
If the cell membrane is semi-permeable. How do the substances get through the cell wall?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Permeability defines as the ability of any membrane to allow substances mainly solutes or solvents to pass through it. While depending upon the membranes they are classified into- freely permeable, semi-permeable, selectively permeable, and impermeable membranes.
Complete answer:
The cell membrane which is also known as the cytoplasmic membrane is semi-permeable (a type of biological membrane) of a cell that surrounds and encloses its contents of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. This cell membrane separates the cell from the surrounding interstitial fluid, the main component of extracellular fluid.
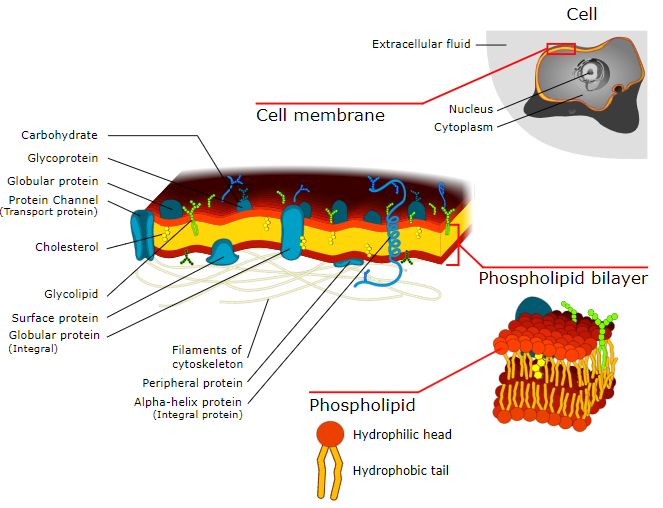
These cell membranes are made up of phospholipids bilayer along with other various lipids, proteins, cholesterol (lipid component). The cell membrane also contains some membrane proteins such as integral proteins and peripheral proteins. The cell membrane controls the movement of the substances in and out of the cells and organelles. These cell membranes serve as a barrier to most, but not all molecules by fencing the majority of organically produced chemicals inside the cell.
Few simple molecules such as water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen can cross the cell membrane by the facilitated diffusion, passive transport (it don not requires energy and allow diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc), active transport (requires cell to spend energy in form of ATP and it transport large molecules), or diffusion process which is one of the principle methods of movement of substances within the cells, as well as the methods for essential small molecules to cross the cell membrane. While osmosis is the diffusion of water across the semipermeable membrane, and the rate at which ions will pass the membrane will depend upon the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the solutes, and permeability of the cell membrane to the respective ions.
Note: Semi-permeable cell membrane allow some solutes and almost all the solvents to pass through them from lower region of concentration to higher concentration so that concentration become equal on both the sides of the membrane and this development of cell membranes that could allow some substances to pass while compelling the movement of other molecules was the main step in the evolution of the cell.
Complete answer:
The cell membrane which is also known as the cytoplasmic membrane is semi-permeable (a type of biological membrane) of a cell that surrounds and encloses its contents of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. This cell membrane separates the cell from the surrounding interstitial fluid, the main component of extracellular fluid.

These cell membranes are made up of phospholipids bilayer along with other various lipids, proteins, cholesterol (lipid component). The cell membrane also contains some membrane proteins such as integral proteins and peripheral proteins. The cell membrane controls the movement of the substances in and out of the cells and organelles. These cell membranes serve as a barrier to most, but not all molecules by fencing the majority of organically produced chemicals inside the cell.
Few simple molecules such as water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen can cross the cell membrane by the facilitated diffusion, passive transport (it don not requires energy and allow diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc), active transport (requires cell to spend energy in form of ATP and it transport large molecules), or diffusion process which is one of the principle methods of movement of substances within the cells, as well as the methods for essential small molecules to cross the cell membrane. While osmosis is the diffusion of water across the semipermeable membrane, and the rate at which ions will pass the membrane will depend upon the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the solutes, and permeability of the cell membrane to the respective ions.
Note: Semi-permeable cell membrane allow some solutes and almost all the solvents to pass through them from lower region of concentration to higher concentration so that concentration become equal on both the sides of the membrane and this development of cell membranes that could allow some substances to pass while compelling the movement of other molecules was the main step in the evolution of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




