
If the electric field to the right of two sheets is $\dfrac{{K\sigma }}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$. Find $K$ ?

Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand gauss law for electro statistics. According to gauss law, net flux enclosed by a closed surface is equal to net charge enclosed by surface divided by permittivity of free space ${\varepsilon _0}$ also the flux is equivalent to $\oint {\vec E.d\vec S} $. Here, $\vec E$ is an electric field and $d\vec S$ is an elemental area vector having direction normal to the plane of the surface. Using this we can calculate electric fields across any surface.
Complete step by step answer:
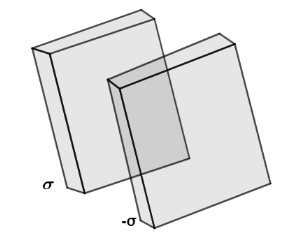
Consider a plane sheet of charge having surface charge distribution $\sigma $.Then using gauss law, we get electric field around sheet as,
$\vec E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}\hat n$
Consider a point P in right side of both sheets, then electric field at P due to plane sheet of charge distribution is, ${E_1} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ having direction away from each other. And, electric field at P due to plane sheet of charge distribution is, ${E_2} = \dfrac{{ - \sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ having direction towards it.So from superposition principle, net electric field is due to,
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
$\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} + \dfrac{{ - \sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$
$\therefore E = 0$
So there is no electric field on the right side of both sheets.Comparing with the given value of $E$ in question we get, $K = 0$.
Note: It should be remembered that gauss law is only applicable for closed surfaces enclosing some net charge. Also the ${q_{net}}$ on right hand side of gauss law implies the total charge enclosed by surface whereas the term $E$ in left hand side of gauss law implies electric field and it is due to all charges on interior, exterior or on the closed surface.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a plane sheet of charge having surface charge distribution $\sigma $.Then using gauss law, we get electric field around sheet as,
$\vec E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}\hat n$
Consider a point P in right side of both sheets, then electric field at P due to plane sheet of charge distribution is, ${E_1} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ having direction away from each other. And, electric field at P due to plane sheet of charge distribution is, ${E_2} = \dfrac{{ - \sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ having direction towards it.So from superposition principle, net electric field is due to,
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
$\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} + \dfrac{{ - \sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$
$\therefore E = 0$
So there is no electric field on the right side of both sheets.Comparing with the given value of $E$ in question we get, $K = 0$.
Note: It should be remembered that gauss law is only applicable for closed surfaces enclosing some net charge. Also the ${q_{net}}$ on right hand side of gauss law implies the total charge enclosed by surface whereas the term $E$ in left hand side of gauss law implies electric field and it is due to all charges on interior, exterior or on the closed surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




