
If Hund's rule violated, then how many unpaired electron(s) is/are present in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] complex ion?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) None
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: We need to know the Hund’s rule and how is it violated during electron pairing. The rule states that for a given electron configuration, the lowest energy term is the one with the greatest value of spin multiplicity. This implies that if two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs. It means every orbital of the same energy must have at least one electron which has identical spin before the second electron is added. In simple words, pairing of electrons in the orbitals belonging to the same subshell [p, d, f], does not take place until each orbital gets singly occupied. Filling of electrons in the respective subshells other than the above manner implies a violation of Hund’s rule.
Complete answer:
As given in the question, for the complex ion in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] ,the central atom is \[Cr\] whose electronic configuration is \[\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^5}4{s^1}\] . In its coordination complex ion, it is in +3 oxidation state which means it has donated its 3 electrons. Therefore, the electronic configuration of \[C{r^{3 + }}\] is \[\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^3}\] .
The electrons in d-orbital is distributed in shells by violating Hund’s rule as,
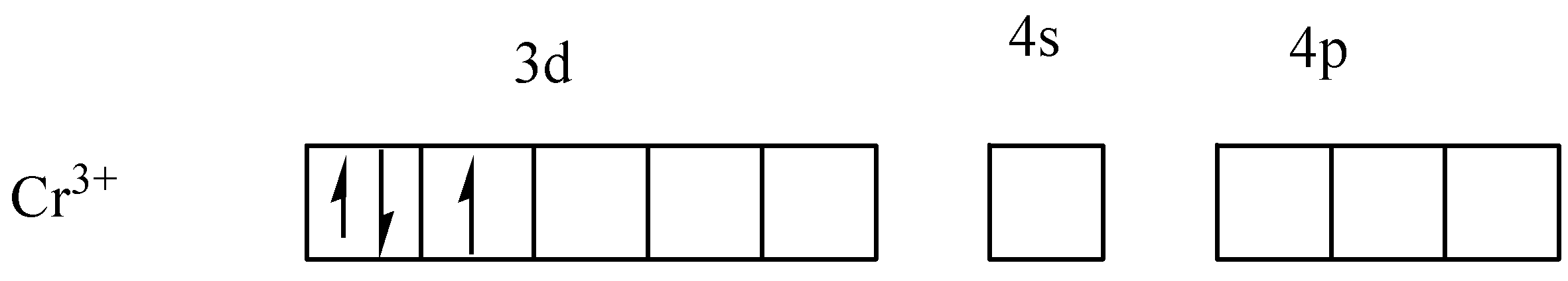
Violating Hund’s rule, i.e, pairing the electrons before filling each subshell, it is clear that \[C{r^{3 + }}\] has only one unpaired electron. Thus it can be said that, if Hund's rule violated, only one unpaired electron(s) is present in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] complex ion.
Hence, the correct option is option (A).
Note:
It must be noted that not only the violation plays a role in the presence of one unpaired electron in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] complex ion, but also that \[N{H_3}\]acts as a strong ligand which pairs the electron in the \[3d\] orbital of \[C{r^{3 + }}\] . Violation is not common. Most elements obey the rule strictly although there are exceptions such as in the case of \[Cu\] . This is because Fully-filled orbitals and half-filled orbitals have extra stability.
Complete answer:
As given in the question, for the complex ion in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] ,the central atom is \[Cr\] whose electronic configuration is \[\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^5}4{s^1}\] . In its coordination complex ion, it is in +3 oxidation state which means it has donated its 3 electrons. Therefore, the electronic configuration of \[C{r^{3 + }}\] is \[\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^3}\] .
The electrons in d-orbital is distributed in shells by violating Hund’s rule as,

Violating Hund’s rule, i.e, pairing the electrons before filling each subshell, it is clear that \[C{r^{3 + }}\] has only one unpaired electron. Thus it can be said that, if Hund's rule violated, only one unpaired electron(s) is present in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] complex ion.
Hence, the correct option is option (A).
Note:
It must be noted that not only the violation plays a role in the presence of one unpaired electron in \[{\left[ {Cr{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] complex ion, but also that \[N{H_3}\]acts as a strong ligand which pairs the electron in the \[3d\] orbital of \[C{r^{3 + }}\] . Violation is not common. Most elements obey the rule strictly although there are exceptions such as in the case of \[Cu\] . This is because Fully-filled orbitals and half-filled orbitals have extra stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




