
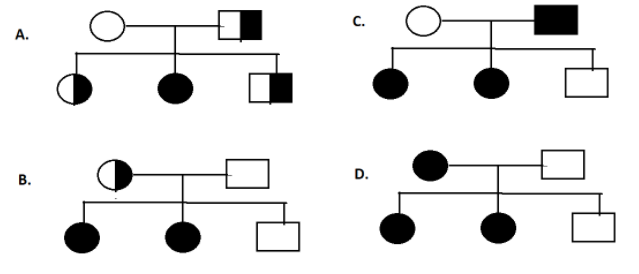
If the husband is a PTC taster and wife is a PTC non-taster. Their daughters are non-tasters but their son is a taster. This is not related to a sex trait. Out of four a, b, c , d which pedigree is correct?

Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: Phenylthiocarbamide (PTC), also known as phenylthiourea (PTU), is a phenyl-containing organosulfur thiourea. It has the odd property of tasting either very sour or almost tasteless, based on the taster's genetic composition. In human population genetics study, PTC taste is a well-known genetic marker.
Complete answer:
PTC tasters are people who can taste the bitter compound phenylthiocarbamide, or PTC, while PTC non-tasters are people who can't taste it. The failure to taste PTC is an autosomal recessive genetic defect, meaning it happens when the allele responsible for the phenotype is found on the autosomes of a homozygous recessive situation.
Since the wife is a PTC non-taster, she has two alleles for this phenotype, while the husband is a PTC taster, he does only have one allele for this trait. However, their son is a taster, as mentioned in the query. This means that the son inherited one autosome from his mother with the allele for this gene, but a regular autosome from his father.
As a result, pedigree D represents this correctly, with the wife affected and the husband unaffected, as well as their son. The daughters may be affected because they will inherit one autosome from their mother and the other from their father, who will also have the PTC allele.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note:
- In 1931, phenylthiocarbamide was synthesized by Arthur Fox, a chemist at DuPont in Wilmington, Delaware (PTC)
- Differences between PTC tasters and non- tasters are that some people ("tasters") find the chemical phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) (OMIM 17120) salty, whereas some find it tasteless ("non-tasters").
- Changes in the TAS2R38 gene, which regulates the activity of bitter taste receptors on the tongue, are responsible for the ability to taste PTC.
Complete answer:
PTC tasters are people who can taste the bitter compound phenylthiocarbamide, or PTC, while PTC non-tasters are people who can't taste it. The failure to taste PTC is an autosomal recessive genetic defect, meaning it happens when the allele responsible for the phenotype is found on the autosomes of a homozygous recessive situation.
Since the wife is a PTC non-taster, she has two alleles for this phenotype, while the husband is a PTC taster, he does only have one allele for this trait. However, their son is a taster, as mentioned in the query. This means that the son inherited one autosome from his mother with the allele for this gene, but a regular autosome from his father.
As a result, pedigree D represents this correctly, with the wife affected and the husband unaffected, as well as their son. The daughters may be affected because they will inherit one autosome from their mother and the other from their father, who will also have the PTC allele.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note:
- In 1931, phenylthiocarbamide was synthesized by Arthur Fox, a chemist at DuPont in Wilmington, Delaware (PTC)
- Differences between PTC tasters and non- tasters are that some people ("tasters") find the chemical phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) (OMIM 17120) salty, whereas some find it tasteless ("non-tasters").
- Changes in the TAS2R38 gene, which regulates the activity of bitter taste receptors on the tongue, are responsible for the ability to taste PTC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




