
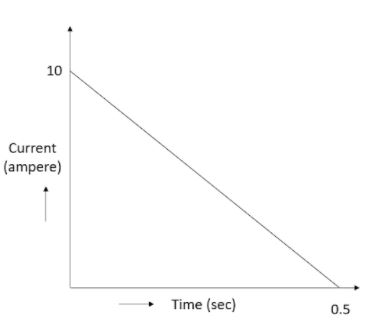
In a coil of resistance $100\Omega $, a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is:
A. 250 Wb
B. 275 Wb
C. 200 Wb
D. 225 Wb

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: First we will find the average current through the coil. And then the average emf required to produce that current. Then using the relation between rate of magnetic flux and induced emf, we will calculate the average rate of change of magnetic flux and using that we will finally find the total change in magnetic flux.
Formula used:
Ohm’s law
$V=IR$
the relation between rate of magnetic flux and induced emf
$\varepsilon =-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
$I=\dfrac{Q}{t}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the total charge that moves through the coil. For that we will need to find the area under the current-time graph.
$Q=It=\dfrac{10\times 0.5}{2}=2.5$Coulomb.
A total charge of 2.5 coulomb flows through the coil in 0.5 seconds so the average current will be
$I=\dfrac{Q}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5$A
The emf required to move that current in the coil will be
$V=IR=5\times 100=500$V.
This will be equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil. We will ignore the directions of magnetic flux and emf as only the magnitude is needed here.
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=500$.
Here instead of derivatives we can take the difference as we have been taking average values.
$\dfrac{\Delta \phi }{\Delta t}=500\Rightarrow \Delta \phi =500\Delta t=500\times 0.5=250$ Wb.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Students must take care that we have taken the average values here because all the relations being used here are linear relations. If they were quadratic or cubic, then we would have to use the exact values at all time intervals by making some sort of mathematical expression for them. We could have done the same here but that would have been a longer and more tedious process. So we could just take averages here for ease of solving.
Formula used:
Ohm’s law
$V=IR$
the relation between rate of magnetic flux and induced emf
$\varepsilon =-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
$I=\dfrac{Q}{t}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the total charge that moves through the coil. For that we will need to find the area under the current-time graph.
$Q=It=\dfrac{10\times 0.5}{2}=2.5$Coulomb.
A total charge of 2.5 coulomb flows through the coil in 0.5 seconds so the average current will be
$I=\dfrac{Q}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5$A
The emf required to move that current in the coil will be
$V=IR=5\times 100=500$V.
This will be equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil. We will ignore the directions of magnetic flux and emf as only the magnitude is needed here.
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=500$.
Here instead of derivatives we can take the difference as we have been taking average values.
$\dfrac{\Delta \phi }{\Delta t}=500\Rightarrow \Delta \phi =500\Delta t=500\times 0.5=250$ Wb.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Students must take care that we have taken the average values here because all the relations being used here are linear relations. If they were quadratic or cubic, then we would have to use the exact values at all time intervals by making some sort of mathematical expression for them. We could have done the same here but that would have been a longer and more tedious process. So we could just take averages here for ease of solving.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




