
If the line $x=\alpha $ divides the area of region R=$\left\{ \left( x,y \right)\in {{R}^{2}}:{{x}^{3}}\le y\le x,0\le x\le 1 \right\}$into two equal parts, then
(a) $2{{\alpha }^{4}}-4{{\alpha }^{2}}+1=0$
(b) ${{\alpha }^{4}}+4{{\alpha }^{2}}-1=0$
(c) $0<\alpha \le \dfrac{1}{2}$
(d) $\dfrac{1}{2}<\alpha <1$
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: First, before proceeding for this, we must graph the following conditions to get the area of the two different regions. Then, from the figure and the condition given in the question says that the area of both regions is equal, we get the equation in terms of $\alpha $. Then, by using the quadratic formula for the quadratic equation of form as $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ given by $x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$, we get the range of $\alpha $.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this question, we are supposed to find the value of range of $\alpha $when the line $x=\alpha $ divides the area of region R=$\left\{ \left( x,y \right)\in {{R}^{2}}:{{x}^{3}}\le y\le x,0\le x\le 1 \right\}$into two equal parts.
So, before proceeding for this, we must graph the following conditions to get the area of the two different regions as:
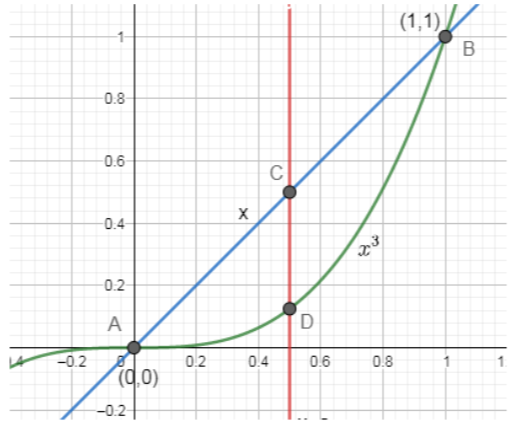
Now, from the figure and the condition given in the question says that the area of both the regions ACD and BCD separated by $x=\alpha $are equal.
Then, by applying the above mentioned condition, we get:
$\int\limits_{0}^{\alpha }{\left( x-{{x}^{3}} \right)dx=}\int\limits_{\alpha }^{1}{\left( x-{{x}^{3}} \right)dx}$
Now, by solving the above integration, we get:
$\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4} \right)_{0}^{\alpha }=\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4} \right)_{\alpha }^{1}$
Then, by substituting the limits on both sides, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4}-0+0 \right)=\left( \dfrac{{{1}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{1}^{4}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{2{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{2{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{4{{\alpha }^{2}}-2{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{2-1}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\alpha }^{2}}-2{{\alpha }^{4}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{\alpha }^{4}}-4{{\alpha }^{2}}+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the above expression gives the option (a) as correct.
Now, to get the value of $\alpha $, we can substitute ${{\alpha }^{2}}=x$ to get the standard quadratic equation as:
$2{{x}^{2}}-4x+1=0$
Then, by using the quadratic formula for the quadratic equation of form as $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ given by:
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
So, by using the above formula and substituting all the values from the equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 2\times 1}}{2\times 2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{16-8}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{8}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm 2\sqrt{2}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=1\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
So, we know that we have used substitution as ${{\alpha }^{2}}=x$ to get value of $\alpha $as:
$\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=1\pm 0.707 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get two different values as:
$\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1+0.707 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=1.707 \\
& \Rightarrow \alpha =1.3 \\
\end{align}$ or $\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1-0.707 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=0.293 \\
& \Rightarrow \alpha =0.54 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the value of $\alpha $in the range as $\dfrac{1}{2}<\alpha <1$ which is 0.54. Hence, options (a) and (d) are correct.
Note: Now, to solve these types of the questions we need to know some of the basic integration formulas beforehand to get the solution correctly. So, the basic integration required is as:
$\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}$
Moreover, we can also the factorization method to calculate the factors of the quadratic equation. Also, we must keep in mind while solving these types of problems that we will not consider any value of $\alpha $ as it is looking like the midpoint of 0 and 1 which is 0.5. However, after calculation, we get a different value of $\alpha $ as 0.54 to get the range of it.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this question, we are supposed to find the value of range of $\alpha $when the line $x=\alpha $ divides the area of region R=$\left\{ \left( x,y \right)\in {{R}^{2}}:{{x}^{3}}\le y\le x,0\le x\le 1 \right\}$into two equal parts.
So, before proceeding for this, we must graph the following conditions to get the area of the two different regions as:

Now, from the figure and the condition given in the question says that the area of both the regions ACD and BCD separated by $x=\alpha $are equal.
Then, by applying the above mentioned condition, we get:
$\int\limits_{0}^{\alpha }{\left( x-{{x}^{3}} \right)dx=}\int\limits_{\alpha }^{1}{\left( x-{{x}^{3}} \right)dx}$
Now, by solving the above integration, we get:
$\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4} \right)_{0}^{\alpha }=\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4} \right)_{\alpha }^{1}$
Then, by substituting the limits on both sides, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4}-0+0 \right)=\left( \dfrac{{{1}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{1}^{4}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{2{{\alpha }^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{2{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{4{{\alpha }^{2}}-2{{\alpha }^{4}}}{4} \right)=\left( \dfrac{2-1}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\alpha }^{2}}-2{{\alpha }^{4}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{\alpha }^{4}}-4{{\alpha }^{2}}+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the above expression gives the option (a) as correct.
Now, to get the value of $\alpha $, we can substitute ${{\alpha }^{2}}=x$ to get the standard quadratic equation as:
$2{{x}^{2}}-4x+1=0$
Then, by using the quadratic formula for the quadratic equation of form as $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ given by:
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
So, by using the above formula and substituting all the values from the equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 2\times 1}}{2\times 2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{16-8}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm \sqrt{8}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4\pm 2\sqrt{2}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=1\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
So, we know that we have used substitution as ${{\alpha }^{2}}=x$ to get value of $\alpha $as:
$\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=1\pm 0.707 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get two different values as:
$\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1+0.707 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=1.707 \\
& \Rightarrow \alpha =1.3 \\
\end{align}$ or $\begin{align}
& {{\alpha }^{2}}=1-0.707 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\alpha }^{2}}=0.293 \\
& \Rightarrow \alpha =0.54 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the value of $\alpha $in the range as $\dfrac{1}{2}<\alpha <1$ which is 0.54. Hence, options (a) and (d) are correct.
Note: Now, to solve these types of the questions we need to know some of the basic integration formulas beforehand to get the solution correctly. So, the basic integration required is as:
$\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}$
Moreover, we can also the factorization method to calculate the factors of the quadratic equation. Also, we must keep in mind while solving these types of problems that we will not consider any value of $\alpha $ as it is looking like the midpoint of 0 and 1 which is 0.5. However, after calculation, we get a different value of $\alpha $ as 0.54 to get the range of it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




