
If one side of a triangle is double that of another and angles opposite to these sides differ by ${{60}^{\circ }}$, then the triangle is:
(a) an isosceles triangle
(b) a right angled triangle
(c) an equilateral triangle
(d) a right angle isosceles triangle
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: It is given that one side of a triangle is double that of the other side. Let us assume the angle opposite to the one side is $\theta $ and the angle opposite to the side which is double of the given side will be $\theta +{{60}^{\circ }}$. And to find the third angle of the triangle, use the property that the sum of the angles of the triangle are ${{180}^{\circ }}$. And to find the value of $\theta $, we are going to use the property of sine which is equal to $\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$. Now, we have given the relationship between two sides and their angles so use any one of the equality in this sine formula.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume the length of one side as x and then the length of the other side which is double the length of this side will be 2x. And let us assume that angle opposite to the side x is $\theta $ and it is also given that the angles opposite to x and 2x sides are differ by ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so the angle opposite to side 2x is $\theta +{{60}^{\circ }}$.
In the below diagram, we have drawn a triangle ABC with length of one side as x and other side as 2x and the angles opposite to these sides.
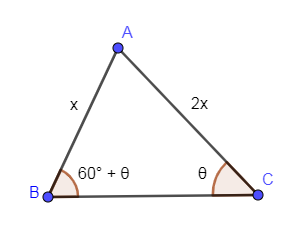
Now, we can find the third angle A by using the properties of the triangle that sum of all the angles of a triangle are ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
\[\begin{align}
& \theta +{{60}^{\circ }}+\theta +\angle A={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\theta +{{60}^{\circ }}+\angle A={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( 2\theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A={{120}^{\circ }}-2\theta ...........Eq.(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We are going to use the sine law in triangle ABC for sides AB and AC and angles opposite to these sides.
We know that sine law for a $\Delta ABC$ with sides a, b and c.
In the below diagram, we have shown a $\Delta ABC$ with sides a, b and c.
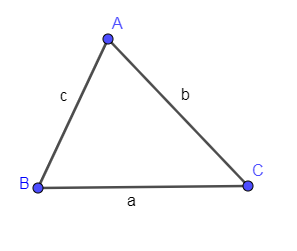
The sine law for above triangle as follows:
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
Using the above sine law in the two sides AB and AC of the above problem we get,
$\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
$\dfrac{2x}{\sin \left( \theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right)}=\dfrac{x}{\sin \theta }$
In the above equation x will be cancelled out from both the sides and then we do the cross multiplication of the above equation.
$2\sin \theta =\sin \left( \theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right)$
We know there is a trigonometric identity $\sin \left( A+B \right)=\sin A\cos B+\cos A\sin B$ so using this relation in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sin \theta =\sin \theta \cos {{60}^{\circ }}+\cos \theta \sin {{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\sin \theta =\sin \theta \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)+\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( 2-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
In the above equation, $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ will be cancelled out from both the sides and we are left with:
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta \left( \sqrt{3} \right)=\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
We know that, $\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\tan \theta $ so using this relation in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta ={{30}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
We got the value of $\theta $ as ${{30}^{\circ }}$ then the angle B equals:
$\begin{align}
& {{30}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
And substituting the value of $\theta $ in eq. (1) we get the value of angle A:
\[\begin{align}
& {{120}^{\circ }}-2\left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& ={{120}^{\circ }}-{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{60}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the value of three angles of triangles that we got is equal to:
$\angle A={{60}^{\circ }};\angle B={{90}^{\circ }};\angle C={{30}^{\circ }}$
If you see the angles of a triangle, you will find that one of the angle is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ which means $\Delta ABC$ is a right angled triangle but we don’t have any two angles are equal so $\Delta ABC$ is not an isosceles triangle.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Generally, what happen in the examination is that in order to quickly solve the problems, when a student got the answer that triangle ABC is a right angled triangle and that answer is given in the options also so they forget to check whether the triangle is isosceles or not so make sure you won’t make this mistake in the examination otherwise it will cost you negative marks.
One more mistake that could be possible is that in the sine law:
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
The common mistake is that you might write the wrong sine of angles given in the above law so the trick to memorize this formula is that if side is “a” then angle is also A for e.g. if you see the above sine law, in numerator there is side “a” and in the denominator the sine of angle A. Similarly, you can remember the other fractions also in this sine law.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume the length of one side as x and then the length of the other side which is double the length of this side will be 2x. And let us assume that angle opposite to the side x is $\theta $ and it is also given that the angles opposite to x and 2x sides are differ by ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so the angle opposite to side 2x is $\theta +{{60}^{\circ }}$.
In the below diagram, we have drawn a triangle ABC with length of one side as x and other side as 2x and the angles opposite to these sides.

Now, we can find the third angle A by using the properties of the triangle that sum of all the angles of a triangle are ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
\[\begin{align}
& \theta +{{60}^{\circ }}+\theta +\angle A={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\theta +{{60}^{\circ }}+\angle A={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A={{180}^{\circ }}-\left( 2\theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A={{120}^{\circ }}-2\theta ...........Eq.(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We are going to use the sine law in triangle ABC for sides AB and AC and angles opposite to these sides.
We know that sine law for a $\Delta ABC$ with sides a, b and c.
In the below diagram, we have shown a $\Delta ABC$ with sides a, b and c.

The sine law for above triangle as follows:
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
Using the above sine law in the two sides AB and AC of the above problem we get,
$\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
$\dfrac{2x}{\sin \left( \theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right)}=\dfrac{x}{\sin \theta }$
In the above equation x will be cancelled out from both the sides and then we do the cross multiplication of the above equation.
$2\sin \theta =\sin \left( \theta +{{60}^{\circ }} \right)$
We know there is a trigonometric identity $\sin \left( A+B \right)=\sin A\cos B+\cos A\sin B$ so using this relation in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sin \theta =\sin \theta \cos {{60}^{\circ }}+\cos \theta \sin {{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\sin \theta =\sin \theta \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)+\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( 2-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\cos \theta \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
In the above equation, $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ will be cancelled out from both the sides and we are left with:
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta \left( \sqrt{3} \right)=\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
We know that, $\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\tan \theta $ so using this relation in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta ={{30}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
We got the value of $\theta $ as ${{30}^{\circ }}$ then the angle B equals:
$\begin{align}
& {{30}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
And substituting the value of $\theta $ in eq. (1) we get the value of angle A:
\[\begin{align}
& {{120}^{\circ }}-2\left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& ={{120}^{\circ }}-{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{60}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the value of three angles of triangles that we got is equal to:
$\angle A={{60}^{\circ }};\angle B={{90}^{\circ }};\angle C={{30}^{\circ }}$
If you see the angles of a triangle, you will find that one of the angle is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ which means $\Delta ABC$ is a right angled triangle but we don’t have any two angles are equal so $\Delta ABC$ is not an isosceles triangle.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Generally, what happen in the examination is that in order to quickly solve the problems, when a student got the answer that triangle ABC is a right angled triangle and that answer is given in the options also so they forget to check whether the triangle is isosceles or not so make sure you won’t make this mistake in the examination otherwise it will cost you negative marks.
One more mistake that could be possible is that in the sine law:
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$
The common mistake is that you might write the wrong sine of angles given in the above law so the trick to memorize this formula is that if side is “a” then angle is also A for e.g. if you see the above sine law, in numerator there is side “a” and in the denominator the sine of angle A. Similarly, you can remember the other fractions also in this sine law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is the Full Form of ISI and RAW

How do you find the valency of chlorine sulphur and class 9 chemistry CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE





