
if we have a trigonometric expression as $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$ , where [ . ] denotes greatest integer function, then the complete set of values of x is
( a ) (cos1, 1]
( b ) ( cos1, - cos1)
( c ) (cot1, 1]
( d ) none of these
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: What we will do is we will first draw the graph of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ and ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ using concept of greatest integer function. Then we will first see for what values of x, ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ and ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ is equals to zero. Then we will take intersection of set of domain of values of x for $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$ and $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]=0$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the question, let us see what is the greatest integer function and what are its properties.
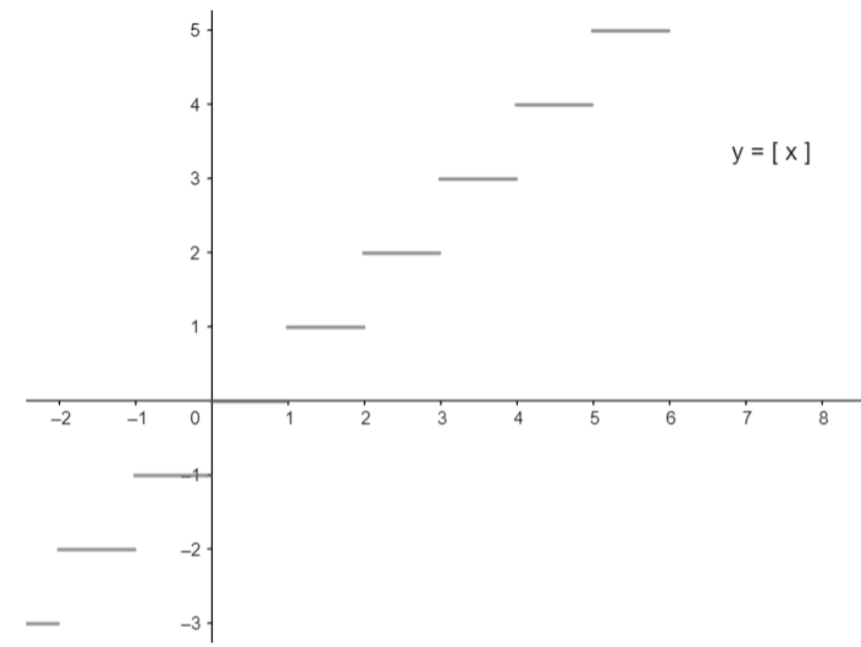
Function y = [ x ] is called greatest integer function which means the greatest integer less than or equals to x. also, if n belongs to set of integer, then y = [ x ] = n if $n\le xFor example if we put x = -3.1 in y = [ x ], then y = - 4 and if we put x = 0.2 in y = [ x ], then y = 0.
Graph of y = [ x ] is given as,
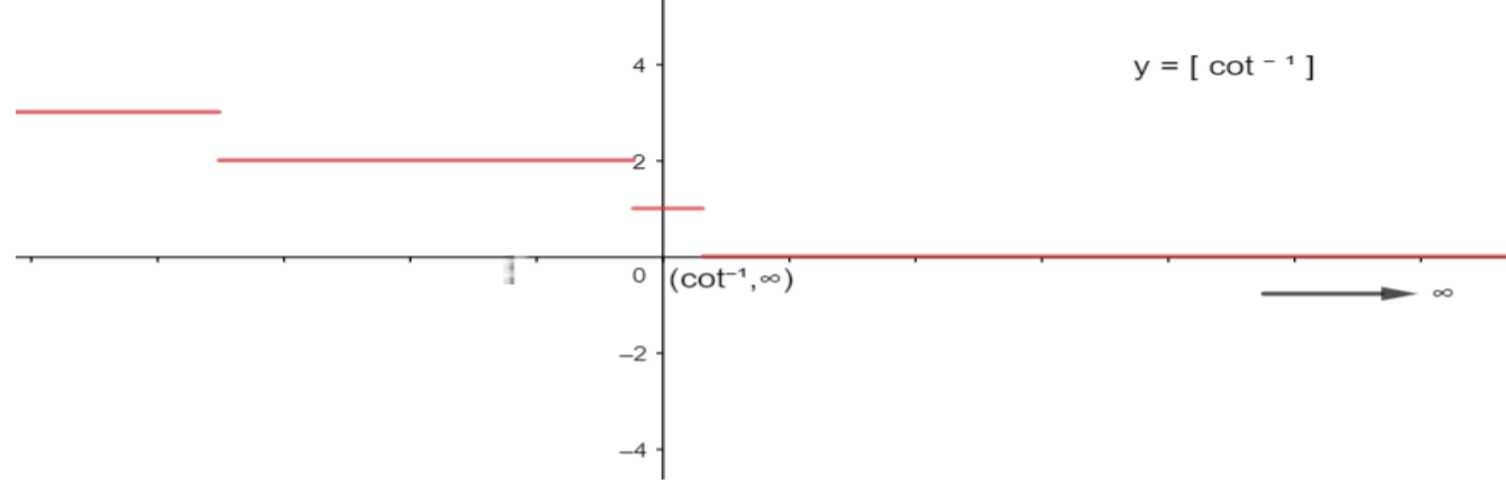
Graph of $y=[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is given as,
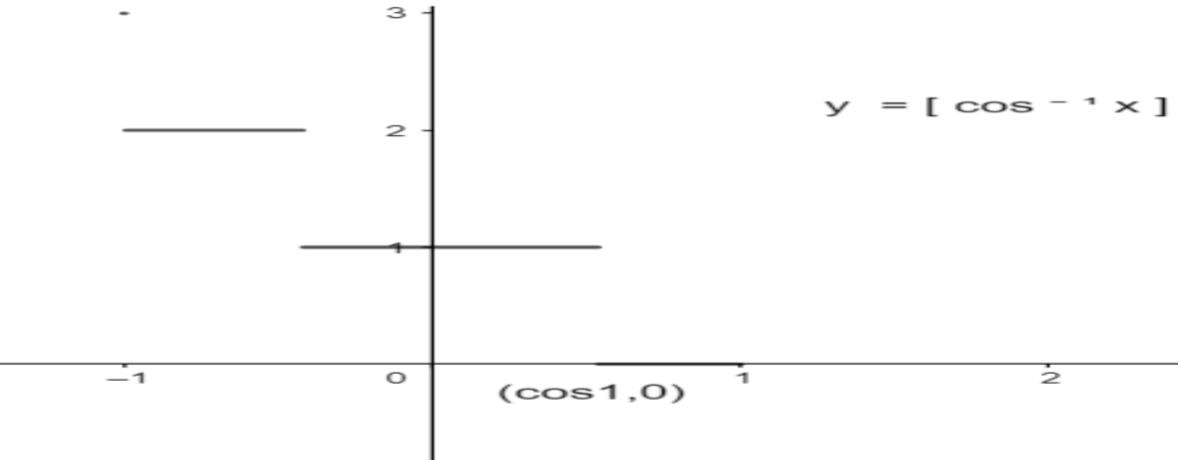
Graph of $y=[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ is given as
Now, in question it is given that $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$
Now, we know that range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is $0\le {{\cos }^{-1}}x\le \pi $.
So from seeing the range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$, we can say that ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is always positive for all values of x. where x belongs to a set of real numbers.
Also, we know that range of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ is $0<{{\cot }^{-1}}x\le \pi $.
So from seeing the range of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$, we can say that ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is always positive for all values of x. where x belongs to a set of real numbers.
Now for, values of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$, $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$is true when both $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ and $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ are equals to zero.
Now, from graph of $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$, $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ is always zero for values between cos1 and 1 that is,
$[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0;x\in (\cos 1,1]$….( i )
Now, from graph of $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$, $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is always zero for values between cot1 and $\infty $ that is,
$[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]=0;x\in (\cot 1,\infty )$……( ii )
Taking intersection of equation ( i ) and ( ii )
So, set of all values x for which $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$ is $x\in (\cot 1,1]$
Hence, option ( c ) is true.
Note: For finding domain of functions which are formed by combination of some function of x and greatest integer function, knowledge of graph is must. If we have $f(x)={{f}_{1}}(x)+{{f}_{2}}(x)$ , then domain of f(x) is equals to domain of ${{f}_{1}}(x)\cap {{f}_{2}}(x)$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the question, let us see what is the greatest integer function and what are its properties.
Function y = [ x ] is called greatest integer function which means the greatest integer less than or equals to x. also, if n belongs to set of integer, then y = [ x ] = n if $n\le x
Graph of y = [ x ] is given as,

Graph of $y=[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is given as,

Graph of $y=[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ is given as

Now, in question it is given that $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$
Now, we know that range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is $0\le {{\cos }^{-1}}x\le \pi $.
So from seeing the range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$, we can say that ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is always positive for all values of x. where x belongs to a set of real numbers.
Also, we know that range of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ is $0<{{\cot }^{-1}}x\le \pi $.
So from seeing the range of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$, we can say that ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$ is always positive for all values of x. where x belongs to a set of real numbers.
Now for, values of ${{\cot }^{-1}}x$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}x$, $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$is true when both $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ and $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ are equals to zero.
Now, from graph of $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$, $[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]$ is always zero for values between cos1 and 1 that is,
$[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0;x\in (\cos 1,1]$….( i )
Now, from graph of $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$, $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is always zero for values between cot1 and $\infty $ that is,
$[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]=0;x\in (\cot 1,\infty )$……( ii )
Taking intersection of equation ( i ) and ( ii )
So, set of all values x for which $[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]+[{{\cos }^{-1}}x]=0$ is $x\in (\cot 1,1]$
Hence, option ( c ) is true.
Note: For finding domain of functions which are formed by combination of some function of x and greatest integer function, knowledge of graph is must. If we have $f(x)={{f}_{1}}(x)+{{f}_{2}}(x)$ , then domain of f(x) is equals to domain of ${{f}_{1}}(x)\cap {{f}_{2}}(x)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




