
If tangent drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to x-axis then at that point-
A. $ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 0 $
B. $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 $
C. $ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 1 $
D. $ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1 $
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: A tangent line to a curve at a certain point is a line that touches the curve only at one point. Given that a tangent line drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to the x-axis. When a line is perpendicular to x-axis, it will be parallel to the y-axis. So, the x-coordinates of the line will not change only the y-coordinates will be changing. Use this info to solve the given question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that a tangent which is drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to x-axis.
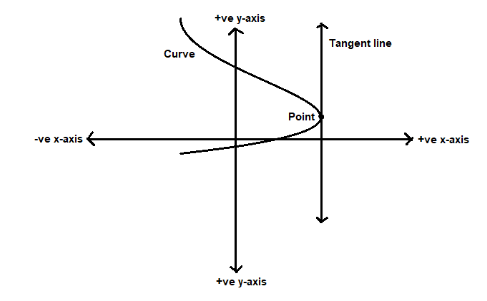
We know that when a line is perpendicular to x-axis, it is parallel to y-axis and when a line is perpendicular to y-axis then it is parallel to x-axis.
We know that the slope of a line m is equal to $ m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} $ , where $ {x_1},{x_2} $ are the x-coordinates of the points of a line and $ {y_1},{y_2} $ are the y-coordinates of the points of the line.
Slope can also be written as $ m = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} $ , where $ dx $ is the change in x-coordinates and $ dy $ is the change in y-coordinates.
But the tangent line is parallel to the y-axis, just its y-coordinates will be changing keeping the x-coordinates constant.
Therefore,
$
dx = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{dy}}{0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = \dfrac{0}{{dy}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 \\
$
So, the correct option is Option B, $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Another approach
Straight line equation with slope m is $ y = mx + c $
Differentiate the line equation with respect to x
$
y = mx + c \\
\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m\dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}} + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}c \\
$
c is a constant, so its differentiation will be zero.
$
\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m\left( 1 \right) + 0\left( {\because \dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}} = 1} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m \\
$
But for a line which is perpendicular to the x-axis the slope is infinity.
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{1}{0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 \\
$
Therefore, if tangent drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to x-axis then at that point $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that a tangent which is drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to x-axis.

We know that when a line is perpendicular to x-axis, it is parallel to y-axis and when a line is perpendicular to y-axis then it is parallel to x-axis.
We know that the slope of a line m is equal to $ m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} $ , where $ {x_1},{x_2} $ are the x-coordinates of the points of a line and $ {y_1},{y_2} $ are the y-coordinates of the points of the line.
Slope can also be written as $ m = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} $ , where $ dx $ is the change in x-coordinates and $ dy $ is the change in y-coordinates.
But the tangent line is parallel to the y-axis, just its y-coordinates will be changing keeping the x-coordinates constant.
Therefore,
$
dx = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{dy}}{0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = \dfrac{0}{{dy}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 \\
$
So, the correct option is Option B, $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Another approach
Straight line equation with slope m is $ y = mx + c $
Differentiate the line equation with respect to x
$
y = mx + c \\
\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m\dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}} + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}c \\
$
c is a constant, so its differentiation will be zero.
$
\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m\left( 1 \right) + 0\left( {\because \dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}} = 1} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = m \\
$
But for a line which is perpendicular to the x-axis the slope is infinity.
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{1}{0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0 \\
$
Therefore, if tangent drawn to a curve at a point is perpendicular to x-axis then at that point $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dy}} = 0$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




