
If A (5,3), B (11, -5) and P (12, y) are the vertices of a right angled triangle at P, then y is….?
$A$ -2,4
$B$ -2, -4
$C$ 2, -4
$D$ 2,4
Answer
624k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we must know the concept of right angle triangle as well as its properties. Along with this, we should also know the Pythagoras theorem to get the angles.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
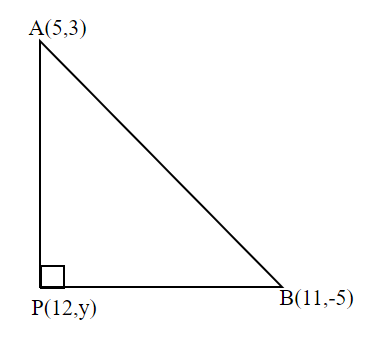
Here, According to the question
Given that A, P, B are the vertices of a right angled triangle at p where
A (5,3)
B (11, -5)
P (12, y)
Now in order to apply Pythagoras theorem, we must convert the vertices.
So we will use the Distance formula –
$ \Rightarrow $ D = $\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $
Now we get
$ \Rightarrow $AP$^2$ = ${\left( {12 - 5} \right)^2}$ + ${\left( {y - 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ BP$^2$ =${\left( {12 - 11} \right)^2}$+${\left( {y + 5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ AB$^2$ = ${\left( {11 - 5} \right)^2}$+${\left( { - 5 - 3} \right)^2}$
So we will now use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow $ AB$^2$= AP$^2$+ BP$^2$
$ \Rightarrow $36+64 = 49 + y$^2$ - 6y + 9 + 1 + y$^2$+ 10y + 25
$ \Rightarrow $100 = 50 + 2 y$^2$+ 34 + 4y
$ \Rightarrow $Simplifying further we get,
$ \Rightarrow $ y$^2$+ 2y – 8 = 0
Now we have to factorise the above calculated quadratic equation to find its root,
$ \Rightarrow $(y + 4) (y – 2) = 0
Thus y = -4, y = 2
$\therefore $ Option C is correct.
Note: To solve this type of question, we should take a simplified quadratic equation so that roots can be easily solved. Along with that one must know the applications of the Pythagoras theorem. This application is appropriate for this type of question as it gives the distance between two points. Hence we will get the desired result.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:

Here, According to the question
Given that A, P, B are the vertices of a right angled triangle at p where
A (5,3)
B (11, -5)
P (12, y)
Now in order to apply Pythagoras theorem, we must convert the vertices.
So we will use the Distance formula –
$ \Rightarrow $ D = $\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $
Now we get
$ \Rightarrow $AP$^2$ = ${\left( {12 - 5} \right)^2}$ + ${\left( {y - 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ BP$^2$ =${\left( {12 - 11} \right)^2}$+${\left( {y + 5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ AB$^2$ = ${\left( {11 - 5} \right)^2}$+${\left( { - 5 - 3} \right)^2}$
So we will now use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow $ AB$^2$= AP$^2$+ BP$^2$
$ \Rightarrow $36+64 = 49 + y$^2$ - 6y + 9 + 1 + y$^2$+ 10y + 25
$ \Rightarrow $100 = 50 + 2 y$^2$+ 34 + 4y
$ \Rightarrow $Simplifying further we get,
$ \Rightarrow $ y$^2$+ 2y – 8 = 0
Now we have to factorise the above calculated quadratic equation to find its root,
$ \Rightarrow $(y + 4) (y – 2) = 0
Thus y = -4, y = 2
$\therefore $ Option C is correct.
Note: To solve this type of question, we should take a simplified quadratic equation so that roots can be easily solved. Along with that one must know the applications of the Pythagoras theorem. This application is appropriate for this type of question as it gives the distance between two points. Hence we will get the desired result.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE




