
If $f:A\to B$ is a constant function which is onto then $B$ is
(a) a singleton set
(b) a null set
(c) an infinite set
(d) a finite set
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, let us first understand what a function is, what a constant function is and what is the condition for a function to be onto.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A function is a process or a relation that associates each element $x$ of a set $X$ to a single element $y$ of another set $Y$ . Here $X$ is domain and $Y$ is co-domain of the function. The domain of a function is the set of possible inputs for the function. For example , the domain of $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is all real numbers, and the domain of $g\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{x}$ is all real numbers except for $x=0$ . Also, the co-domain of a function is the set into which all of the output of the function is constrained to fall. We can understand this by taking the example of $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ .
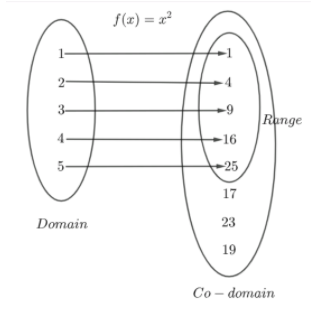
We can see that the domain of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is the set $\left\{ 1,2,3,4,5 \right\}$ . Co-domain of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is the set $\left\{ 1,4,9,16,25,17,23,19 \right\}$ . Here, we also have a range. So, let us know about range. A range is the set of all $f$ images of all the elements of domain.
According to the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ , the set $\left\{ 1,4,9,16,25 \right\}$ is the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ .
Now, let us know about onto function. A function $f$ from a set $X$ to a set $Y$ is onto, if for every element $y$ in the co-domain $Y$ of $f$ , there is at least one element $x$ in the domain $X$ of $f$ such that $f\left( x \right)=y$ . We can also show it as
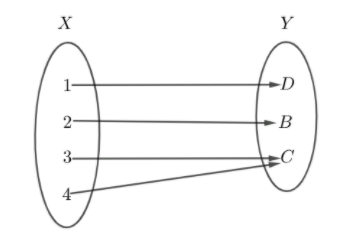
Here, we can see that each element of $X$ has a $f-image$ in $Y$ . We can also say that if a function is onto then the range set will be equal to the co-domain set.
Now, let us solve the given problem .
It is given that $f:A\to B$ is a constant function which is onto.
$f:A\to B$ is a constant function means for each element in $A$ there is some $f-image$ in $B$ .
Also, $f:A\to B$ is onto which means $f\left( A \right)=B$ i.e. , range set is equal to domain set . Therefore we conclude that $B$ has only one element.
Thus, $B$ is a singleton set.
Hence the correct option is (a).
Note: Alternate shortcut:
$f\left( x \right)$ is a constant function $\Rightarrow $ Range of $f\left( x \right)$ is a singleton set.
For $f$to be an onto function, Co-domain $B$ should be equal to range.
$\therefore B$ should be a singleton set.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A function is a process or a relation that associates each element $x$ of a set $X$ to a single element $y$ of another set $Y$ . Here $X$ is domain and $Y$ is co-domain of the function. The domain of a function is the set of possible inputs for the function. For example , the domain of $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is all real numbers, and the domain of $g\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{x}$ is all real numbers except for $x=0$ . Also, the co-domain of a function is the set into which all of the output of the function is constrained to fall. We can understand this by taking the example of $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ .

We can see that the domain of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is the set $\left\{ 1,2,3,4,5 \right\}$ . Co-domain of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ is the set $\left\{ 1,4,9,16,25,17,23,19 \right\}$ . Here, we also have a range. So, let us know about range. A range is the set of all $f$ images of all the elements of domain.
According to the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ , the set $\left\{ 1,4,9,16,25 \right\}$ is the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$ .
Now, let us know about onto function. A function $f$ from a set $X$ to a set $Y$ is onto, if for every element $y$ in the co-domain $Y$ of $f$ , there is at least one element $x$ in the domain $X$ of $f$ such that $f\left( x \right)=y$ . We can also show it as

Here, we can see that each element of $X$ has a $f-image$ in $Y$ . We can also say that if a function is onto then the range set will be equal to the co-domain set.
Now, let us solve the given problem .
It is given that $f:A\to B$ is a constant function which is onto.
$f:A\to B$ is a constant function means for each element in $A$ there is some $f-image$ in $B$ .
Also, $f:A\to B$ is onto which means $f\left( A \right)=B$ i.e. , range set is equal to domain set . Therefore we conclude that $B$ has only one element.
Thus, $B$ is a singleton set.
Hence the correct option is (a).
Note: Alternate shortcut:
$f\left( x \right)$ is a constant function $\Rightarrow $ Range of $f\left( x \right)$ is a singleton set.
For $f$to be an onto function, Co-domain $B$ should be equal to range.
$\therefore B$ should be a singleton set.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




