
Identify the position where electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) is most favourable.
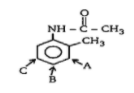
(A)- A
(B)- B
(C)- C
(D)- A and C

Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The groups attached on the benzene ring cause its activation or deactivation on the basis of their nature, depicted through either inductive effect or the resonance effect. The electrophile attaches to the highly electron-dense position on the ring, due to the substituents on the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given compound, we have a benzene ring with an alkyl group $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ and $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ groups attached to it. Both the groups are ring activating groups.
The $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group activates the benzene ring through positive inductive effect at the ortho- and para- position. Similarly, the $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ also activates the benzene ring through resonance effect due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom, at the ortho- and the para—position.
But the activation due to resonance by $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ group is dominant over the inductive effect by $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group. Thus, the ortho- and para- position due to $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ is favoured.
Due to the activation of the ring by substituent, the electron-density at ortho- and para position is high, thus making it susceptible for the electrophile to attack on it.
Also, due to interference by the bulky substituent $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ attached. It causes steric hindrance at the ortho-position closer to it. Thus, the para- position B is favourable for the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Therefore, the position where electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) is most favourable is option (B)- B.
Note: During the electrophilic substitution mechanism, the electron-donating substituents as they activate the ring, they also cause the stabilisation of the adjacent carbocation along the reaction through resonance, which makes the ring more susceptible for the substitution than in case of simple benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given compound, we have a benzene ring with an alkyl group $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ and $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ groups attached to it. Both the groups are ring activating groups.
The $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group activates the benzene ring through positive inductive effect at the ortho- and para- position. Similarly, the $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ also activates the benzene ring through resonance effect due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom, at the ortho- and the para—position.
But the activation due to resonance by $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ group is dominant over the inductive effect by $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group. Thus, the ortho- and para- position due to $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ is favoured.
Due to the activation of the ring by substituent, the electron-density at ortho- and para position is high, thus making it susceptible for the electrophile to attack on it.
Also, due to interference by the bulky substituent $-NHCOC{{H}_{3}}$ attached. It causes steric hindrance at the ortho-position closer to it. Thus, the para- position B is favourable for the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Therefore, the position where electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) is most favourable is option (B)- B.
Note: During the electrophilic substitution mechanism, the electron-donating substituents as they activate the ring, they also cause the stabilisation of the adjacent carbocation along the reaction through resonance, which makes the ring more susceptible for the substitution than in case of simple benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




