
In a meter bridge experiment, the balance length is$40cm$. The resistance in the gap opposite to the length wire is $8\Omega $.The resistance of the other gap is:
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint:In this question the most important part is to remember that a meter bridge experiment is nothing but a simple Wheatstone bridge. Now, we can use the formula for a Wheatstone bridge or the Wheatstone condition to find the value of the unknown resistance given in this numerical problem.
Formula Used:If P and Q denote the two resistances and l denotes the balance length then according to the Wheatstone condition:
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{l}{{100 - l}}$
Step by step answer:
The figure given below can be used to understand the numerical problem in much more detail.
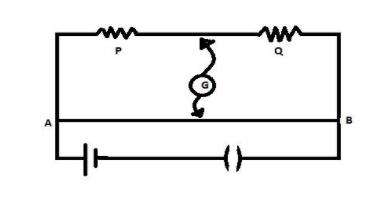
From the figure given above, we can see that the length of AB is given as $100cm$. Let us assume that the value of the resistor P is as given in the numerical problem.
Thus, $P = 8\Omega $and $l = 40cm$
Substituting these values in the mathematical expression for Wheatstone condition, we get
\[\dfrac{8}{Q} = \dfrac{{40}}{{60}}\]
Now since we are interested in obtaining the value of the unknown resistance Q, we have to use Q as the subject of the formula. Thus, we have:
$Q = \dfrac{{60 \times 8}}{{40}}$
Calculating the value of the above equation, we get:
$Q = 12\Omega $
Thus, the unknown resistance or the resistance of the other gap is 12 Ohm.
Note:Students usually forget that a metre bridge works on the same principle as a Wheatstone bridge. This confuses them and they do not arrive at the right answer. It is important to know all the important uses of electrical formulae and their applications. For example, a moving coil galvanometer works in the principle that when a current carrying coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field it is acted upon by a torque which causes a deflection in the coil.
Formula Used:If P and Q denote the two resistances and l denotes the balance length then according to the Wheatstone condition:
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{l}{{100 - l}}$
Step by step answer:
The figure given below can be used to understand the numerical problem in much more detail.

From the figure given above, we can see that the length of AB is given as $100cm$. Let us assume that the value of the resistor P is as given in the numerical problem.
Thus, $P = 8\Omega $and $l = 40cm$
Substituting these values in the mathematical expression for Wheatstone condition, we get
\[\dfrac{8}{Q} = \dfrac{{40}}{{60}}\]
Now since we are interested in obtaining the value of the unknown resistance Q, we have to use Q as the subject of the formula. Thus, we have:
$Q = \dfrac{{60 \times 8}}{{40}}$
Calculating the value of the above equation, we get:
$Q = 12\Omega $
Thus, the unknown resistance or the resistance of the other gap is 12 Ohm.
Note:Students usually forget that a metre bridge works on the same principle as a Wheatstone bridge. This confuses them and they do not arrive at the right answer. It is important to know all the important uses of electrical formulae and their applications. For example, a moving coil galvanometer works in the principle that when a current carrying coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field it is acted upon by a torque which causes a deflection in the coil.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




