
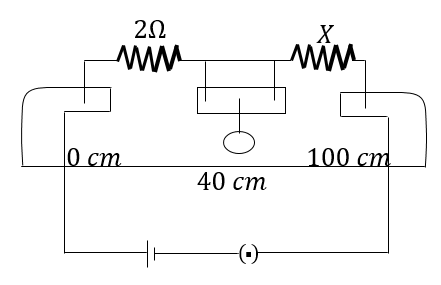
In a meter bridge circuit, resistance in the left hand gap is 2Ω and an unknown resistance $X$ is in the right hand gap as shown in Figure. The null point is found to be 40cm from the left end of the wire. What resistance should be connected to $X$ so that the new null point is 50cm from the left end of the wire?

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: According to the figure,
$
\dfrac{2}{x} = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}} = \dfrac{4}{6} \\
X = 3\Omega \\
$
Let $R\Omega $ be connected with $X$ in parallel to obtain the null point at $5cm$ from left.
Complete step by step answer:
The meter bridge uses the same principle as the Wheatstone bridge. It is used to find the unknown resistance of the materials.
Case1:
Null point is found at ${l_1} = 40cm$
Using a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
According to the Condition,
$\dfrac{2}{x} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{100 - {l_1}}}$
As we know ${l_1} = 40cm$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{X} = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}}$
Simplifying the equation to find the value of $X$.
$2X = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}} = X = 3\Omega $
Now Case 2:
Null point is found at ${l_2} = 50cm$
Using balanced Wheatstone bridge
Conditions,
$\dfrac{2}{{{X^1}}} = \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{{100 - {l_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{{{X_1}}} = \dfrac{{50}}{{100 - 50}}$
Simplifying, to find the value of $X$.
${X^1} = 2\Omega $
Since the unknown resistance gets decreased, thus we have to connect a resistance $R$in parallel to $X$so that ${X^1}$ comes out to be $2\Omega $.
Thus resistance of parallel Combination,
${X^1} = \dfrac{{XR}}{{X + R}}$
$\Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{3R}}{{3 + R}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 6\Omega $
Hence $6\Omega $ must be connected in parallel to unknown resistance $X$.
Additional Information:
We know that the Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the unknown resistance connected in a circuit. It consists of four resistors of which two resistors are unknown resistors, one variable resistor and one unknown resistor. It also consists of a galvanometer. The bridge has two series parallel arrangements of resistors. The Wheatstone bridge consists of four arms Examples: $AD,DC,CB$ and $BA$ which has fixed and variable resistors. Resistors resists the flow of electric current. Its measure is called Resistance. The variable resistor is the resistor which restricts and also can control the flow of electric current. The galvanometer is also connected between the terminals. They are called the galvanometer arm. As the cell is connected between the terminals it is called a battery arm.
Note:
To find unknown resistance cut the resistance wire of the points where it leaves the terminals, stretch it and find its length by using a meter scale measure the diameter of the wire at least at four places. In two mutually perpendicular directions at each place with the help of screw gauge Record your observation in tables.
$
\dfrac{2}{x} = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}} = \dfrac{4}{6} \\
X = 3\Omega \\
$
Let $R\Omega $ be connected with $X$ in parallel to obtain the null point at $5cm$ from left.
Complete step by step answer:
The meter bridge uses the same principle as the Wheatstone bridge. It is used to find the unknown resistance of the materials.
Case1:
Null point is found at ${l_1} = 40cm$
Using a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
According to the Condition,
$\dfrac{2}{x} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{100 - {l_1}}}$
As we know ${l_1} = 40cm$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{X} = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}}$
Simplifying the equation to find the value of $X$.
$2X = \dfrac{{40}}{{100 - 40}} = X = 3\Omega $
Now Case 2:
Null point is found at ${l_2} = 50cm$
Using balanced Wheatstone bridge
Conditions,
$\dfrac{2}{{{X^1}}} = \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{{100 - {l_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{{{X_1}}} = \dfrac{{50}}{{100 - 50}}$
Simplifying, to find the value of $X$.
${X^1} = 2\Omega $
Since the unknown resistance gets decreased, thus we have to connect a resistance $R$in parallel to $X$so that ${X^1}$ comes out to be $2\Omega $.
Thus resistance of parallel Combination,
${X^1} = \dfrac{{XR}}{{X + R}}$
$\Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{3R}}{{3 + R}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 6\Omega $
Hence $6\Omega $ must be connected in parallel to unknown resistance $X$.
Additional Information:
We know that the Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the unknown resistance connected in a circuit. It consists of four resistors of which two resistors are unknown resistors, one variable resistor and one unknown resistor. It also consists of a galvanometer. The bridge has two series parallel arrangements of resistors. The Wheatstone bridge consists of four arms Examples: $AD,DC,CB$ and $BA$ which has fixed and variable resistors. Resistors resists the flow of electric current. Its measure is called Resistance. The variable resistor is the resistor which restricts and also can control the flow of electric current. The galvanometer is also connected between the terminals. They are called the galvanometer arm. As the cell is connected between the terminals it is called a battery arm.
Note:
To find unknown resistance cut the resistance wire of the points where it leaves the terminals, stretch it and find its length by using a meter scale measure the diameter of the wire at least at four places. In two mutually perpendicular directions at each place with the help of screw gauge Record your observation in tables.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




