
In a circuit L, C and R are connected in series with an alternating voltage source of frequency f. The current leads the voltage by \[{{45}^{\circ }}\]. The value of C is:
A. $\dfrac{1}{\pi f(2\pi fL+R)}$
B. $\dfrac{1}{\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$
C. $\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL+R)}$
D. $\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we can use the help of the relation between Capacitive Resistance (${{X}_{C}}$) and Inductive Resistance (${{X}_{L}}$). A calculation of the resistance of a capacitor to AC (alternating current) is capacitive reactance. Inductive reactance is the name assigned to a shifting current flow to the opposition. Much like resistance, this impedance is measured in ohms,
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
Before solving the question, let us take a look at all the given parameters
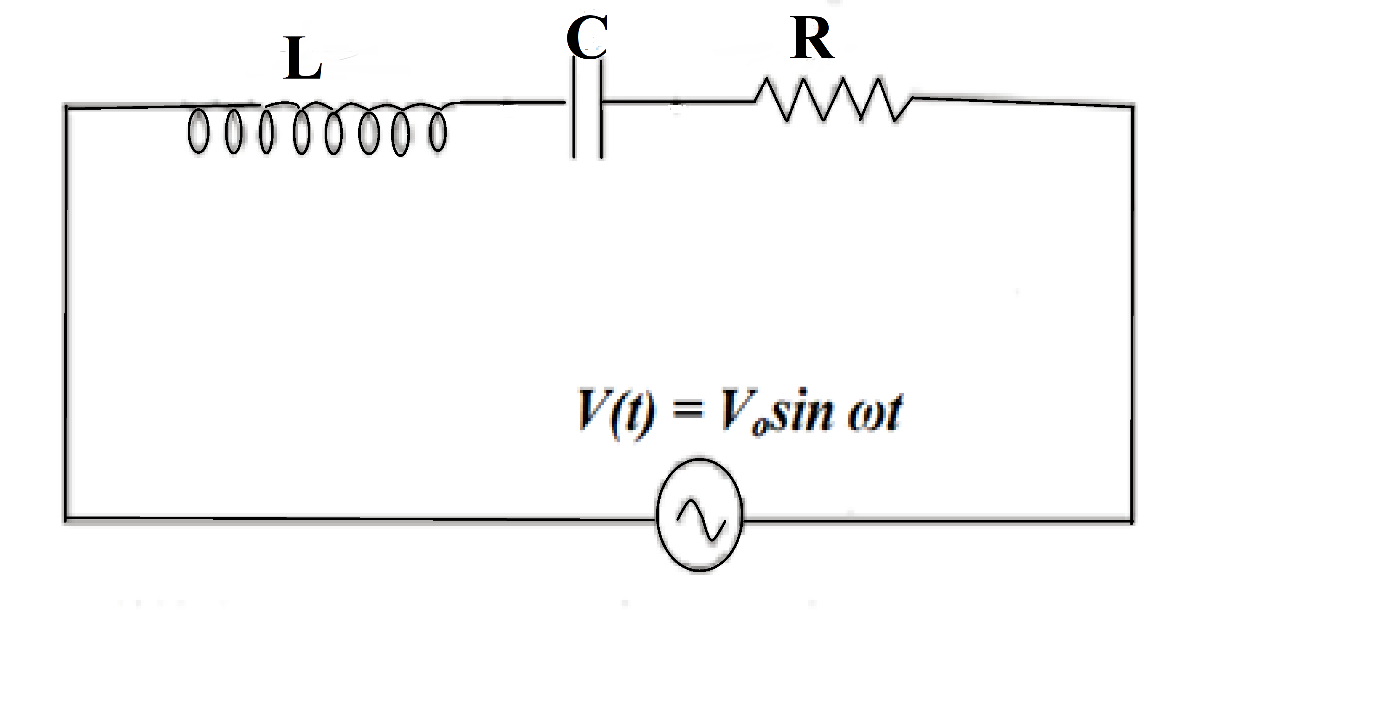
$\phi ={{45}^{\circ }}$
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi fL$
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}\]
Now, using the above values
We have,
$\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}={{X}_{L}}-R$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}=2\pi fL-R\]
$\Rightarrow 2\pi fC=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fL-R}$
$\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$
So, the correct answer to this question is $C=\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$, i.e., Option D
Note:
In the above question, an LCR circuit has been discussed. An electrical circuit consisting of an inductor ( L), capacitor (C) and resistor (R) connected in series or parallel is an LCR circuit, also known as a resonant circuit, tuned circuit, or an RLC circuit. In terms of Phasors, the LCR circuit analysis can be best understood.
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
Before solving the question, let us take a look at all the given parameters

$\phi ={{45}^{\circ }}$
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi fL$
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}\]
Now, using the above values
We have,
$\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}={{X}_{L}}-R$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}=2\pi fL-R\]
$\Rightarrow 2\pi fC=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fL-R}$
$\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$
So, the correct answer to this question is $C=\dfrac{1}{2\pi f(2\pi fL-R)}$, i.e., Option D
Note:
In the above question, an LCR circuit has been discussed. An electrical circuit consisting of an inductor ( L), capacitor (C) and resistor (R) connected in series or parallel is an LCR circuit, also known as a resonant circuit, tuned circuit, or an RLC circuit. In terms of Phasors, the LCR circuit analysis can be best understood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




