
Identify which product can be formed
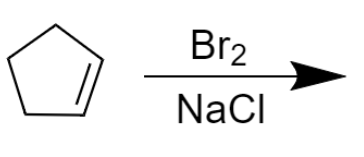
A.
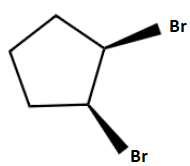
B.
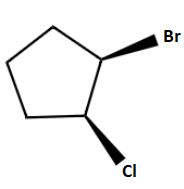
C.
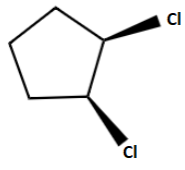
D.
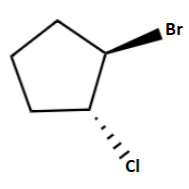




Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: When there is a halogenation of alkenes, it is an electrophilic substitution reaction. The electrophiles add to the double bond of alkenes and break the \[\pi \] bond forming an alkane. The addition of molecular bromine or chlorine to produce vicinal dihalides does not require any catalysts. Bromine or Chlorine are the best for halogenation of alkenes.
Complete answer:
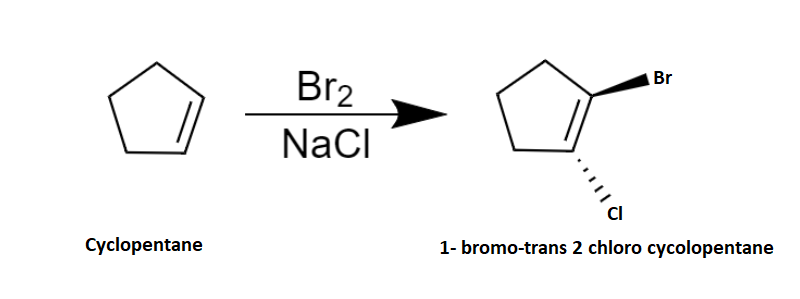
Here we are discussing bromination of alkene with \[NaCl\] . The alkene given is cyclopentene. The process is a two-step mechanism proceeding through an intermediate carbenium ion.
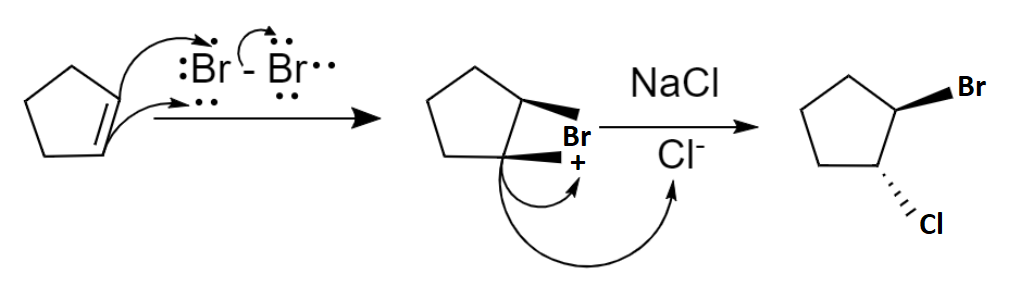
The mechanism of bromination can be explained in two steps. In the first step, the bromine molecule is polarized by the nucleophilic \[\pi \] electron cloud on approaching the cyclopentene and results in a formation of partially positive and partially negative bromine atoms. Then the bromine-bromine bond breaks heterolytically forming an intermediate cyclic bromonium ion by the addition of partially positively charged bromine atoms to the double bond. Now the intermediate is an electrophile. So, the next step is a nucleophilic attack and it can only occur from the opposite side due to the steric hindrance which results in the trans product majorly. Hence the second step follows \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. Chlorine atom is the given nucleophile and it attacks from the opposite side due to the repulsion from bromine and forms a trans product 1-bromo-trans 2-chlorocyclopentane.
The reaction is as shown below:
The mechanism of bromination of alkene with \[NaCl\] is as shown below:
So, the right option is option (d).
Note:
If this was a chlorination reaction with \[NaBr\] then the positions of bromide and chloride would have been altered. The product formed would be 1-chloro-trans 2-bromocyclopentane. If chlorine and bromine attack together, even then chlorine would have attacked first because chlorine is more electrophilic than bromine atom.
Complete answer:
Here we are discussing bromination of alkene with \[NaCl\] . The alkene given is cyclopentene. The process is a two-step mechanism proceeding through an intermediate carbenium ion.
The mechanism of bromination can be explained in two steps. In the first step, the bromine molecule is polarized by the nucleophilic \[\pi \] electron cloud on approaching the cyclopentene and results in a formation of partially positive and partially negative bromine atoms. Then the bromine-bromine bond breaks heterolytically forming an intermediate cyclic bromonium ion by the addition of partially positively charged bromine atoms to the double bond. Now the intermediate is an electrophile. So, the next step is a nucleophilic attack and it can only occur from the opposite side due to the steric hindrance which results in the trans product majorly. Hence the second step follows \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. Chlorine atom is the given nucleophile and it attacks from the opposite side due to the repulsion from bromine and forms a trans product 1-bromo-trans 2-chlorocyclopentane.
The reaction is as shown below:

The mechanism of bromination of alkene with \[NaCl\] is as shown below:

So, the right option is option (d).
Note:
If this was a chlorination reaction with \[NaBr\] then the positions of bromide and chloride would have been altered. The product formed would be 1-chloro-trans 2-bromocyclopentane. If chlorine and bromine attack together, even then chlorine would have attacked first because chlorine is more electrophilic than bromine atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




