
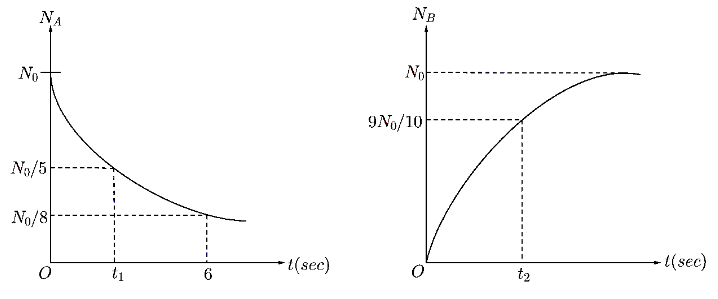
In a radioactive decay process $A$ decays to $B$ . Two graphs of the number of nuclei of $A$ and $B$ versus time are given. Then choose the correct option(s)
A. ${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=4\sec $
B. ${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=2\sec $
C. ${{t}_{1}}=2{{\log }_{2}}5\sec $
D. ${{t}_{2}}={{\log }_{2}}100\sec $

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint:
Complete step by step answer:
We can use the Exponential law of radioactive disintegration here as the nuclei $A$ is disintegrated into nuclei $B$ , which is expressed as
$N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Now, from the graph for nuclei $A$ , we can obtain that at time $t=6sec$ , the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{N_0}{8}$ . Substituting this values in the equation of law of disintegration,
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{8}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda (6)}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{8}={{e}^{-\lambda (6)}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{8} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-6\lambda }}$
From the logarithmic theorems, we know $\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)=-\ln b$ and ${{\ln }_{a}}{{a}^{b}}=b$ . Applying these theorems in the above equations
$-\ln 8=-6\lambda $
$\Rightarrow \ln {{2}^{3}}=6\lambda $
Using the logarithmic theorem $\ln {{a}^{b}}=b\ln a$ in the above equation, we get
$3\ln 2=6\lambda $
$\Rightarrow\lambda =\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}$..... $(1)$
Now, at time $t=t_1$ , the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{5}$ . Substituting all the given values in Law of disintegration
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{5}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{5}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{5} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying logarithmic theorems,
$-\ln 5=-\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}{{t}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$…… $(2)$
From the logarithmic theorem $\dfrac{\ln a}{\ln b}={{\ln }_{b}}a$ , the above equation can be written as
$\therefore {{t}_{1}}=2{{\ln }_{2}}5$
Now, for the disintegration curve of $B$ , at time $t=t_2$ , the given number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{9{{N}_{0}}}{10}$
Hence, the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N={{N}_{0}}-\dfrac{9{{N}_{0}}}{10}=\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{10}$
Substituting the values in the law of disintegration,
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{10}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\therefore \ln \left( \dfrac{1}{10} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying logarithmic theorems,
$-\ln 10=-\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}{{t}_{2}}$
$\therefore {{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2\ln 10}{\ln 2}$...…… $(2)$
From the logarithmic theorem $\ln {{a}^{b}}=b\ln a$ and $\dfrac{\ln a}{\ln b}={{\ln }_{b}}a$ , the above equation can be written as
${{t}_{1}}={{\ln }_{2}}100$
Now, taking the difference of the equation $(1)$ and $(2)$ ,
${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 10}{\ln 2}-\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
$\Rightarrow{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln (5\times 2)}{\ln 2}-\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
From the logarithmic theorem $\ln (ab)=\ln a+\ln b$ ,
${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 5+2\ln 2-2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
$\therefore {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=2\sec $
Hence, the correct answers are option B , C , D.
Note: Here, to avoid the use of log tables and approximation values, we have the logarithmic values as it is till the end. We can find their values from natural log tables in the initial step also. Also for the nuclei $B$ , the graph shows the disintegrated or the number of new nuclei formed after disintegration, while the law of disintegration required the disintegrated nuclei. Hence, we must remember to take the disintegrated nuclei which can be calculated by subtracting the value from the total number of nuclei.
Complete step by step answer:
We can use the Exponential law of radioactive disintegration here as the nuclei $A$ is disintegrated into nuclei $B$ , which is expressed as
$N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Now, from the graph for nuclei $A$ , we can obtain that at time $t=6sec$ , the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{N_0}{8}$ . Substituting this values in the equation of law of disintegration,
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{8}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda (6)}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{8}={{e}^{-\lambda (6)}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{8} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-6\lambda }}$
From the logarithmic theorems, we know $\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)=-\ln b$ and ${{\ln }_{a}}{{a}^{b}}=b$ . Applying these theorems in the above equations
$-\ln 8=-6\lambda $
$\Rightarrow \ln {{2}^{3}}=6\lambda $
Using the logarithmic theorem $\ln {{a}^{b}}=b\ln a$ in the above equation, we get
$3\ln 2=6\lambda $
$\Rightarrow\lambda =\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}$..... $(1)$
Now, at time $t=t_1$ , the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{5}$ . Substituting all the given values in Law of disintegration
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{5}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{5}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\ln \left( \dfrac{1}{5} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying logarithmic theorems,
$-\ln 5=-\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}{{t}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$…… $(2)$
From the logarithmic theorem $\dfrac{\ln a}{\ln b}={{\ln }_{b}}a$ , the above equation can be written as
$\therefore {{t}_{1}}=2{{\ln }_{2}}5$
Now, for the disintegration curve of $B$ , at time $t=t_2$ , the given number of disintegrated nuclei is $N=\dfrac{9{{N}_{0}}}{10}$
Hence, the number of disintegrated nuclei is $N={{N}_{0}}-\dfrac{9{{N}_{0}}}{10}=\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{10}$
Substituting the values in the law of disintegration,
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{10}={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying natural log on both sides,
$\therefore \ln \left( \dfrac{1}{10} \right)=\ln {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Applying logarithmic theorems,
$-\ln 10=-\dfrac{\ln 2}{2}{{t}_{2}}$
$\therefore {{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2\ln 10}{\ln 2}$...…… $(2)$
From the logarithmic theorem $\ln {{a}^{b}}=b\ln a$ and $\dfrac{\ln a}{\ln b}={{\ln }_{b}}a$ , the above equation can be written as
${{t}_{1}}={{\ln }_{2}}100$
Now, taking the difference of the equation $(1)$ and $(2)$ ,
${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 10}{\ln 2}-\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
$\Rightarrow{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln (5\times 2)}{\ln 2}-\dfrac{2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
From the logarithmic theorem $\ln (ab)=\ln a+\ln b$ ,
${{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2\ln 5+2\ln 2-2\ln 5}{\ln 2}$
$\therefore {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=2\sec $
Hence, the correct answers are option B , C , D.
Note: Here, to avoid the use of log tables and approximation values, we have the logarithmic values as it is till the end. We can find their values from natural log tables in the initial step also. Also for the nuclei $B$ , the graph shows the disintegrated or the number of new nuclei formed after disintegration, while the law of disintegration required the disintegrated nuclei. Hence, we must remember to take the disintegrated nuclei which can be calculated by subtracting the value from the total number of nuclei.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




