
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
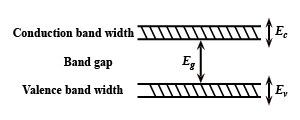
A) All ${E_C}$, ${E_g}$, ${E_v}$ increases.
B) ${E_C}$, and${E_v}$ increases but ${E_g}$ decreases
C) ${E_C}$, and ${E_v}$ decreases but ${E_g}$ increases
D) All ${E_C}$, ${E_g}$, ${E_v}$ decreases.
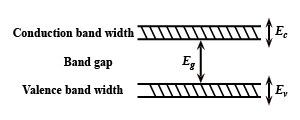
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: A crystal structure is composed in three dimensions on a lattice. The spacing between unit calls in various directions is called its lattice parameters or constants increasing these lattice constants will increase or widens the bend gap ${E_g}$, which means more energy would be required by an electron to reach the conduction band from the valence band automatically ${E_c}$ and ${E_v}$ decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
The lattice constant is the side length of the cube. Lattice represents the distance between molecules or atoms which construct the lattice. So generally decrease in lattice constant means the electrons are more tightly bound to the atom, and hence require more energy to remove, leading to an increased band gap.
Step 2:
A crystal structure is composed of a unit cell, a set of atoms arranged in a particle in a particle way which is periodically repeated in three dimensions on a lattice.
The spacing between unit calls in various directions is called its lattice parameters or constants increasing these lattice constants will increase or widens the bend gap ${E_g}$, which means more energy would be required by an electron to reach the conduction band from the valence band automatically ${E_c}$ and ${E_v}$ decreases.
Hence, ${E_c}$ and ${E_V}$ decreases but ${E_g}$ increases. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
By controlling the doping, the way electrical current moves through a semiconductor can be controlled. In a typical conductor, like copper, electrons carry the current and act as the charge carrier. In semiconductors, both electrons and holes (the absence of an electron) act as charge carriers.
Note:
Semiconductors possess specific electrical properties. A substance that conducts electricity is called a conductor, and a substance that does not conduct electricity is called an insulator. Semiconductors are substances with properties somewhere between them. Electrical properties can be indicated by resistivity.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
The lattice constant is the side length of the cube. Lattice represents the distance between molecules or atoms which construct the lattice. So generally decrease in lattice constant means the electrons are more tightly bound to the atom, and hence require more energy to remove, leading to an increased band gap.
Step 2:
A crystal structure is composed of a unit cell, a set of atoms arranged in a particle in a particle way which is periodically repeated in three dimensions on a lattice.
The spacing between unit calls in various directions is called its lattice parameters or constants increasing these lattice constants will increase or widens the bend gap ${E_g}$, which means more energy would be required by an electron to reach the conduction band from the valence band automatically ${E_c}$ and ${E_v}$ decreases.
Hence, ${E_c}$ and ${E_V}$ decreases but ${E_g}$ increases. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
By controlling the doping, the way electrical current moves through a semiconductor can be controlled. In a typical conductor, like copper, electrons carry the current and act as the charge carrier. In semiconductors, both electrons and holes (the absence of an electron) act as charge carriers.
Note:
Semiconductors possess specific electrical properties. A substance that conducts electricity is called a conductor, and a substance that does not conduct electricity is called an insulator. Semiconductors are substances with properties somewhere between them. Electrical properties can be indicated by resistivity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




