the maximum voltage that the alternating quantity has during a complete one cycle. Maximum voltage is another term used for the peak voltage. Generally, Sinusoidal quantity has its peak value at ${90^ \circ }$. Also, root mean square values can be found out by finding the square root of the average or mean value of the squared function.
Formula used: We will use the expression for root mean square velocity.
${V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{V_L}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{V_R}} \right)}^2}} $
Where ${V_{rms}}$ is the root mean square voltage, ${V_L}$ is the voltage across the inductor and ${V_R}$is the voltage across the resistor.
Also, we will use the relation between rms voltage and maximum voltage.
${V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \;{V_{rms}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The voltage across the resistor is ${V_R} = 12\;{\rm{V}}$ .
The voltage across the inductor is ${V_L} = 14\;{\rm{V}}$.
Let us say \[V\] represents the source voltage in the circuit and ${V_{rms}}$ is the root mean square voltage.
We will assume $R$ as the ohmic resistance and $L$ as the inductance in series. Also, we will assume $I$ as the current flowing in the circuit.

Now, we will write the expression for the emf $V$ which is applied by the source voltage as
$V = {V_o}\sin \omega t$

We will now write the expression for the potential difference across the inductance $L$ due to current $I$.
${V_L} = I{X_L}$
where ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
Then, we will now write the expression for the potential difference across the resistance $R$ due to current $I$.
${V_R} = IR$
We know that $I$ and ${V_R}$ are in the same phase but ${V_L}$ lead ${V_R}$ by ${90^ \circ }$ .

Hence, we can write
${V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{V_L}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{V_R}} \right)}^2}} $
Now we will substitute $12\;{\rm{V}}$for ${V_R}$and $14\;{\rm{V}}$ for ${V_L}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_{rms}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {12\;{\rm{V}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {14\;{\rm{V}}} \right)}^2}} \\
{V_{rms}} = \sqrt {144 + 196} \;{\rm{V}}\\
{V_{rms}} = 18.43\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
We know that the peak value of source voltage is the $\sqrt 2 $ times of ${V_{rms}}$. This can be expressed as:
${V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \;{V_{rms}}$
We will substitute $18.43\;{\rm{V}}$for ${V_{rms}}$ in the above expression.
$\begin{array}{l}
{V_{\max }} = \sqrt 2 \; \times 18.43\;{\rm{V}}\\
{V_{\max }} = 26.07\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the peak value of the source voltage is $26.07\;{\rm{V}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We can define the peak value of the voltage as the maximum voltage that the alternating quantity has during a complete one cycle. Maximum voltage is another term used for the peak voltage. Generally, Sinusoidal quantity has its peak value at ${90^ \circ }$. Also, root mean square values can be found out by finding the square root of the average or mean value of the squared function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




