
If \[y = x{e^{ - x}}\], what are the points of inflection of the graph \[f(x)\]?
Answer
491.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we will learn some new concepts like concavity, points of inflection of functions and so on. To find the points of inflection, first we need to find a second derivative of this function. If the first derivative and the second derivative of this functions exist and continuous, the,
The inflection point is \['a'\] for which \[f''(a) = 0{\text{ or undefined}}\]
We will solve the problem by using some derivative formulas like \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^x} = {e^x}\] and \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}\]
And also, we will use the product rule which is \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}uv = u\dfrac{d}{{dx}}v + v\dfrac{d}{{dx}}u\] where \[u{\text{ and }}v\] are functions in \[x\].
Complete step by step answer:
Inflection points are the points at which the graph changes its concavity. Concavity means the concave or convex nature of a graph. It also defines the concave-up or concave-down nature of graphs.
Suppose that there is a function \[y = f(x)\].
If the first derivative and the second derivative of this functions exist and continuous, the,
The inflection point is \['a'\] for which \[f''(a) = 0{\text{ or undefined}}\]
So, in the question, the given function is \[y = x{e^{ - x}}\]
To find the points of inflection, first we need to find a second derivative of this function.
Let us first find the first derivative.
\[y' = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}x{e^{ - x}}\]
By applying product rule, (as there are two functions as a single term)
\[ \Rightarrow y' = x\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}} + {e^{ - x}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y' = x( - {e^{ - x}}) + {e^{ - x}}\]
So, we get the first derivative as,
\[ \Rightarrow y' = {e^{ - x}}(1 - x)\]
Now, let us find the second derivative.
\[y'' = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}}(1 - x)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(1 - x) + (1 - x)\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}}\]
Now, on simplification, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = - {e^{ - x}} + (1 - x)( - {e^{ - x}})\]
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}(x - 2)\]
Now, to get points of inflection, equate the second derivative to zero.
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}(x - 2) = 0\]
So, on solving, we get \[x = 2\]
So, the point of inflection is \[x = 2\].
At this point the graph changes its concavity.
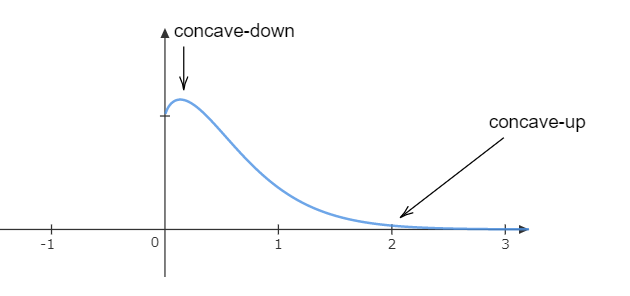
This is the graph for \[y = x{e^{ - x}}\].
Note:
In geometry and calculus, the point of inflection is also called inflection point or flex or inflection.
If the function is a decreasing function, then the point of inflection is called A falling point of inflection.
If the function is an increasing function, then the point of inflection is called A rising point of inflection.
The inflection point is \['a'\] for which \[f''(a) = 0{\text{ or undefined}}\]
We will solve the problem by using some derivative formulas like \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^x} = {e^x}\] and \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}\]
And also, we will use the product rule which is \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}uv = u\dfrac{d}{{dx}}v + v\dfrac{d}{{dx}}u\] where \[u{\text{ and }}v\] are functions in \[x\].
Complete step by step answer:
Inflection points are the points at which the graph changes its concavity. Concavity means the concave or convex nature of a graph. It also defines the concave-up or concave-down nature of graphs.
Suppose that there is a function \[y = f(x)\].
If the first derivative and the second derivative of this functions exist and continuous, the,
The inflection point is \['a'\] for which \[f''(a) = 0{\text{ or undefined}}\]
So, in the question, the given function is \[y = x{e^{ - x}}\]
To find the points of inflection, first we need to find a second derivative of this function.
Let us first find the first derivative.
\[y' = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}x{e^{ - x}}\]
By applying product rule, (as there are two functions as a single term)
\[ \Rightarrow y' = x\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}} + {e^{ - x}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y' = x( - {e^{ - x}}) + {e^{ - x}}\]
So, we get the first derivative as,
\[ \Rightarrow y' = {e^{ - x}}(1 - x)\]
Now, let us find the second derivative.
\[y'' = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}}(1 - x)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(1 - x) + (1 - x)\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ - x}}\]
Now, on simplification, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = - {e^{ - x}} + (1 - x)( - {e^{ - x}})\]
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}(x - 2)\]
Now, to get points of inflection, equate the second derivative to zero.
\[ \Rightarrow y'' = {e^{ - x}}(x - 2) = 0\]
So, on solving, we get \[x = 2\]
So, the point of inflection is \[x = 2\].
At this point the graph changes its concavity.

This is the graph for \[y = x{e^{ - x}}\].
Note:
In geometry and calculus, the point of inflection is also called inflection point or flex or inflection.
If the function is a decreasing function, then the point of inflection is called A falling point of inflection.
If the function is an increasing function, then the point of inflection is called A rising point of inflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




