
If a polygenic trait is controlled by three gene pairs then what will be the probability of individuals in \[{F_2}\] generation showing exact phenotype to \[{F_1}\] progeny?
A. \[6/16\]
B. \[4/64\]
C. \[20/64\]
D. \[1/16\]
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Polygenic inheritance is a type of deviation from Mendelian inheritance where a character is controlled by more than two genes. The genes involved are more in number or quantity but in effect they are small.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question, we can see that the trait is controlled by three genes. The genes are named \[A\], \[B\] and \[C\] for dominant and \[a,b\] and \[c\] recessive. Let's work out across to understand the process.
The parent generation \[({P_1})\] \[ \to \] \[AABBCC \times aabbcc\]
Gametes \[ \to \] \[ABC\], \[abc\]
\[{F_1}\] generation \[ \to \]\[AaBbCc\]
Now there is selfing of \[{F_1}\] progeny,
\[{P_2}\] generation \[ \to \]\[AaBbCc\]\[ \times \] \[AaBbCc\]
\[{F_2}\]generation \[ \to \]
We use a formula to calculate the number of offsprings where n is the number of genes. Here the number of genes is three. So, \[{4^3} = 64\]
We can also note that the phenotypic ratio from the above cross is \[1:6:15:20:15:6:1\]
The phenotypic ratio is in the order of the number of dominant alleles starting from \[6\] dominant alleles in the first to no dominant alleles in the last having one offspring each. The number of offsprings with \[5\] dominant alleles is \[6\] and so on.
Going back to the question now. The question is what probability of offsprings in \[{F_2}\] will have the same phenotype as \[{F_1}\]. The phenotype in \[{F_1}\] has \[3\] dominant alleles. Coming to the \[{F_2}\] generation, \[20\] individuals out of the total (sixty four) show the same phenotype as the \[{F_1}\] generation.
Hence, the probability is \[20/64\] and the correct option is C.
Note: Polygenic inheritance is also called the multiple gene inheritance since many genes are involved. The dominant genes in this type of inheritance are additive meaning each dominant allele adds up to the phenotype. More dominant alleles meaning, more the phenotypic expression of a particular character.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question, we can see that the trait is controlled by three genes. The genes are named \[A\], \[B\] and \[C\] for dominant and \[a,b\] and \[c\] recessive. Let's work out across to understand the process.
The parent generation \[({P_1})\] \[ \to \] \[AABBCC \times aabbcc\]
Gametes \[ \to \] \[ABC\], \[abc\]
\[{F_1}\] generation \[ \to \]\[AaBbCc\]
Now there is selfing of \[{F_1}\] progeny,
\[{P_2}\] generation \[ \to \]\[AaBbCc\]\[ \times \] \[AaBbCc\]
\[{F_2}\]generation \[ \to \]
| Gametes | \[ABC\] | \[ABc\] | \[AbC\] | \[Abc\] | \[aBC\] | \[aBC\] | \[abc\] | \[abc\] |
| \[ABC\] | \[6\] | \[5\] | \[5\] | \[4\] | \[5\] | \[4\] | \[4\] | \[3\] |
| \[ABc\] | \[5\] | \[4\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] |
| \[AbC\] | \[5\] | \[4\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] |
| \[Abc\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[2\] | \[1\] |
| \[aBC\] | \[5\] | \[4\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] |
| \[aBC\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[2\] | \[1\] |
| \[abc\] | \[4\] | \[3\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[2\] | \[1\] |
| \[abc\] | \[3\] | \[2\] | \[2\] | \[1\] | \[2\] | \[1\] | \[1\] | 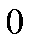
|
We use a formula to calculate the number of offsprings where n is the number of genes. Here the number of genes is three. So, \[{4^3} = 64\]
We can also note that the phenotypic ratio from the above cross is \[1:6:15:20:15:6:1\]
The phenotypic ratio is in the order of the number of dominant alleles starting from \[6\] dominant alleles in the first to no dominant alleles in the last having one offspring each. The number of offsprings with \[5\] dominant alleles is \[6\] and so on.
Going back to the question now. The question is what probability of offsprings in \[{F_2}\] will have the same phenotype as \[{F_1}\]. The phenotype in \[{F_1}\] has \[3\] dominant alleles. Coming to the \[{F_2}\] generation, \[20\] individuals out of the total (sixty four) show the same phenotype as the \[{F_1}\] generation.
Hence, the probability is \[20/64\] and the correct option is C.
Note: Polygenic inheritance is also called the multiple gene inheritance since many genes are involved. The dominant genes in this type of inheritance are additive meaning each dominant allele adds up to the phenotype. More dominant alleles meaning, more the phenotypic expression of a particular character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




