
If the focus of a parabola divided a focal chord of the parabola in segments of length $3$ and$2$ the length of the latus rectum of the parabola is?
A) $\dfrac{3}{2}$
B) $\dfrac{6}{5}$
C) $\dfrac{12}{5}$
D) $\dfrac{24}{4}$
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: A parabola is a U-shaped plane curve where any point is at an equal distance from a fixed point (known as the focus) and from a fixed straight line which is known as the directrix. Actually parabola is an integral part of the conic section. The above given question is related to the parabola. Latus rectum is used in the given question. The latus rectum of a parabola is the chord that passes through the focus and is perpendicular to the x-axis of the parabola. Now what is a focal chord? Any chord passes through the focus of the parabola is a fixed chord of the parabola.
Complete step by step solution:
Let's draw a parabola with focus G.
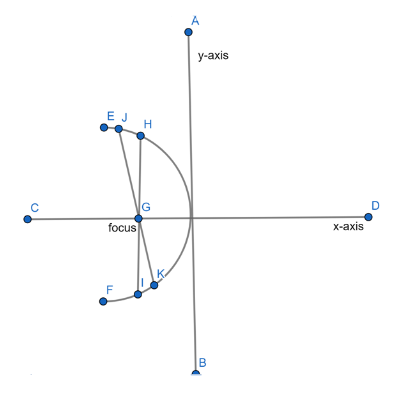
In this parabola HI is a latus rectum and JK is focal chord which is passing through the focus of the parabola.
To solve the given question let`s G(a,0) be the focus of the given parabola. And let the endpoints of the focal chord be $J\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$ and $K\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$ .
We know focus divides the focal length two parts. So GJ and GK are of equal length with length let c and d respectively.
The length of the focal chord from the focus is given as $c=3$ and $d=2$
We know to find out the focal chord we have,
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=\left| \dfrac{x+a}{1} \right|\]
So here $x=a{{t}^{2}}$ and$y=2at$ , then putting these in the above expression we get
\[\] $\Rightarrow GJ=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}}=a{{t}^{2}}+a=a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)$
Similarly, we can calculate GK as where $x=\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}}$ and $y=\dfrac{-2a}{t}$
$\Rightarrow GK=\sqrt{{{\left( a-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{4{{a}^{2}}}{{{t}^{2}}}}=a\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}+1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)$
And it is given that $GJ=3$ and $GK=2$
Now we have to find the length of the latus rectum which is a, for this we will write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}+\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
\end{align}$
Now by more simplifying the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3+2}{6}=\dfrac{5}{6}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{6}{5} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the length of the latus rectum is $a=\dfrac{6}{5}$ .
Note: sometimes students get confused in parabola and hyperbola. The basic difference between parabola and hyperbola is that a parabola has a single focus and directrix , but hyperbola has two foci and two directrices. For the parabola the equation is ${{y}^{2}}=-4ax$ .
Complete step by step solution:
Let's draw a parabola with focus G.

In this parabola HI is a latus rectum and JK is focal chord which is passing through the focus of the parabola.
To solve the given question let`s G(a,0) be the focus of the given parabola. And let the endpoints of the focal chord be $J\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$ and $K\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$ .
We know focus divides the focal length two parts. So GJ and GK are of equal length with length let c and d respectively.
The length of the focal chord from the focus is given as $c=3$ and $d=2$
We know to find out the focal chord we have,
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=\left| \dfrac{x+a}{1} \right|\]
So here $x=a{{t}^{2}}$ and$y=2at$ , then putting these in the above expression we get
\[\] $\Rightarrow GJ=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}}=a{{t}^{2}}+a=a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)$
Similarly, we can calculate GK as where $x=\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}}$ and $y=\dfrac{-2a}{t}$
$\Rightarrow GK=\sqrt{{{\left( a-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{4{{a}^{2}}}{{{t}^{2}}}}=a\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}+1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)$
And it is given that $GJ=3$ and $GK=2$
Now we have to find the length of the latus rectum which is a, for this we will write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}+\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{a\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{GJ}+\dfrac{1}{GK}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
\end{align}$
Now by more simplifying the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3+2}{6}=\dfrac{5}{6}=\dfrac{1}{a} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{6}{5} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the length of the latus rectum is $a=\dfrac{6}{5}$ .
Note: sometimes students get confused in parabola and hyperbola. The basic difference between parabola and hyperbola is that a parabola has a single focus and directrix , but hyperbola has two foci and two directrices. For the parabola the equation is ${{y}^{2}}=-4ax$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




