
Identify the rate of decarboxylation of isomeric pyridine acetic acids by the similar mechanism.
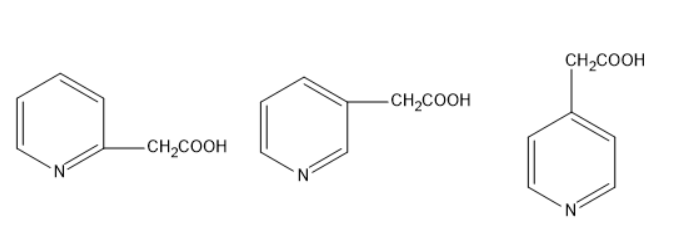
A. \[1 > 2 > 3\]
B. \[1 > 3 > 2\]
C. \[3 > 2 > 1\]
D. \[2 > 1 > 3\]

Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint: The decarboxylation is the process of removal of carbon dioxide from the molecule. The rate of decarboxylation may be different for different molecules. If any bridges are molecules that are present between the carboxylic acid group and the neighboring groups then the decarboxylation will be easy.
Complete answer:
Given molecules are derivatives of pyridine. Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound consisting of a hetero atom nitrogen. The molecular formula of pyridine is \[{C_5}{H_5}N\]. Given that the acetic acid is present as a substitute on pyridine. But acetic acid is present on pyridine in three positions.
The first molecule is pyridine- \[1\]-acetic acid, pyridine- \[2\]-acetic acid and pyridine- \[3\]-acetic acid.
In the first molecule, the nitrogen atom in pyridine has lone pair of electrons and the hydrogen in acetic acid is least electronegative compared to nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, this hydrogen atom between oxygen and nitrogen is involved in hydrogen bond, which means the hydrogen acts as a bridge between the nitrogen and carboxylate ion. Thus, the carbon dioxide can be removed easily in the first molecule.
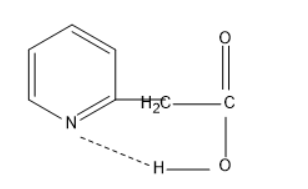
The rate of decarboxylation will be higher in the first molecule than the second followed by the third molecule. Thus, the order is \[1 > 2 > 3\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The first molecule is ortho derivative of pyridine, the second molecule is meta derivative of pyridine and the third molecule is para derivative of pyridine. The ortho involved in intramolecular hydrogen bonding and the carbon dioxide can be removed easily due to the hydrogen bridge between carbon dioxide and nitrogen atom.
Complete answer:
Given molecules are derivatives of pyridine. Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound consisting of a hetero atom nitrogen. The molecular formula of pyridine is \[{C_5}{H_5}N\]. Given that the acetic acid is present as a substitute on pyridine. But acetic acid is present on pyridine in three positions.
The first molecule is pyridine- \[1\]-acetic acid, pyridine- \[2\]-acetic acid and pyridine- \[3\]-acetic acid.
In the first molecule, the nitrogen atom in pyridine has lone pair of electrons and the hydrogen in acetic acid is least electronegative compared to nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, this hydrogen atom between oxygen and nitrogen is involved in hydrogen bond, which means the hydrogen acts as a bridge between the nitrogen and carboxylate ion. Thus, the carbon dioxide can be removed easily in the first molecule.

The rate of decarboxylation will be higher in the first molecule than the second followed by the third molecule. Thus, the order is \[1 > 2 > 3\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The first molecule is ortho derivative of pyridine, the second molecule is meta derivative of pyridine and the third molecule is para derivative of pyridine. The ortho involved in intramolecular hydrogen bonding and the carbon dioxide can be removed easily due to the hydrogen bridge between carbon dioxide and nitrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




