
If a circle is inscribed in a right angled triangle having right angle at \[B\], then find the diameter of the circle.
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: First we have to define what the terms we need to solve the problem are,
The right angled triangle $ABC$having right angle at$B$,
The area of right angled triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (base$ \times $perpendicular)
Complete step-by-step solution:
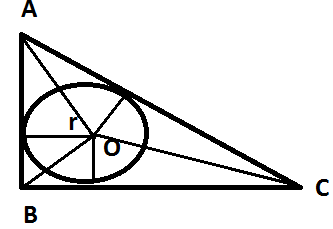
As we know, $\vartriangle ABC$ is right angle triangle,
Since, area of right angle triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (base$ \times $perpendicular)
Base = $AB$ and perpendicular = $BC$that is area of $\vartriangle ABC$=$\dfrac{1}{2}AB \times BC$
Also we can see in the figure that
Area of $\vartriangle ABC$= area of $\vartriangle AOB$$ + $ area of $\vartriangle BOC$$ + $ area of $\vartriangle AOC$ $(2)$
For area of$\vartriangle AOB$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $AB$
That is area of $\vartriangle AOB$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times AB$(base $ \times $perpendicular of$\vartriangle AOB$)
For area of$\vartriangle BOC$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $BC$
Similarly, area of $\vartriangle BOC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times BC$
And for area of$\vartriangle AOC$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $CA$
That is area of $\vartriangle AOC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times CA$
Now substitute all equations in $(2)$we get
Area of $\vartriangle ABC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times AB$$ + $ $ + $$\dfrac{1}{2}r \times CA$
Therefore area of $\vartriangle ABC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times (AB + BC + CA)$[taking common terms] $(3)$
Equating equation $(1)$ and $(3)$we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}AB \times BC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times (AB + BC + CA)$
Cancelling $\dfrac{1}{2}$ on both sides
$AB \times BC$= $r \times (AB + BC + CA)$[cross multiplying on both sides]
$2r = \dfrac{{2AB \times BC}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$[Multiply 2 on both sides]
Now ${(AB + BC)^2} - (A{B^2} + B{C^2}) = 2AB \times BC$ substitute in above equation
$2r = \dfrac{{{{(AB + BC)}^2} - (A{B^2} + B{C^2})}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Now by Pythagoras theorem, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of other two sides which is,$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$ substitute this theorem in above equation we get
$2r = \dfrac{{{{(AB + BC)}^2} - A{C^2}}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Thus $2r = \dfrac{{(AB + BC - AC) \times (AB + BC + CA)}}{{(AB + BC + CA)}}$[taking common terms out]
Cancelling $\dfrac{{AB + BC + CA}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Hence $2r = AB + BC - CA$
Note: The diameter of the circle is and having right triangle at $\vartriangle ABC$
Pythagoras theorem, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of other two sides which is (perpendicular)$^2$= (base)$^2$$ + $(hypotenuse)$^2$
The right angled triangle $ABC$having right angle at$B$,
The area of right angled triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (base$ \times $perpendicular)
Complete step-by-step solution:

As we know, $\vartriangle ABC$ is right angle triangle,
Since, area of right angle triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (base$ \times $perpendicular)
Base = $AB$ and perpendicular = $BC$that is area of $\vartriangle ABC$=$\dfrac{1}{2}AB \times BC$
Also we can see in the figure that
Area of $\vartriangle ABC$= area of $\vartriangle AOB$$ + $ area of $\vartriangle BOC$$ + $ area of $\vartriangle AOC$ $(2)$
For area of$\vartriangle AOB$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $AB$
That is area of $\vartriangle AOB$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times AB$(base $ \times $perpendicular of$\vartriangle AOB$)
For area of$\vartriangle BOC$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $BC$
Similarly, area of $\vartriangle BOC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times BC$
And for area of$\vartriangle AOC$, base = $r$ and perpendicular = $CA$
That is area of $\vartriangle AOC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times CA$
Now substitute all equations in $(2)$we get
Area of $\vartriangle ABC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times AB$$ + $ $ + $$\dfrac{1}{2}r \times CA$
Therefore area of $\vartriangle ABC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times (AB + BC + CA)$[taking common terms] $(3)$
Equating equation $(1)$ and $(3)$we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}AB \times BC$= $\dfrac{1}{2}r \times (AB + BC + CA)$
Cancelling $\dfrac{1}{2}$ on both sides
$AB \times BC$= $r \times (AB + BC + CA)$[cross multiplying on both sides]
$2r = \dfrac{{2AB \times BC}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$[Multiply 2 on both sides]
Now ${(AB + BC)^2} - (A{B^2} + B{C^2}) = 2AB \times BC$ substitute in above equation
$2r = \dfrac{{{{(AB + BC)}^2} - (A{B^2} + B{C^2})}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Now by Pythagoras theorem, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of other two sides which is,$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$ substitute this theorem in above equation we get
$2r = \dfrac{{{{(AB + BC)}^2} - A{C^2}}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Thus $2r = \dfrac{{(AB + BC - AC) \times (AB + BC + CA)}}{{(AB + BC + CA)}}$[taking common terms out]
Cancelling $\dfrac{{AB + BC + CA}}{{AB + BC + CA}}$
Hence $2r = AB + BC - CA$
Note: The diameter of the circle is and having right triangle at $\vartriangle ABC$
Pythagoras theorem, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of other two sides which is (perpendicular)$^2$= (base)$^2$$ + $(hypotenuse)$^2$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




