
If $\alpha ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right),\beta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)$ where $0<\alpha ,\beta <\dfrac{\pi }{2},$then $\alpha -\beta $ is equal to:
A. ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
B. ${{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{14} \right)$
C. ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
D. ${{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
Answer
621.3k+ views
Hint: Using the basic definition of the trigonometric ratio first find the values of the sides of the triangle. Then apply Pythagoras theorem to find the other side of the triangle. Next find the values of $\text{sin, cos, tan}$ of $\alpha ,\beta $ respectively and then simplify to get the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
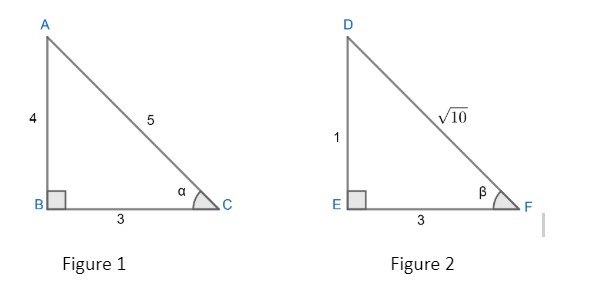
In the question we are given $\alpha ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)\text{ and }\beta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)$
Now, let’s consider a right angled triangle with an included angle $'\alpha '$ and another right angled triangle with an included angle $'\beta '$ which is shown in figure 1 and figure 2 respectively.
F
We are given $\alpha ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{3}{5}$
But we know, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{adjacent side}}{hypotenuse}$ , so in $\Delta ABC,$
$\cos \alpha =\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
So, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
$\begin{align}
& AB=\sqrt{{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}} \\
& AB=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}}=4 \\
\end{align}$
Now we know, $sin\theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{hypotenuse}$, so we get
$\sin \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{AC}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\sin \alpha =\dfrac{4}{5}$
Now we know, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ , so we can write
$tan\alpha =\dfrac{\sin \alpha }{\cos \alpha }$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$tan\alpha =\dfrac{\dfrac{4}{5}}{\dfrac{3}{5}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Now we got all the sine, cosine and tan of $'\alpha '$.
Now consider figure 2;
We are given,
$\beta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \tan \beta =\dfrac{1}{3}$
Now we know, $tan\theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{\text{adjacent side}}$.
In $\Delta DEF,$, we can write
$\tan \beta =\dfrac{DE}{EF}=\dfrac{1}{3}$
So, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( DF \right)}^{2}}={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( EF \right)}^{2}} \\
& DF=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}=\sqrt{10} \\
\end{align}\]
Using the value of sides of the triangle, we will find the corresponding sine, cosine values.
$\sin \beta =\dfrac{DE}{DF}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}$
Now we know, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ , so we can write
$tan\beta =\dfrac{\sin \beta }{\cos \beta }$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}}{\cos \beta } \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \beta =\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}$
Now we got all the sine, cosine and tan of $'\beta '$.
Now, we will use the identity,
$\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\sin \alpha \cos \beta -\cos \alpha \sin \beta $
We know the values of $\sin \alpha ,\cos \alpha ,\sin \beta \text{ and }\cos \beta $. So, by substituting we get;
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\times \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}-\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& \sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{12-3}{5\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we see that;
$\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}$
Then $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
Now, we will use the identity,
$\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\cos \alpha \cos \beta +\sin \alpha \sin \beta $
We know the values of $\sin \alpha ,\cos \alpha ,\sin \beta \text{ and }\cos \beta $. So, by substituting we get;
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}+\dfrac{4}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& =\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}+\dfrac{4}{5\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we see that;
$\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}}$
Then $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
Now, we will use the identity,
$\tan \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)}{\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)}$
As, we got that $\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}\text{ and cos}\left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}}$
So, $\tan \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{13}$
Then$\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{13} \right)$
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The identities of all the trigonometric ratios must be known by heart by the students to work on these kinds of problems at a quick pace. Also, the calculation part must be done with care to avoid silly mistakes.
Student generally calculate the value of $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$, then they stop thinking we got the answer. But they should find other values too for comparing.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question we are given $\alpha ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)\text{ and }\beta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)$
Now, let’s consider a right angled triangle with an included angle $'\alpha '$ and another right angled triangle with an included angle $'\beta '$ which is shown in figure 1 and figure 2 respectively.

F
We are given $\alpha ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{3}{5}$
But we know, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{adjacent side}}{hypotenuse}$ , so in $\Delta ABC,$
$\cos \alpha =\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
So, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
$\begin{align}
& AB=\sqrt{{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}} \\
& AB=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}}=4 \\
\end{align}$
Now we know, $sin\theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{hypotenuse}$, so we get
$\sin \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{AC}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\sin \alpha =\dfrac{4}{5}$
Now we know, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ , so we can write
$tan\alpha =\dfrac{\sin \alpha }{\cos \alpha }$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$tan\alpha =\dfrac{\dfrac{4}{5}}{\dfrac{3}{5}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Now we got all the sine, cosine and tan of $'\alpha '$.
Now consider figure 2;
We are given,
$\beta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \tan \beta =\dfrac{1}{3}$
Now we know, $tan\theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{\text{adjacent side}}$.
In $\Delta DEF,$, we can write
$\tan \beta =\dfrac{DE}{EF}=\dfrac{1}{3}$
So, by Pythagoras theorem, we have
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( DF \right)}^{2}}={{\left( DE \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( EF \right)}^{2}} \\
& DF=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}=\sqrt{10} \\
\end{align}\]
Using the value of sides of the triangle, we will find the corresponding sine, cosine values.
$\sin \beta =\dfrac{DE}{DF}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}$
Now we know, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ , so we can write
$tan\beta =\dfrac{\sin \beta }{\cos \beta }$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}}{\cos \beta } \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \beta =\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}$
Now we got all the sine, cosine and tan of $'\beta '$.
Now, we will use the identity,
$\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\sin \alpha \cos \beta -\cos \alpha \sin \beta $
We know the values of $\sin \alpha ,\cos \alpha ,\sin \beta \text{ and }\cos \beta $. So, by substituting we get;
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\times \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}-\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& \sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{12-3}{5\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we see that;
$\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}$
Then $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
Now, we will use the identity,
$\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\cos \alpha \cos \beta +\sin \alpha \sin \beta $
We know the values of $\sin \alpha ,\cos \alpha ,\sin \beta \text{ and }\cos \beta $. So, by substituting we get;
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}+\dfrac{4}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& =\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}+\dfrac{4}{5\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we see that;
$\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}}$
Then $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$
Now, we will use the identity,
$\tan \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)}{\cos \left( \alpha -\beta \right)}$
As, we got that $\sin \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}}\text{ and cos}\left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{13}{5\sqrt{10}}$
So, $\tan \left( \alpha -\beta \right)=\dfrac{9}{13}$
Then$\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{13} \right)$
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The identities of all the trigonometric ratios must be known by heart by the students to work on these kinds of problems at a quick pace. Also, the calculation part must be done with care to avoid silly mistakes.
Student generally calculate the value of $\left( \alpha -\beta \right)={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{5\sqrt{10}} \right)$, then they stop thinking we got the answer. But they should find other values too for comparing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




