
: In a mating of pea plants the F1 generation yielded offsprings in the following quantities: 595 yellow smooth : 198 green smooth: 198 yellow wrinkled: 66 green wrinkled. What were the likely genotypes of the P generation that produced these results?
A. YYRR x yyrr
B. YyRr x YyRr
C. Yyrr x YyRr
D. YYRR x yyRr
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:-In the name dihybrid cross the “ di “ indicates that there are two traits involved example R and Y and the “ hybrid “ indicates that each trait has two different alleles example R and r , or Y or y , and “ cross “ means that there are two individuals ( usually father and mother ) who are combing or crossing their genetic information.
Complete Answer:-a dihybrid cross allows us to look at the pattern of inheritance of two different traits at the same time. For example, say we are crossing two pea plants. The two traits we are looking at are the seed colour and shape. The first seed is green and wrinkly and the second is yellow and smooth.
The given example is of dihybrid cross involving seed colour and seed shape. The number of plants obtained in the \[{F_1}\] generation yielded offsprings were 595 yellow smooth : 198 green smooth : 198 yellow wrinkled : 66 green wrinkled. This count can be approximated to the phenotypic ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. this ratio can be obtained by crossing the plants of the P generation with genotype YyRr x YyRr
The dihybrid cross is easy to visualize using a punnett square of dimension 16. as shown below:
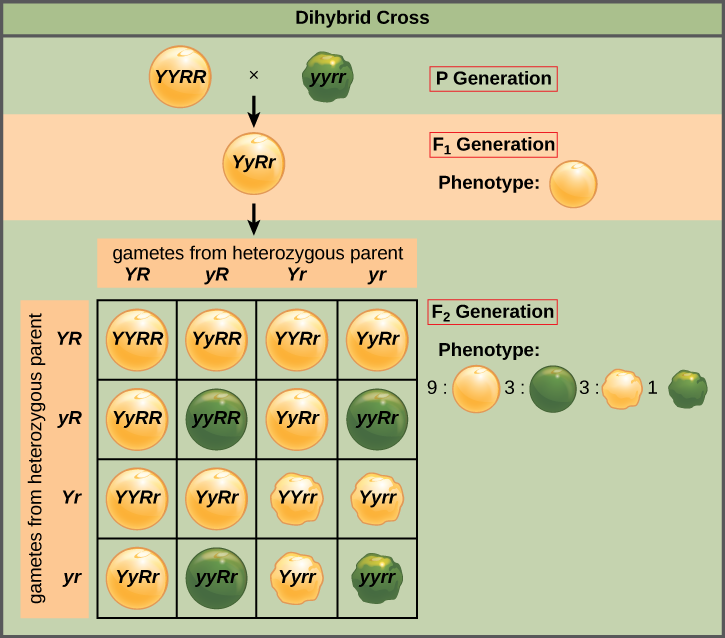
Note:- Dihybrid cross is a cross between two different lines / genes that differ in two observed traits. in the dihybrid cross the genotypes can be grouped into four phenotypes, for example 1 YYRR + 2 YYRr + 2 YyRR + 4 YyRr = 9 Y-R- smooth yellow peas. The ratio of these phenotypes is of course 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Complete Answer:-a dihybrid cross allows us to look at the pattern of inheritance of two different traits at the same time. For example, say we are crossing two pea plants. The two traits we are looking at are the seed colour and shape. The first seed is green and wrinkly and the second is yellow and smooth.
The given example is of dihybrid cross involving seed colour and seed shape. The number of plants obtained in the \[{F_1}\] generation yielded offsprings were 595 yellow smooth : 198 green smooth : 198 yellow wrinkled : 66 green wrinkled. This count can be approximated to the phenotypic ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. this ratio can be obtained by crossing the plants of the P generation with genotype YyRr x YyRr
The dihybrid cross is easy to visualize using a punnett square of dimension 16. as shown below:

Note:- Dihybrid cross is a cross between two different lines / genes that differ in two observed traits. in the dihybrid cross the genotypes can be grouped into four phenotypes, for example 1 YYRR + 2 YYRr + 2 YyRR + 4 YyRr = 9 Y-R- smooth yellow peas. The ratio of these phenotypes is of course 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




