
In a face-centred cubic lattice, atom A occupies the corner position and atom B occupies the face centre positions. If one atom of B is missing from one of the face-centred points, the formula of the compound is :
(A)- ${{A}_{2}}B$
(B)- $A{{B}_{2}}$
(C)- ${{A}_{2}}{{B}_{3}}$
(D)- ${{A}_{2}}{{B}_{5}}$
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: A face-centred cubic contains all the atoms at all the corners of the crystal lattice and the centre of all the faces of the cube. The atom present at the face-centred is shared between two adjacent unit cells and thus makes an only half contribution to an individual cell. The atom present in the corner is shared by eight corners and hence contributes a one-eight part to every corner.
Complete step by step solution:
-Unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of the crystal lattice and is the building block of a crystal.
-The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, molecules or ions inside a crystal lattice is known as a crystal lattice.
-A unit centre may be either primitive cubic, body-centred cubic (BCC) or face-centred cubic (FCC).
-Number of atoms in FCC can be given as-
(i) Atoms of the corners = 8 corners $\times $1/8 per corner atom$=\dfrac{1}{8}\times 8=1$
(ii) Atoms of face-centred = 6 face-centred atoms $\times $ 1/2 atom per unit cell $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 6=3$
Therefore, a total number of atoms in a unit cell $=1+3=4$ atoms.
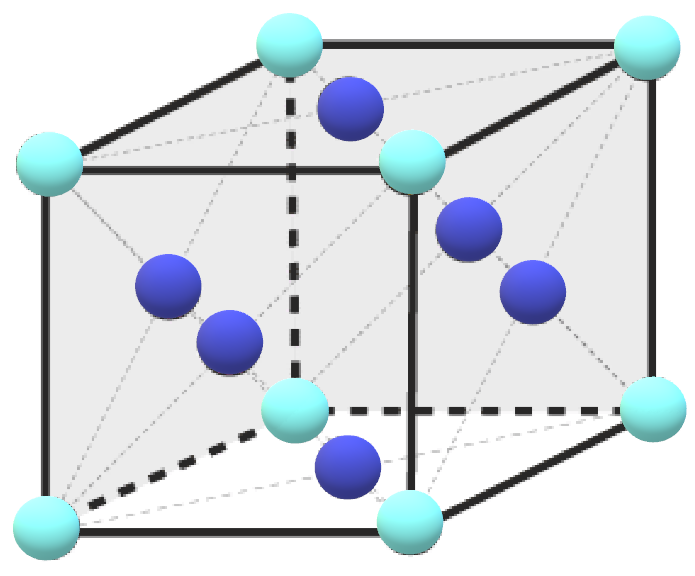
-So, according to question, atom A occupies the corner position and atom B occupies the face-centred position.
-As the molecule is possessing FCC structure, let us assume the formula of the compound be ${{A}_{x}}{{B}_{y}}$.
We need to find the value of x and y in the formula,
Number of atoms of A$=8\times \dfrac{1}{8}=1$
Number of atoms of B$=5\times \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}=2.5$
Thus, the formula of the compound is $A{{B}_{2.5}}$or ${{A}_{2}}{{B}_{5}}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The number of nearest neighbours of a central atom in a structure is known as the coordination number of the unit cell. Each sphere is a face centred cubic and has coordination number 12. The face centred cubic system resembles closely to the hexagonal close packing system, where two systems differ only in the relative placements of their hexagonal layers.
Complete step by step solution:
-Unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of the crystal lattice and is the building block of a crystal.
-The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, molecules or ions inside a crystal lattice is known as a crystal lattice.
-A unit centre may be either primitive cubic, body-centred cubic (BCC) or face-centred cubic (FCC).
-Number of atoms in FCC can be given as-
(i) Atoms of the corners = 8 corners $\times $1/8 per corner atom$=\dfrac{1}{8}\times 8=1$
(ii) Atoms of face-centred = 6 face-centred atoms $\times $ 1/2 atom per unit cell $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 6=3$
Therefore, a total number of atoms in a unit cell $=1+3=4$ atoms.

-So, according to question, atom A occupies the corner position and atom B occupies the face-centred position.
-As the molecule is possessing FCC structure, let us assume the formula of the compound be ${{A}_{x}}{{B}_{y}}$.
We need to find the value of x and y in the formula,
Number of atoms of A$=8\times \dfrac{1}{8}=1$
Number of atoms of B$=5\times \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}=2.5$
Thus, the formula of the compound is $A{{B}_{2.5}}$or ${{A}_{2}}{{B}_{5}}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The number of nearest neighbours of a central atom in a structure is known as the coordination number of the unit cell. Each sphere is a face centred cubic and has coordination number 12. The face centred cubic system resembles closely to the hexagonal close packing system, where two systems differ only in the relative placements of their hexagonal layers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




