
In a convex lens of focal length F, the minimum distance between an object and its real image must be:
A) 3F
B) 4F
C) 5F
D) 6F
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Lenses give images depending on the properties of the lens, i.e., their focal length, and the distance between the position of the object and the lens. We can get both real and virtual images using an optical device such as a lens or mirror.
Complete answer:
We can very easily find any object distance, image distance or the focal length of the lens used by employing the lens’ formula given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where, f is the focal length of the lens,
v is the image distance from the lens,
u is the object distance from the lens.
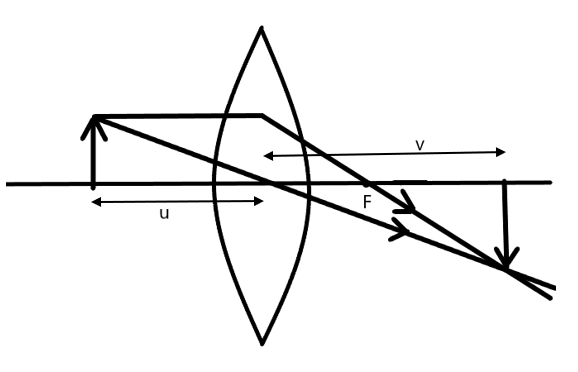
In the given situation, we have to find the minimum distance between the object and the real image caused by the lens.
To find this, we need to find a condition such that there is a turning point, i.e., at that point the real image gets converted to the virtual image.
We already know that when substituting the values in the lens’ formula, if we get a positive image distance, it implies that the image is real and inverted. The negative image distance is due to the virtual and erect.
So, we need to find the condition when the image distance, v is positive.
Also, we know the required distance is the sum of the image and object distance.
Let d be the distance between the object and image, u the image distance and \[v=d-u\] be the image distance.
Substituting in the lens’ formula –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{d-u}-\dfrac{1}{-u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{u+d-u}{ud-{{u}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{ud-{{u}^{2}}}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{u}^{2}}-ud+fd=0 \\
& \text{For u to be real, } \\
& \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\sqrt{{{(-d)}^{2}}-4(1)(f)}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}-4f}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{d}^{2}}-4f\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ d}\ge 4f \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get that the object to image distance should be 4f for the real image to form.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
These conditions of convex lenses are almost true for the concave mirrors also. These two optics systems, the concave mirror and convex lens are called converging in nature, as they form real images by convergence unlike the convex mirror and concave lens.
Complete answer:
We can very easily find any object distance, image distance or the focal length of the lens used by employing the lens’ formula given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where, f is the focal length of the lens,
v is the image distance from the lens,
u is the object distance from the lens.

In the given situation, we have to find the minimum distance between the object and the real image caused by the lens.
To find this, we need to find a condition such that there is a turning point, i.e., at that point the real image gets converted to the virtual image.
We already know that when substituting the values in the lens’ formula, if we get a positive image distance, it implies that the image is real and inverted. The negative image distance is due to the virtual and erect.
So, we need to find the condition when the image distance, v is positive.
Also, we know the required distance is the sum of the image and object distance.
Let d be the distance between the object and image, u the image distance and \[v=d-u\] be the image distance.
Substituting in the lens’ formula –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{d-u}-\dfrac{1}{-u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{u+d-u}{ud-{{u}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }f=\dfrac{ud-{{u}^{2}}}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{u}^{2}}-ud+fd=0 \\
& \text{For u to be real, } \\
& \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\sqrt{{{(-d)}^{2}}-4(1)(f)}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}-4f}\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{d}^{2}}-4f\ge 0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ d}\ge 4f \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get that the object to image distance should be 4f for the real image to form.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
These conditions of convex lenses are almost true for the concave mirrors also. These two optics systems, the concave mirror and convex lens are called converging in nature, as they form real images by convergence unlike the convex mirror and concave lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




