
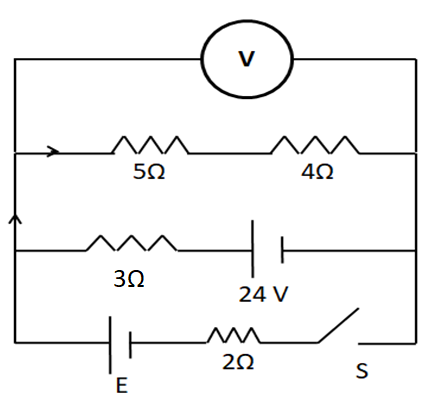
If the high resistance voltmeter V shows a reading of $ 18{\text{V}} $ when the switch S is closed, then the emf of the cell E must be
(A) $ {\text{42V}} $
(B) $ {\text{6V}} $
(C) $ {\text{24V}} $
(D) $ 18{\text{V}} $

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint
To solve this question, we have to determine the currents in the different branches of the circuit by applying KVL and KCL. Then, with the help of these current values, we can find out the required emf.
Complete step by step answer
As the resistance of the voltmeter is high, no current will pass through it. So for the circuit analysis, we take it out of the circuit. On closing the switch S, the circuit looks like
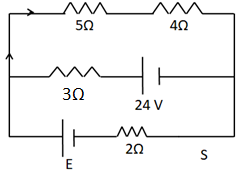
Now, we can see that the $ 5\Omega $ and the $ 4\Omega $ resistances are in series. So, their equivalent resistance is
$ R = 5 + 4 = 9\Omega $. So the above circuit reduces to
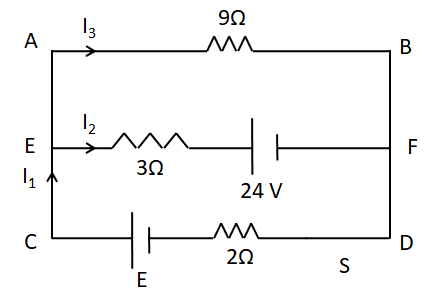
Since the voltmeter shows a reading of $ 18{\text{V}} $ so the potential difference between the points A and B is $ {V_{ab}} = 18{\text{V}} $
From the above circuit diagram
$\Rightarrow {V_{ab}} = 9{I_3} $
$\Rightarrow 18 = 9{I_3} $
Dividing by $ 9 $ we get
$\Rightarrow {I_3} = 2{\text{A}} $ …..(1)
Applying KVL in the loop EFBA
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} + 24 - 9{I_3} = 0 $
Substituting from (1)
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} + 24 - 9\left( 2 \right) = 0 $
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} = - 6 $
Dividing by $ 3 $ we get
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = - 2{\text{A}} $
Applying KCL, we have
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3} $
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = - 2 + 2 = 0{\text{A}} $ …...(2)
Now, applying KVL in the loop ABDC, we have
$\Rightarrow 9{I_3} + 2{I_1} - E = 0 $
From (1) and (2)
$\Rightarrow 9(2) + 2\left( 0 \right) - E = 0 $
$\Rightarrow E = 18{\text{V}} $
So the emf of cell E is equal to $ 18{\text{V}} $
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note
The same question can be attempted very easily without entirely depending upon KVL and KCL. We can calculate the net emf and net resistance of the bottommost two branches, thereby reducing these two branches into a single branch. Then using the value of the reading of the voltmeter and applying the KVL, we can determine the emf of the unknown cell. Using this method will reduce the chances of committing the calculation mistakes.
To solve this question, we have to determine the currents in the different branches of the circuit by applying KVL and KCL. Then, with the help of these current values, we can find out the required emf.
Complete step by step answer
As the resistance of the voltmeter is high, no current will pass through it. So for the circuit analysis, we take it out of the circuit. On closing the switch S, the circuit looks like

Now, we can see that the $ 5\Omega $ and the $ 4\Omega $ resistances are in series. So, their equivalent resistance is
$ R = 5 + 4 = 9\Omega $. So the above circuit reduces to

Since the voltmeter shows a reading of $ 18{\text{V}} $ so the potential difference between the points A and B is $ {V_{ab}} = 18{\text{V}} $
From the above circuit diagram
$\Rightarrow {V_{ab}} = 9{I_3} $
$\Rightarrow 18 = 9{I_3} $
Dividing by $ 9 $ we get
$\Rightarrow {I_3} = 2{\text{A}} $ …..(1)
Applying KVL in the loop EFBA
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} + 24 - 9{I_3} = 0 $
Substituting from (1)
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} + 24 - 9\left( 2 \right) = 0 $
$\Rightarrow 3{I_2} = - 6 $
Dividing by $ 3 $ we get
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = - 2{\text{A}} $
Applying KCL, we have
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3} $
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = - 2 + 2 = 0{\text{A}} $ …...(2)
Now, applying KVL in the loop ABDC, we have
$\Rightarrow 9{I_3} + 2{I_1} - E = 0 $
From (1) and (2)
$\Rightarrow 9(2) + 2\left( 0 \right) - E = 0 $
$\Rightarrow E = 18{\text{V}} $
So the emf of cell E is equal to $ 18{\text{V}} $
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note
The same question can be attempted very easily without entirely depending upon KVL and KCL. We can calculate the net emf and net resistance of the bottommost two branches, thereby reducing these two branches into a single branch. Then using the value of the reading of the voltmeter and applying the KVL, we can determine the emf of the unknown cell. Using this method will reduce the chances of committing the calculation mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




