
In a potentiometer experiment, the balancing length of a cell is at length $240cm$. After shunting the cell with a resistance of $2\Omega $, the balancing length becomes $120cm$. The internal resistance of cell is
A. $1\Omega $
B. $0.5\Omega $
C. $4\Omega $
D. $2\Omega $
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The potentiometer wire works on the principle – the potential drop across a given part of wire is directly proportional to the length of that part of the wire. This potential drop is always proportional to the resistance, according to ohm’s law. Once the cell is shunted, the effective resistance of the secondary circuit changes. Using these both conditions we can find the internal resistance of the cell.
Formula used:
$r = {R_s}\left( {\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{{{L_2}}} - 1} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
The initial potentiometer circuit and shunted potentiometer circuit are given by
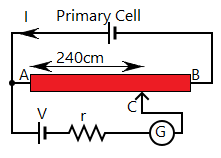
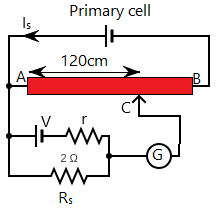
From the principle of potentiometer, $V \propto L$ and from ohm’s law $V \propto R$. Using both the relations we have $R \propto L$.
If we consider that ${R_1}$ is the resistance of the initial secondary circuit and the balancing length is ${L_1}$. And, ${R_2}$ is the resistance of shunted secondary circuit and balancing length ${L_2}$, respectively. We will have,
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{L_1}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{L_2}}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{{{L_1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{R_s} \times r}}{{{R_s} + r}}}}{{{L_2}}} \Rightarrow r = {R_s}\left( {\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{{{L_2}}} - 1} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow r = 2\left( {\dfrac{{240}}{{120}} - 1} \right) = 2\Omega \cr
& \therefore r = 2\Omega \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
In the shunted circuit, the shunt resistance is parallel to the internal resistance of the cell. So, the effective resistance is obtained by using the formula for resistances in parallel, ${R_P} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$.
The internal resistance is not an isolated resistance, it is the resistance offered by the battery. We show it as a separate entity, for calculation.
Formula used:
$r = {R_s}\left( {\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{{{L_2}}} - 1} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
The initial potentiometer circuit and shunted potentiometer circuit are given by


From the principle of potentiometer, $V \propto L$ and from ohm’s law $V \propto R$. Using both the relations we have $R \propto L$.
If we consider that ${R_1}$ is the resistance of the initial secondary circuit and the balancing length is ${L_1}$. And, ${R_2}$ is the resistance of shunted secondary circuit and balancing length ${L_2}$, respectively. We will have,
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{L_1}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{L_2}}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{{{L_1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{R_s} \times r}}{{{R_s} + r}}}}{{{L_2}}} \Rightarrow r = {R_s}\left( {\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{{{L_2}}} - 1} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow r = 2\left( {\dfrac{{240}}{{120}} - 1} \right) = 2\Omega \cr
& \therefore r = 2\Omega \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
In the shunted circuit, the shunt resistance is parallel to the internal resistance of the cell. So, the effective resistance is obtained by using the formula for resistances in parallel, ${R_P} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$.
The internal resistance is not an isolated resistance, it is the resistance offered by the battery. We show it as a separate entity, for calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




