
In a compound AB, the ionic radii of ${A^ + }$ and ${B^ - }$ are $88\,\,pm$ and $200\,\,pm$ respectively the coordination number of ${A^ + }$ is:
(A) $6$
(B) $8$
(C) $4$
(D) $12$
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we must first understand how we can determine the Coordination number by using the ionic radii or radius ratio. Then we need to assess the concepts and use the correct formula to evaluate the coordination number and then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts about the radius ratio rule:
Radius Ratio refers to the ratio of smaller ionic radius (cation) by the ratio of larger ionic radius (anion). Hence, Radius ratio:
\[\rho {\text{ }} = \,\,{r_{cation}}/{r_{anion}}\] .
This rule helps in the determination of arrangement of ions in various types of crystal structures.
It also helps to determine the stability of an ionic crystal structure. For instance, larger cations will fill the larger voids like cubic sites whereas smaller cations will fill the smaller voids such as tetrahedral sites.
The different ranges of Radius Ratio results in different coordination number and coordination as follows:
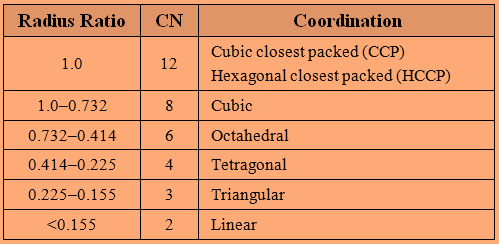
Now, let’s find the radius ratio for the given entity:
$\rho = \,\,\dfrac{{{r^ + }}}{{{r^ - }}}\,\, = \,\,\dfrac{{88}}{{200}}\,\, = $ $0.44$
So, the radius ratio is $0.44$ and it lies in the range of $0.732 - 0.414$ .
Therefore, the coordination number of ${A^ + }$ is $6$ .
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option (A).
Note:The electrostatic interaction between charged spheres is responsible for the formation of bonding in an ionic model. The determination of the sizes of the ionic radius is possible by the internuclear separation of the separate contributions of the anion from cation.
Complete step-by-step solution:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts about the radius ratio rule:
Radius Ratio refers to the ratio of smaller ionic radius (cation) by the ratio of larger ionic radius (anion). Hence, Radius ratio:
\[\rho {\text{ }} = \,\,{r_{cation}}/{r_{anion}}\] .
This rule helps in the determination of arrangement of ions in various types of crystal structures.
It also helps to determine the stability of an ionic crystal structure. For instance, larger cations will fill the larger voids like cubic sites whereas smaller cations will fill the smaller voids such as tetrahedral sites.
The different ranges of Radius Ratio results in different coordination number and coordination as follows:

Now, let’s find the radius ratio for the given entity:
$\rho = \,\,\dfrac{{{r^ + }}}{{{r^ - }}}\,\, = \,\,\dfrac{{88}}{{200}}\,\, = $ $0.44$
So, the radius ratio is $0.44$ and it lies in the range of $0.732 - 0.414$ .
Therefore, the coordination number of ${A^ + }$ is $6$ .
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option (A).
Note:The electrostatic interaction between charged spheres is responsible for the formation of bonding in an ionic model. The determination of the sizes of the ionic radius is possible by the internuclear separation of the separate contributions of the anion from cation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




