
In a pyramid of biomass, primary producers have a dry biomass of 809 \[kg/{m^2}\]. The biomass at tertiary consumer level would be
A. 37 \[kg/{m^2}\]
B. 11 \[kg/{m^2}\]
C. 5 \[kg/{m^2}\]
D. 1.5 \[kg/{m^2}\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The above problem can be solved by using Lindeman’s law. According to this law, nearly \[10\% \] energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next. Considering this fact, biomass at the tertiary level can be calculated.
Complete answer:
Primary producers have dry biomass of 809 \[kg/{m^2}\]. According to Lindeman’s law, \[10\% \] energy (in the form of dry biomass) is passed on from one trophic level to the next.
In another way, it can be said that nearly\[\;90\% \] of energy is lost as we move from one trophic level to another. So, primary consumers would have a biomass of 37 \[kg/{m^2}\]. The secondary consumer level would have a biomass of 11 kg/m2.
Then at the tertiary consumer level, it would be 1.5 \[kg/{m^2}\].
In Ecology, a pyramid of biomass is a graphical portrayal which indicates the biomass at each trophic level. In this representation, there is a sharp decrease in biomass at higher trophic levels.
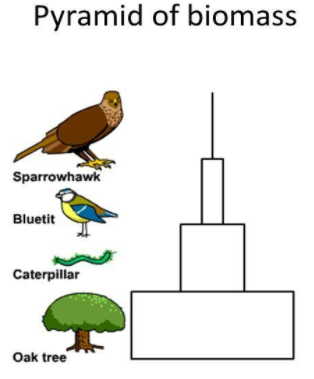
So, the correct option is D. 1.5 \[kg/{m^2}\]
Note: In an ecosystem, producer refers to the photoautotrophs that can produce their own food and food, e.g. green plants.
The consumer usually refers to the subsequent trophic level members who feed upon producers or consumers of lower trophic levels, e.g. herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. Decomposers are the organisms that feed upon residual organic matter, e.g. some bacterial species, fungi species, etc.
Complete answer:
Primary producers have dry biomass of 809 \[kg/{m^2}\]. According to Lindeman’s law, \[10\% \] energy (in the form of dry biomass) is passed on from one trophic level to the next.
In another way, it can be said that nearly\[\;90\% \] of energy is lost as we move from one trophic level to another. So, primary consumers would have a biomass of 37 \[kg/{m^2}\]. The secondary consumer level would have a biomass of 11 kg/m2.
Then at the tertiary consumer level, it would be 1.5 \[kg/{m^2}\].
In Ecology, a pyramid of biomass is a graphical portrayal which indicates the biomass at each trophic level. In this representation, there is a sharp decrease in biomass at higher trophic levels.

So, the correct option is D. 1.5 \[kg/{m^2}\]
Note: In an ecosystem, producer refers to the photoautotrophs that can produce their own food and food, e.g. green plants.
The consumer usually refers to the subsequent trophic level members who feed upon producers or consumers of lower trophic levels, e.g. herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. Decomposers are the organisms that feed upon residual organic matter, e.g. some bacterial species, fungi species, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




