
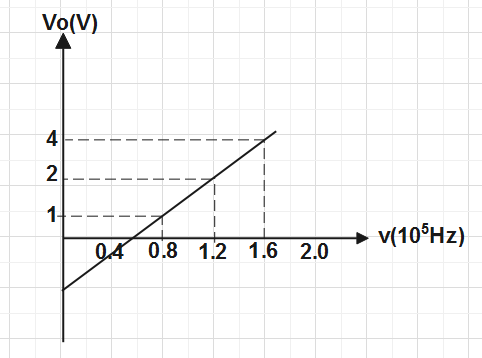
In a photocell circuit the stopping potential,\[{{V}_{0}}\] is a measure of the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons. The following graph shows experimentally measured values of stopping potential versus frequency \[\upsilon \] of incident light.
The values of Planck's constant and the work function as determined from the graph are (taking the magnitude of electric charge to be\[e=1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C\])
\[\begin{align}
& A)6.4\times {{10}^{-34}}Js,2.0eV \\
& B)6.0\times {{10}^{-34}}Js,2.0eV \\
& C)6.4\times {{10}^{-34}}Js,3.2eV \\
& D)6.0\times {{10}^{-34}}Js,3.2eV \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
510k+ views
Hint: In this type of graphical question in which graph of Stopping potential and frequency is given then we have to use the slope of graph to find the value of planck's constant represented by h and using the intercept on y axis from the graph to find the work function of the metal surface which is represented by \[{{W}_{o}}\] .
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation using the conservation of energy.
Energy of the incident photon= Maximum Kinetic energy of photoelectrons Work Function.
The maximum Kinetic energy of photoelectron is given by-
\[{{K}_{\max }}=h\nu -{{W}_{0}}\] (Equation 1)
If \[{{V}_{0}}\] is the stopping potential ,then
\[{{K}_{\max }}=e{{V}_{0}}\]
\[\therefore e{{V}_{0}}=h\nu -{{W}_{o}}\]
\[\therefore {{V}_{0}}=(\dfrac{h}{e})\nu -\dfrac{{{W}_{o}}}{e}\] (Equation 2)
Compare this equation with the straight line equation,
\[y=mx+c\](Equation 3)
where m is the slope of the line and c is the intercept on the y-axis.
Compare these two equations 2 & Equation 3
We get,
Slope of graph \[m=\dfrac{h}{e}\]
Intercept on y axis \[c=-\dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{e}\]
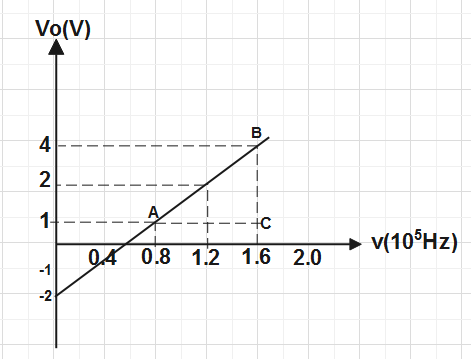
Now we have a consider a triangle ABC in the graph for calculating the slope of graph & intercept on
y- axis so that we are able to calculate the value of planck's constant and work function.
Slope of graph \[m=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\].
Now this slope will become equal to above slope and we get
\[\dfrac{h}{e}=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\times e\]
Put the value of BC and AC from the graph and value of e is given in the question , we get\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{(4-1)}{(1.6-0.8)\times {{10}^{15}}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{3}{0.8\times {{10}^{15}}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}\]
\[\therefore h=6\times {{10}^{-34}}Js\]
This is the required value of Planck’s constant.
Now we have to calculate the work function using the relation
Intercept on y axis \[c=\dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{e}\].
Here from this equation, we get
Work function is equal to e times the magnitude of the intercept on the vertical axis.
\[{{W}_{0}}=ce\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{o}}=(2)(1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}) \\
& \therefore {{W}_{0}}=3.2\times {{10}^{-19}}J \\
\end{align}\]
Now we have to convert this value of energy in joule into eV, for calculating the energy in eV we have to divide the value of the energy in joule by e.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{0}}=\dfrac{3.2\times {{10}^{-19}}}{1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}}eV \\
& \therefore {{W}_{0}}=2eV \\
\end{align}\].
So, final values of planck's constant and work function is \[6.0\times {{10}^{-34}}J-s;2eV\].
So, the correct option is B.
Note: Einstein explained the photoelectric effect on the basis of Planck’s quantum theory according to which light radiation travels in the form of discrete photons. Photoelectric emission is the result of interaction of two particles – one a photon of incident radiation and the other an electron of photosensitive metal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation using the conservation of energy.
Energy of the incident photon= Maximum Kinetic energy of photoelectrons Work Function.
The maximum Kinetic energy of photoelectron is given by-
\[{{K}_{\max }}=h\nu -{{W}_{0}}\] (Equation 1)
If \[{{V}_{0}}\] is the stopping potential ,then
\[{{K}_{\max }}=e{{V}_{0}}\]
\[\therefore e{{V}_{0}}=h\nu -{{W}_{o}}\]
\[\therefore {{V}_{0}}=(\dfrac{h}{e})\nu -\dfrac{{{W}_{o}}}{e}\] (Equation 2)
Compare this equation with the straight line equation,
\[y=mx+c\](Equation 3)
where m is the slope of the line and c is the intercept on the y-axis.
Compare these two equations 2 & Equation 3
We get,
Slope of graph \[m=\dfrac{h}{e}\]
Intercept on y axis \[c=-\dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{e}\]

Now we have a consider a triangle ABC in the graph for calculating the slope of graph & intercept on
y- axis so that we are able to calculate the value of planck's constant and work function.
Slope of graph \[m=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\].
Now this slope will become equal to above slope and we get
\[\dfrac{h}{e}=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{BC}{AC}\times e\]
Put the value of BC and AC from the graph and value of e is given in the question , we get\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{(4-1)}{(1.6-0.8)\times {{10}^{15}}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{3}{0.8\times {{10}^{15}}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}\]
\[\therefore h=6\times {{10}^{-34}}Js\]
This is the required value of Planck’s constant.
Now we have to calculate the work function using the relation
Intercept on y axis \[c=\dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{e}\].
Here from this equation, we get
Work function is equal to e times the magnitude of the intercept on the vertical axis.
\[{{W}_{0}}=ce\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{o}}=(2)(1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}) \\
& \therefore {{W}_{0}}=3.2\times {{10}^{-19}}J \\
\end{align}\]
Now we have to convert this value of energy in joule into eV, for calculating the energy in eV we have to divide the value of the energy in joule by e.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{0}}=\dfrac{3.2\times {{10}^{-19}}}{1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}}eV \\
& \therefore {{W}_{0}}=2eV \\
\end{align}\].
So, final values of planck's constant and work function is \[6.0\times {{10}^{-34}}J-s;2eV\].
So, the correct option is B.
Note: Einstein explained the photoelectric effect on the basis of Planck’s quantum theory according to which light radiation travels in the form of discrete photons. Photoelectric emission is the result of interaction of two particles – one a photon of incident radiation and the other an electron of photosensitive metal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




