
If the input frequency of a full wave rectifier is $50Hz$ AC. Its output frequency is
(A). $50Hz$ pulsating DC
(B). $100Hz$ pulsating DC
(C). $200Hz$ pulsating DC
(D). $500Hz$ pulsating DC
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: Rectifiers are used to convert C into DC. There are different types of rectifiers of which a full wave rectifier gives output double the input. It consists of two diodes connected to a load. Each diode is operable for different cycles of AC. The diodes rectify different cycles of AC and hence the double of input is received as output.
Complete answer:
A rectifier is used to convert AC current into DC current
A full wave rectifier takes AC as input. It consists of two diodes which convert each half of the cycle into pulsating DC so the input gets rectified at each diode and the output received is double that of input.
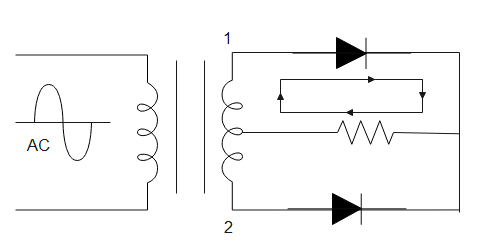
The figure given above is the figure of a full wave rectifier. During the positive half cycle of AC, the point 1 is at higher potential and point 2 is at lower potential. Therefore, the above diode is forward biased and allows current to flow through it while the diode below is reverse biased and restricts the flow of current through it. Similarly, during the negative half cycle of the AC cycle, point 2 is now at higher potential and point 1 is at lower potential. The current now flows through the diode given below.
This is how the input of the full wave rectifier is doubled.
Given, frequency of input AC is $50Hz$. The frequency will be doubled at the output. Thus, the frequency at output will be $100Hz$.
Therefore, the output frequency is $100Hz$ of pulsating DC.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Diodes are semiconductor devices which allow current to flow through them only in one direction. The output in a rectifier is received at the load connected in the middle. A rectifier is an application of diodes. Other applications of diodes are amplifiers, gates, inverters etc.
Complete answer:
A rectifier is used to convert AC current into DC current
A full wave rectifier takes AC as input. It consists of two diodes which convert each half of the cycle into pulsating DC so the input gets rectified at each diode and the output received is double that of input.

The figure given above is the figure of a full wave rectifier. During the positive half cycle of AC, the point 1 is at higher potential and point 2 is at lower potential. Therefore, the above diode is forward biased and allows current to flow through it while the diode below is reverse biased and restricts the flow of current through it. Similarly, during the negative half cycle of the AC cycle, point 2 is now at higher potential and point 1 is at lower potential. The current now flows through the diode given below.
This is how the input of the full wave rectifier is doubled.
Given, frequency of input AC is $50Hz$. The frequency will be doubled at the output. Thus, the frequency at output will be $100Hz$.
Therefore, the output frequency is $100Hz$ of pulsating DC.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Diodes are semiconductor devices which allow current to flow through them only in one direction. The output in a rectifier is received at the load connected in the middle. A rectifier is an application of diodes. Other applications of diodes are amplifiers, gates, inverters etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




