
Identify the number of reagents which can distinguish betweeen the following compounds?
I- $ AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH $
II- $ HCl+ZnC{{l}_{2}}(anhydrous) $
III-Neutral $ FeC{{l}_{3}} $
IV- $ {{I}_{2}}/NaOH $
V- $ 2,4-DNP $
VI- $ aq.NaHC{{O}_{3}} $
VII- $ N{{H}_{4}}OH+C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} $
VIII- $ Na-metal $


Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint The reagents given above are classic test reagents for various functional groups. Identify the functional group in the structures given.
Complete step by step solution:
So in the question various reagents are given and we have to say the test which helps in the distinguish process between the two compounds.
For that we should know the groups in the two compounds.
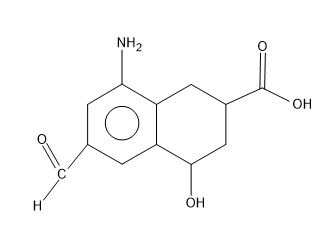
In the first molecule there is an aldehyde group $ \left( CHO \right) $ , the amine group $ \left( N{{H}_{2}} \right) $ , hydroxyl group i.e. an alcohol $ \left( OH \right) $ , and then a carboxylic acid group $ \left( COOH \right) $ .
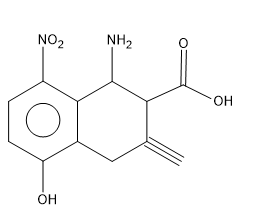
Now let’s analyse the functional groups in the second molecule.In the molecule there is a amine group $ \left( N{{H}_{2}} \right) $ , hydroxyl group $ \left( OH \right) $ , nitro group $ \left( N{{O}_{2}} \right) $ , carboxylic acid group $ \left( COOH \right) $ and a terminal alkyne is present in the molecule ie a triple bond.
So now let’s discuss the reaction of various reagents with the compounds.
- $ AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH $ -The reagent is silver nitrate along with ammonium hydroxide and the reagent is called as the Tollen’s reagent which is used to distinguish aldehyde from other compounds.Since the aldehydes will give positive results for Tollen’s reagent.
The Tollen’s reagent on reaction with aldehyde will form a silver mirror on the inner sides of the test tube due to the precipitation of Ag.
The reaction can be written as:
$ 2{{\left[ Ag{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right] }^{+}}+RCHO+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2A{{g}_{(s)}}+4N{{H}_{3}}+RCOOH+2{{H}^{+}} $
- $ HCl+ZnC{{l}_{2}}(anhydrous) $ -The reagent given is called as Lucas reagent which gives a positive test result with alcohols.This reagent is used to classify between the alcohols as primary, secondary and tertiary.Here the observation is the colour change of colourless to turbid solution and alcohols are classified with the ease with which reaction takes place.The turbidity is due to the formation of chloroalkane.
The reaction is as follows:
$ ROH+HCl\to RCl+{{H}_{2}}O $
-Neutral $ FeC{{l}_{3}} $ -So the reagent neutral $ FeC{{l}_{3}} $ solution is used to identify if phenol is present in the mixture,since the reagent forms a complex with ferric ion( $ F{{e}^{3+}} $ ) and the complex formed will have a colour varying from blue to green according to the nature of the phenol present.
$ 6PhOH+F{{e}^{3+}}\to {{\left[ Fe{{\left( OPh \right)}_{6}} \right] }^{3-}} $
- $ {{I}_{2}}/NaOH $ - the reagent is used for the iodoform reaction, here the molecule will not give this test since iodoform reaction takes place for only those secondary alcohols which possess a methyl group in its alpha position and for ketones.
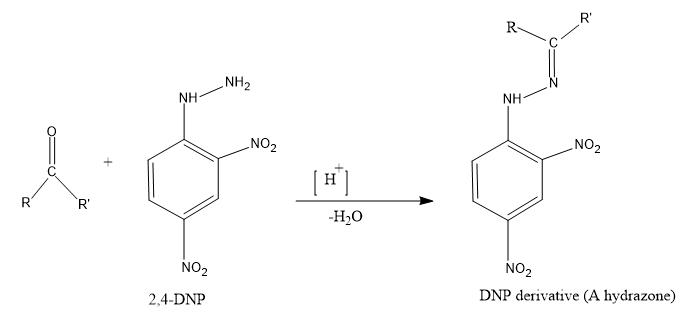
- $ 2,4-DNP $ -In this test with the reagent on reaction with the aldehyde will give a yellow, orange or reddish-orange precipitate by the formation of a hydrazone.
- $ aq.NaHC{{O}_{3}} $ - This reagent is used to distinguish the carboxylic group from others.When the unknown sample is treated with $ aq.NaHC{{O}_{3}} $ , the brisk effervescence due to the evolution of carbon dioxide is the observation.
The reaction is as follows:
$ RCOOH+NaHC{{O}_{3}}\to RCOONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\uparrow $
- $ N{{H}_{4}}OH+C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} $ -this reagent is used for Glaser reaction which is a test for terminal alkyne which yields a brown or red precipitates due to the formation of Cu acetylides.
$ R-C\equiv C-H+C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+N{{H}_{3}}\to R-C\equiv C-Cu+N{{H}_{4}}Cl $
The reaction further proceeds in the presence of oxygen and undergoes the dimerisation reaction of the obtained alkynes.
$ 2R-C\equiv C-Cu\xrightarrow[N{{H}_{3}}/EtOH] {{{O}_{2}}}R-C\equiv C-C\equiv C-R $
- $ Na-metal $ -The sodium metal reacts efficiently with alcohol which liberates hydrogen gas which can be observed as effervescence.
The reaction is :
$ 2R-OH+2Na\to 2R-{{O}^{-}}+2N{{a}^{+}}+H $
Note: There are exceptions in many cases of the compounds which will give the positive test even though they don't come under the groups that show the test reaction.So the exceptions cases should be studied separately to avoid the confusion.
Complete step by step solution:
So in the question various reagents are given and we have to say the test which helps in the distinguish process between the two compounds.
For that we should know the groups in the two compounds.
In the first molecule there is an aldehyde group $ \left( CHO \right) $ , the amine group $ \left( N{{H}_{2}} \right) $ , hydroxyl group i.e. an alcohol $ \left( OH \right) $ , and then a carboxylic acid group $ \left( COOH \right) $ .
Now let’s analyse the functional groups in the second molecule.In the molecule there is a amine group $ \left( N{{H}_{2}} \right) $ , hydroxyl group $ \left( OH \right) $ , nitro group $ \left( N{{O}_{2}} \right) $ , carboxylic acid group $ \left( COOH \right) $ and a terminal alkyne is present in the molecule ie a triple bond.
So now let’s discuss the reaction of various reagents with the compounds.
- $ AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH $ -The reagent is silver nitrate along with ammonium hydroxide and the reagent is called as the Tollen’s reagent which is used to distinguish aldehyde from other compounds.Since the aldehydes will give positive results for Tollen’s reagent.
The Tollen’s reagent on reaction with aldehyde will form a silver mirror on the inner sides of the test tube due to the precipitation of Ag.
The reaction can be written as:
$ 2{{\left[ Ag{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right] }^{+}}+RCHO+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2A{{g}_{(s)}}+4N{{H}_{3}}+RCOOH+2{{H}^{+}} $
- $ HCl+ZnC{{l}_{2}}(anhydrous) $ -The reagent given is called as Lucas reagent which gives a positive test result with alcohols.This reagent is used to classify between the alcohols as primary, secondary and tertiary.Here the observation is the colour change of colourless to turbid solution and alcohols are classified with the ease with which reaction takes place.The turbidity is due to the formation of chloroalkane.
The reaction is as follows:
$ ROH+HCl\to RCl+{{H}_{2}}O $
-Neutral $ FeC{{l}_{3}} $ -So the reagent neutral $ FeC{{l}_{3}} $ solution is used to identify if phenol is present in the mixture,since the reagent forms a complex with ferric ion( $ F{{e}^{3+}} $ ) and the complex formed will have a colour varying from blue to green according to the nature of the phenol present.
$ 6PhOH+F{{e}^{3+}}\to {{\left[ Fe{{\left( OPh \right)}_{6}} \right] }^{3-}} $
- $ {{I}_{2}}/NaOH $ - the reagent is used for the iodoform reaction, here the molecule will not give this test since iodoform reaction takes place for only those secondary alcohols which possess a methyl group in its alpha position and for ketones.
- $ 2,4-DNP $ -In this test with the reagent on reaction with the aldehyde will give a yellow, orange or reddish-orange precipitate by the formation of a hydrazone.

- $ aq.NaHC{{O}_{3}} $ - This reagent is used to distinguish the carboxylic group from others.When the unknown sample is treated with $ aq.NaHC{{O}_{3}} $ , the brisk effervescence due to the evolution of carbon dioxide is the observation.
The reaction is as follows:
$ RCOOH+NaHC{{O}_{3}}\to RCOONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\uparrow $
- $ N{{H}_{4}}OH+C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} $ -this reagent is used for Glaser reaction which is a test for terminal alkyne which yields a brown or red precipitates due to the formation of Cu acetylides.
$ R-C\equiv C-H+C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+N{{H}_{3}}\to R-C\equiv C-Cu+N{{H}_{4}}Cl $
The reaction further proceeds in the presence of oxygen and undergoes the dimerisation reaction of the obtained alkynes.
$ 2R-C\equiv C-Cu\xrightarrow[N{{H}_{3}}/EtOH] {{{O}_{2}}}R-C\equiv C-C\equiv C-R $
- $ Na-metal $ -The sodium metal reacts efficiently with alcohol which liberates hydrogen gas which can be observed as effervescence.
The reaction is :
$ 2R-OH+2Na\to 2R-{{O}^{-}}+2N{{a}^{+}}+H $
Note: There are exceptions in many cases of the compounds which will give the positive test even though they don't come under the groups that show the test reaction.So the exceptions cases should be studied separately to avoid the confusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




