
If the length of a vernier scale having 25 divisions correspond to 23 main scale divisions, then given that, \[M.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1mm\] the least count of the vernier calipers is:
A.80mm
B.0.04mm
C.0.08cm
D.None of the above
Answer
551.4k+ views
Hint: We will first calculate the value of V.S.D from the equation given in the problem, i.e. \[25{\text{ }}V.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}23{\text{ }}M.S.D\] . Then calculate the value of least count by using the equation \[L.C = 1M.S.D - 1V.S.D\]
Complete answer:
The Vernier caliper gives a direct reading of the distance measured with high accuracy and precision. Vernier calipers are functionally identical, with different ways of reading the results. These calipers compromise a calibrated scale with a fixed jaw, and another jaw, with a pointer, that slides along the scale.
Vernier calipers can measure internal dimensions. This probe is slender and can get into deep grooves that may prove difficult for other measuring tools. The simplest method is to read the position of the pointer directly on the scale.
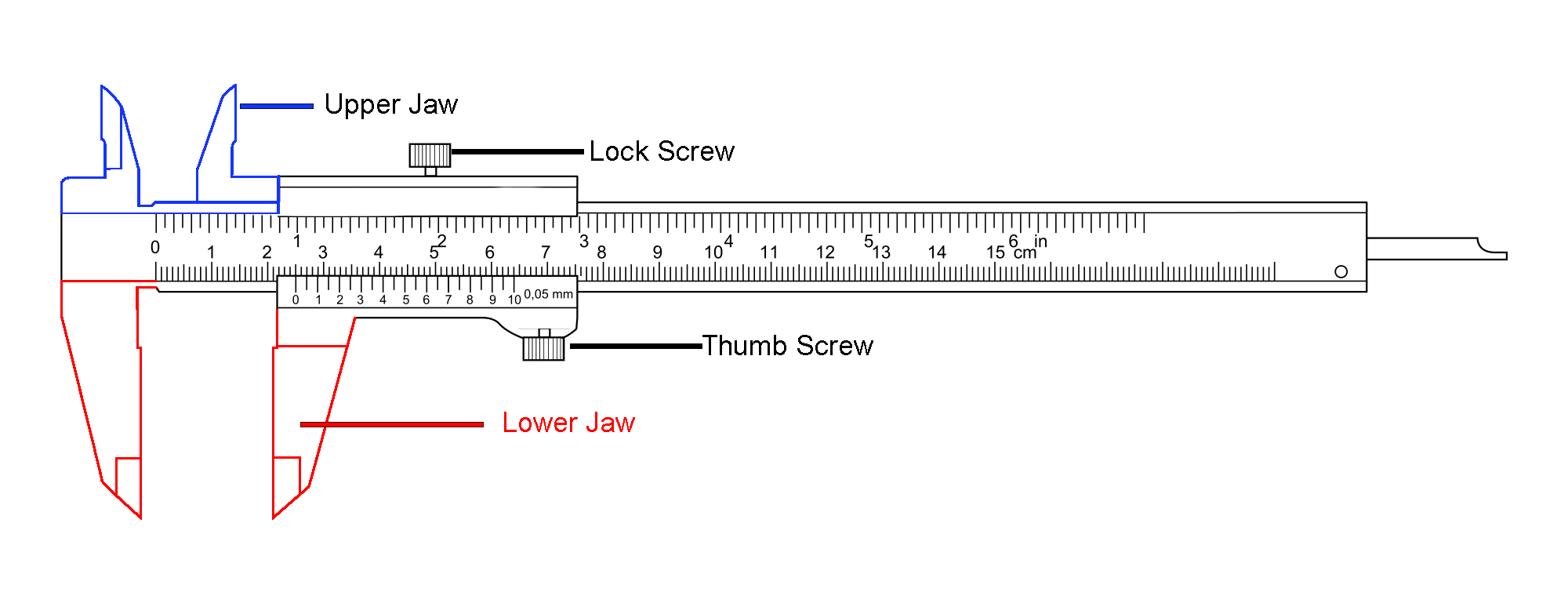
The Vernier scales may include metric measurements on the lower part of the scale and inch measurements on the upper or vice-versa. A Vernier scale allows more accurate interpolation and is the universal practice. Vernier calipers are commonly used in industry to provide a precision to 0.01mm.
M.S.D - The gap between two successive marks on the main scale is one main scale division (M.S.D).
V.S.D - The distance between two consecutive marks on the main scale is one main scale division (M.S.D).
Now we are given in the problem, \[M.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1mm\]
\[25{\text{ }}V.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}23{\text{ }}M.S.D\]
\[ \Rightarrow V.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{23}}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
Now we know that the least count of a verniers calipers is given by the equation
\[L.C = 1M.S.D - 1V.S.D\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = 1M.S.D - \dfrac{{23}}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = \dfrac{2}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = \dfrac{2}{{25}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{1mm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = 0.8mm = 0.08cm\]
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note:
In measurement science, the smallest and most precise value in the calculated quantity that can be resolved on the instrument's scale is the least count of a measuring instrument. The least count is related to the precision of an instrument; an instrument that can calculate smaller changes in a value compared to another instrument.
Complete answer:
The Vernier caliper gives a direct reading of the distance measured with high accuracy and precision. Vernier calipers are functionally identical, with different ways of reading the results. These calipers compromise a calibrated scale with a fixed jaw, and another jaw, with a pointer, that slides along the scale.
Vernier calipers can measure internal dimensions. This probe is slender and can get into deep grooves that may prove difficult for other measuring tools. The simplest method is to read the position of the pointer directly on the scale.

The Vernier scales may include metric measurements on the lower part of the scale and inch measurements on the upper or vice-versa. A Vernier scale allows more accurate interpolation and is the universal practice. Vernier calipers are commonly used in industry to provide a precision to 0.01mm.
M.S.D - The gap between two successive marks on the main scale is one main scale division (M.S.D).
V.S.D - The distance between two consecutive marks on the main scale is one main scale division (M.S.D).
Now we are given in the problem, \[M.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1mm\]
\[25{\text{ }}V.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}23{\text{ }}M.S.D\]
\[ \Rightarrow V.S.D{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{23}}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
Now we know that the least count of a verniers calipers is given by the equation
\[L.C = 1M.S.D - 1V.S.D\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = 1M.S.D - \dfrac{{23}}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = \dfrac{2}{{25}}{\text{ M}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.D}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = \dfrac{2}{{25}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{1mm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L.C = 0.8mm = 0.08cm\]
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note:
In measurement science, the smallest and most precise value in the calculated quantity that can be resolved on the instrument's scale is the least count of a measuring instrument. The least count is related to the precision of an instrument; an instrument that can calculate smaller changes in a value compared to another instrument.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




