
Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson’s synthesis for the preparation of certain types of ethers.
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: The reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. A few limitations of Williamson Ether Synthesis are tertiary alkyl halides or hindered primary or secondary alkyl halides undergo elimination in the presence of an alkoxide, this nucleophile also acts as a base.
Complete step by step answer:
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from a deprotonated alcohol (alkoxide) and organohalide. Reaction involves reactants as alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halide through ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ or bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism. This is a coupling reaction.
The general reaction mechanism is-
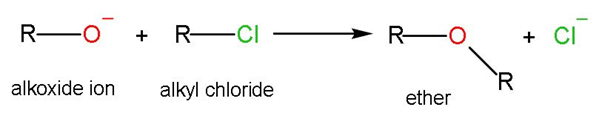
An example of this reaction is
${{\left[ {{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{O} \right]}^{-}}{{\left[ \text{Na} \right]}^{+}}+{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{Cl}\to
{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{O}{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}+\text{NaCl}$; where sodium ethoxide reacts with chloroethane to form diethyl ether.
-Limitations of Williamson’s synthesis:
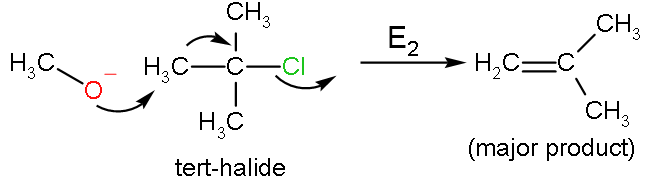
For ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction, there must be a good leaving group which is strongly electronegative mainly a halide. In the Williamson ether reaction, there is an alkoxide ion ($\text{R}{{\text{O}}^{-}}$) which acts as the nucleophile, attacks the electrophilic carbon with leaving group, which is an alkyl tosylate. The leaving site should be a primary carbon, because secondary and tertiary carbon prefers an elimination reaction. This reaction does not favour the formation of bulky ethers such as di-tert butyl ether, due to steric hindrance and formation of alkenes is largely preferred.
Note:
The reaction between tert-butyl alcohol with primary halide is ether formation takes place, but primary alkoxide reacts with tert-butyl halide to do elimination.
Complete step by step answer:
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from a deprotonated alcohol (alkoxide) and organohalide. Reaction involves reactants as alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halide through ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ or bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism. This is a coupling reaction.
The general reaction mechanism is-

An example of this reaction is
${{\left[ {{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{O} \right]}^{-}}{{\left[ \text{Na} \right]}^{+}}+{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{Cl}\to
{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{O}{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}+\text{NaCl}$; where sodium ethoxide reacts with chloroethane to form diethyl ether.
-Limitations of Williamson’s synthesis:
For ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction, there must be a good leaving group which is strongly electronegative mainly a halide. In the Williamson ether reaction, there is an alkoxide ion ($\text{R}{{\text{O}}^{-}}$) which acts as the nucleophile, attacks the electrophilic carbon with leaving group, which is an alkyl tosylate. The leaving site should be a primary carbon, because secondary and tertiary carbon prefers an elimination reaction. This reaction does not favour the formation of bulky ethers such as di-tert butyl ether, due to steric hindrance and formation of alkenes is largely preferred.
Note:
The reaction between tert-butyl alcohol with primary halide is ether formation takes place, but primary alkoxide reacts with tert-butyl halide to do elimination.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




