
If $\tan \left( {{\sec }^{-1}}x \right)=\sin \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ , then $x=$
A.$\pm \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{5}}$
B.$\pm \dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}$
C.$\pm \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{5}$
D.None of these
Answer
606k+ views
Hint: Express ${{\sec }^{-1}}x$ inside tan function to ${{\tan }^{-1}}$ by making a right angles triangle using $\sec \theta =\left( \dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Base}} \right)$ . Use Pythagoras theorem ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Perpendicular} \right)}^{2}}$ to get the other side of triangle. Now, express ${{\sec }^{-1}}$ to ${{\tan }^{-1}}$ using $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$ . Similarly, make a triangle using ${{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$ for R.H.S by following result:
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}$
Use Pythagoras theorem to get the other side of this triangle as well. Now, convert ${{\cos }^{-1}}$ to ${{\sin }^{-1}}$ function using $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Use the following results: $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $ and $\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $
Here, we have to determine value of x, if $\tan \left( {{\sec }^{-1}}x \right)=\sin \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ ……………………(i)
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, let us simplify LHS and RHS of the above equation individually. So, LHS of the equation (i) is given as
$\Rightarrow LHS=\tan \left( {{\sec }^{-1}}x \right)$ ………………………………………(ii)
Now, as we know the trigonometric relation for $\sec \theta $ is given as
$\Rightarrow \sec \theta =\left( \dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Base}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sec }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse }}{\text{Base}} \right)$ ………………………………………..(iii)
Now, we can draw a right angle triangle with the help of expression ${{\sec }^{-1}}x$ inside tan of equation (ii) and using equation (iii) as well.
So, we can suppose angle $\theta $ in a right angle triangle using relation
$\theta ={{\sec }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x}{1} \right)$ ……………………………………(iv)
Hence, a right angled triangle with Hypotenuse $=x$ and Base $=1$ can be drawn as
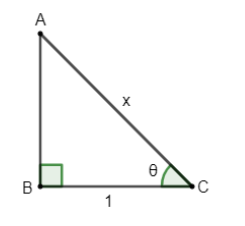
Now, as we know the Pythagoras theorem for a right angled triangle is given as: -
${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Perpendicular} \right)}^{2}}$ …………………………………….(v)
So, we get the above equation with help of $\Delta ABC$ as
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{1}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-1$
Taking square root to both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$
Now, as we know $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$
Hence, we get the value of $\tan \theta $ from $\Delta ABC$ as: -
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}{1}$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$ ………………………………..(vi)
Now, we can get from equation (iv) and (vi) that
${{\sec }^{-1}}x={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$
Hence, equation (ii) can be written as
$\Rightarrow LHS=\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$ ………………………………………(vii)
Now, as we know $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $ …………………………………….(viii)
Hence, we get equation (vii) as
LHS $=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$ ………………………………….(ix)
Now, RHS of the equation (i) is given as
$\Rightarrow RHS=\sin \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right) \right)$ ……………………………………(x)
Now, as we know $\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}$ $\Rightarrow \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse} \right)$ …………………….(xi)
So, on comparing the above equation with the term ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ inside the function sin of the equation (x). We get $\theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ …………………………….(xii)
So, we can draw right angle triangle with Base $=1$, Hypotenuse $=\sqrt{5}$
Hence, we can draw a triangle as
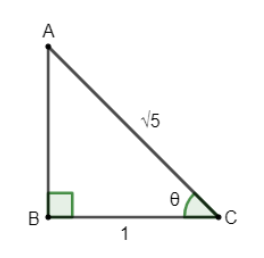
Now, using equation (v), we get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+1$
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=5-1=4\]
\[\Rightarrow AB=2\]
Hence, we know \[\sin \theta \] is defined as $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\] \[\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \right)\] ………………………………(xiii)
Hence, we can rewrite equation (x) using equation (xii) and (xiii) as
RHS \[=\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \right) \right)\]
Now, as we know \[\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta \]
So, we get RHS \[=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\] ……………………………………..(xiv)
Now, we can rewrite equation (i) using equations (ix) and (xiv) as
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\]
On squaring both the sides of the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-1=\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=1+\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{9}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{9}{5}\]
Taking square root on both the sides of the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow x=\pm \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{5}}\]
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: One need to be careful with the identities $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)=x$ and $\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}x \right)=x$. One may confuse with the identities of \[\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}x \right)\] and $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)$ which will not always be x. So, be careful with them. Don’t confuse yourself with these relations.
One may use direct identities to convert ${{\sec }^{-1}}x$ to \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\] and \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\] function to \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\] . These are given as
\[{{\sec }^{-1}}x={{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}\]
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}x={{\sin }^{-1}}\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}\]
So, we do not need to make a right angle triangle to get solve the problem instead, we can use the above identities as well.
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}$
Use Pythagoras theorem to get the other side of this triangle as well. Now, convert ${{\cos }^{-1}}$ to ${{\sin }^{-1}}$ function using $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Use the following results: $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $ and $\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $
Here, we have to determine value of x, if $\tan \left( {{\sec }^{-1}}x \right)=\sin \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ ……………………(i)
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, let us simplify LHS and RHS of the above equation individually. So, LHS of the equation (i) is given as
$\Rightarrow LHS=\tan \left( {{\sec }^{-1}}x \right)$ ………………………………………(ii)
Now, as we know the trigonometric relation for $\sec \theta $ is given as
$\Rightarrow \sec \theta =\left( \dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}}{\text{Base}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sec }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse }}{\text{Base}} \right)$ ………………………………………..(iii)
Now, we can draw a right angle triangle with the help of expression ${{\sec }^{-1}}x$ inside tan of equation (ii) and using equation (iii) as well.
So, we can suppose angle $\theta $ in a right angle triangle using relation
$\theta ={{\sec }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x}{1} \right)$ ……………………………………(iv)
Hence, a right angled triangle with Hypotenuse $=x$ and Base $=1$ can be drawn as

Now, as we know the Pythagoras theorem for a right angled triangle is given as: -
${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Perpendicular} \right)}^{2}}$ …………………………………….(v)
So, we get the above equation with help of $\Delta ABC$ as
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{1}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-1$
Taking square root to both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$
Now, as we know $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$
Hence, we get the value of $\tan \theta $ from $\Delta ABC$ as: -
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}{1}$
$\Rightarrow \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$ ………………………………..(vi)
Now, we can get from equation (iv) and (vi) that
${{\sec }^{-1}}x={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$
Hence, equation (ii) can be written as
$\Rightarrow LHS=\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1} \right)$ ………………………………………(vii)
Now, as we know $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta $ …………………………………….(viii)
Hence, we get equation (vii) as
LHS $=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$ ………………………………….(ix)
Now, RHS of the equation (i) is given as
$\Rightarrow RHS=\sin \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right) \right)$ ……………………………………(x)
Now, as we know $\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}$ $\Rightarrow \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse} \right)$ …………………….(xi)
So, on comparing the above equation with the term ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ inside the function sin of the equation (x). We get $\theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \right)$ …………………………….(xii)
So, we can draw right angle triangle with Base $=1$, Hypotenuse $=\sqrt{5}$
Hence, we can draw a triangle as

Now, using equation (v), we get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+1$
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=5-1=4\]
\[\Rightarrow AB=2\]
Hence, we know \[\sin \theta \] is defined as $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\] \[\Rightarrow \theta ={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \right)\] ………………………………(xiii)
Hence, we can rewrite equation (x) using equation (xii) and (xiii) as
RHS \[=\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \right) \right)\]
Now, as we know \[\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}\theta \right)=\theta \]
So, we get RHS \[=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\] ……………………………………..(xiv)
Now, we can rewrite equation (i) using equations (ix) and (xiv) as
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\]
On squaring both the sides of the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-1=\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=1+\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{9}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{9}{5}\]
Taking square root on both the sides of the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow x=\pm \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{5}}\]
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: One need to be careful with the identities $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)=x$ and $\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}x \right)=x$. One may confuse with the identities of \[\sin \left( {{\sin }^{-1}}x \right)\] and $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)$ which will not always be x. So, be careful with them. Don’t confuse yourself with these relations.
One may use direct identities to convert ${{\sec }^{-1}}x$ to \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\] and \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\] function to \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\] . These are given as
\[{{\sec }^{-1}}x={{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}\]
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}x={{\sin }^{-1}}\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}\]
So, we do not need to make a right angle triangle to get solve the problem instead, we can use the above identities as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




