
If we have a inverse trigonometric equation as $\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x \right)=1$ , then find the value of x.
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: The above question is related to inverse trigonometric function and for solving the problem, you need to use the property that ${{\sin }^{-1}}x+{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Before starting with the solution to the above question, we will first talk about the required details of different inverse trigonometric ratios. So, we must remember that inverse trigonometric ratios are completely different from trigonometric ratios and have many constraints related to their range and domain. So, to understand these constraints and the behavior of inverse trigonometric functions, let us look at some of the important graphs. First, let us see the graph of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$.
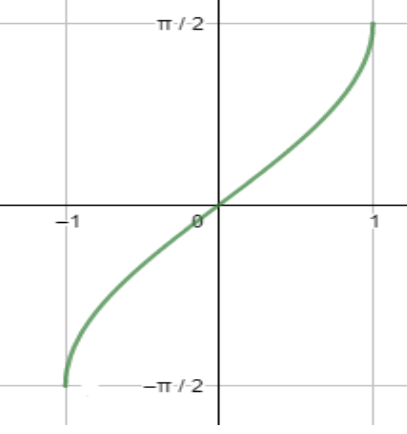
Now let us draw the graph of $co{{s}^{-1}}x$ .
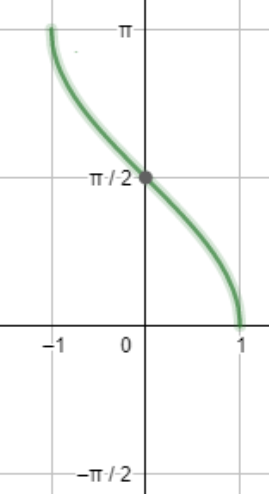
Also, we will draw the graph of ${{\tan }^{-1}}x$ as well.
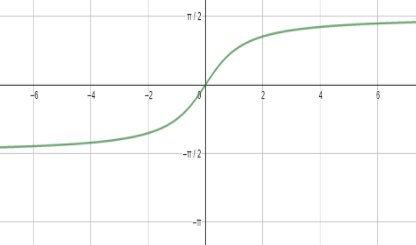
Now moving to the solution to the above question, we will start with the simplification of the equation given in the question.
$\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x \right)=1$
Now we know that the value of sine function is 1, if and only if the angle is of the form $2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ , where n is a integer. We also know that the range of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x\text{ is }\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ and the range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x\text{ is }\left[ 0,\pi \right]$ , so the maximum and minimum possible values of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x+{{\cos }^{-1}}x$ are $\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\text{ and }\dfrac{-\pi }{2}$ , respectively. So, the only possible value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Now, from the above results we know that ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . We also know that for any value of x lying in the domain, the value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}a+{{\cos }^{-1}}a=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . So, we can say that the value of x is $\dfrac{1}{5}$.
Note: While dealing with inverse trigonometric functions, it is preferred to know about the domains and ranges of the different inverse trigonometric functions. For example: the domain of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is $[-1,1]$ and the range is $\left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ .
Complete step-by-step solution -
Before starting with the solution to the above question, we will first talk about the required details of different inverse trigonometric ratios. So, we must remember that inverse trigonometric ratios are completely different from trigonometric ratios and have many constraints related to their range and domain. So, to understand these constraints and the behavior of inverse trigonometric functions, let us look at some of the important graphs. First, let us see the graph of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$.

Now let us draw the graph of $co{{s}^{-1}}x$ .

Also, we will draw the graph of ${{\tan }^{-1}}x$ as well.

Now moving to the solution to the above question, we will start with the simplification of the equation given in the question.
$\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x \right)=1$
Now we know that the value of sine function is 1, if and only if the angle is of the form $2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ , where n is a integer. We also know that the range of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x\text{ is }\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ and the range of ${{\cos }^{-1}}x\text{ is }\left[ 0,\pi \right]$ , so the maximum and minimum possible values of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x+{{\cos }^{-1}}x$ are $\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\text{ and }\dfrac{-\pi }{2}$ , respectively. So, the only possible value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Now, from the above results we know that ${{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{5}+{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . We also know that for any value of x lying in the domain, the value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}a+{{\cos }^{-1}}a=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . So, we can say that the value of x is $\dfrac{1}{5}$.
Note: While dealing with inverse trigonometric functions, it is preferred to know about the domains and ranges of the different inverse trigonometric functions. For example: the domain of ${{\sin }^{-1}}x$ is $[-1,1]$ and the range is $\left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




