
In a medium of refractive index 1.6 and having a convex surface has a point object in it at a distance of $12cm$ from the pole. The radius of curvature of is $6cm$. Locate the image as seen from air.
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint:The relation between refractive index, image distance and radius of curvature is given as follows:
$\dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{\mu } = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
In this mathematical expression, $v$is the image distance, $R$is the radius of curvature and ${\mu _1},{\mu _2}$ are the refractive indices of the two media.
Step by step solution:
The numerical problem may be represented by the following figure:
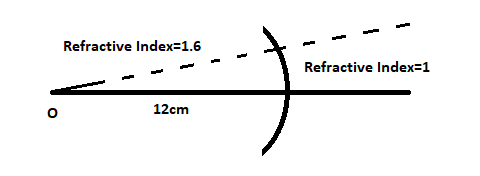
We know that one of the media is air which has a refractive index of 1. So let ${\mu _2} = 1$be the refractive index of air. Thus the refractive index of the medium is given as ${\mu _1} = 1.6$.
Consider the image to be at a distance of $v$.
Now, the centre of curvature of the lens is given as $12cm$. We know that the radius of curvature is half of the centre of curvature. Thus:
$R = \dfrac{C}{2} = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = 6cm$
Now substituting these values in the mathematical expression given above, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.6}}{1} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.6}}{{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{{1.6}}{{12}} = 0.1$
Making the image distance as the subject of the formula, we get:
$v = - 30cm$
Thus, the image is obtained at a distance of $30cm$ at the right hand side of the lens.
Note:Students usually make mistakes in the placement of the positive and negative signs. It is important to grasp the concepts of sign convention before moving to numerical problems of this type.
$\dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{\mu } = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
In this mathematical expression, $v$is the image distance, $R$is the radius of curvature and ${\mu _1},{\mu _2}$ are the refractive indices of the two media.
Step by step solution:
The numerical problem may be represented by the following figure:

We know that one of the media is air which has a refractive index of 1. So let ${\mu _2} = 1$be the refractive index of air. Thus the refractive index of the medium is given as ${\mu _1} = 1.6$.
Consider the image to be at a distance of $v$.
Now, the centre of curvature of the lens is given as $12cm$. We know that the radius of curvature is half of the centre of curvature. Thus:
$R = \dfrac{C}{2} = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = 6cm$
Now substituting these values in the mathematical expression given above, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.6}}{1} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.6}}{{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{{1.6}}{{12}} = 0.1$
Making the image distance as the subject of the formula, we get:
$v = - 30cm$
Thus, the image is obtained at a distance of $30cm$ at the right hand side of the lens.
Note:Students usually make mistakes in the placement of the positive and negative signs. It is important to grasp the concepts of sign convention before moving to numerical problems of this type.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




